Abstract
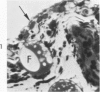
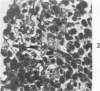
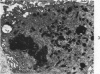
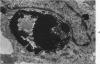
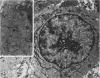
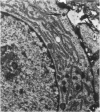
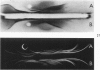
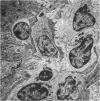
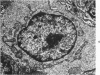
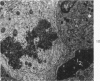
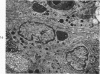
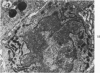
Synovitis was produced in rabbits by daily intra-articular injections of the heterologous antigen horseradish peroxidase. The resulting “peroxidase arthritis” resembled rheumatoid arthritis histologically. Many of the subsynovial plasma cells, plasmablasts and immunoblasts contained specific antibody to horseradish peroxidase; the remainder appeared to contain immunoglobulins of other specificities. Peroxidase arthritis has unique advantages for the study of the cellular and subcellular events in the pathogenesis of the local immune inflammatory response to heterologous antigen. Antigen and specific antibody can be localized precisely by ultrastructural cytochemical technics. The reaction can be terminated at any stage, permitting observation of the early events in its pathogenesis.
Full text
PDF













Images in this article
Selected References
These references are in PubMed. This may not be the complete list of references from this article.
- Aström K. E., Webster H. D., Arnason B. G. The initial lesion in experimental allergic neuritis. A phase and electron microscopic study. J Exp Med. 1968 Sep 1;128(3):469–495. doi: 10.1084/jem.128.3.469. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Avrameas S., Leduc E. H. Detection of simultaneous antibody synthesis in plasma cells and specialized lymphocytes in rabbit lymph nodes. J Exp Med. 1970 Jun 1;131(6):1137–1168. doi: 10.1084/jem.131.6.1137. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Avrameas S., Taudou B., Chuilon S. Glutaraldehyde, cyanuric chloride and tetrazotized O-dianisidine as coupling reagents in the passive hemagglutination test. Immunochemistry. 1969 Jan;6(1):67–76. doi: 10.1016/0019-2791(69)90179-7. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Barden J. A., Decker J. L. Mycoplasma hyorhinis swine arthritis. I. Clinical and microbiologic features. Arthritis Rheum. 1971 Mar-Apr;14(2):193–201. doi: 10.1002/art.1780140202. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Barnett E. V., Bienenstock J., Bloch K. J. Antinuclear factors in synovia. Possible participants in the rheumatoid inclusion body. JAMA. 1966 Oct 10;198(2):143–148. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Brandt K. D., Cathcart E. S., Cohen A. S. Studies of immune deposits in synovial membranes and corresponding synovial fluids. J Lab Clin Med. 1968 Oct;72(4):631–647. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Brånemark P. I., Ekholm R., Goldie I. To the question of angiopathy in rheumatoid arthritis. An electron microscopic study. Acta Orthop Scand. 1969;40(2):153–175. doi: 10.3109/17453676908989496. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- CHRISTIAN C. L. RHEUMATOID ARTHRITIS--ETIOLOGIC CONSIDERATIONS. Arthritis Rheum. 1964 Oct;7:455–466. doi: 10.1002/art.1780070502. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- DUMONDE D. C., GLYNN L. E. The production of arthritis in rabbits by an immunological reaction to fibrin. Br J Exp Pathol. 1962 Aug;43:373–383. [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Ennis R. S., Dalgard D., Willerson J. T., Barden J. A., Decker J. L. Mycoplasma hyorhinis swine arthritis. II. Morphologic features. Arthritis Rheum. 1971 Mar-Apr;14(2):202–211. doi: 10.1002/art.1780140203. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- FOSTIROPOULOS G., AUSTEN K. F., BLOCH K. J. TOTAL HEMOLYTIC COMPLEMENT (CH50) AND SECOND COMPONENT OF COMPLEMENT (C2 HU) ACTIVITY IN SERUM AND SYNOVIAL FLUID. Arthritis Rheum. 1965 Apr;8:219–232. doi: 10.1002/art.1780080206. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Gardner D. L. The Experimental Production of Arthritis: A Review. Ann Rheum Dis. 1960 Dec;19(4):297–317. doi: 10.1136/ard.19.4.297. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Glynn L. E. The chronicity of inflammation and its significance in rheumatoid arthritis. Ann Rheum Dis. 1968 Mar;27(2):105–121. doi: 10.1136/ard.27.2.105. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Graham R. C., Jr, Karnovsky M. J. The early stages of absorption of injected horseradish peroxidase in the proximal tubules of mouse kidney: ultrastructural cytochemistry by a new technique. J Histochem Cytochem. 1966 Apr;14(4):291–302. doi: 10.1177/14.4.291. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- KULKA J. P., BOCKING D., ROPES M. W., BAUER W. Early joint lesions of rheumatoid arthritis; report of eight cases, with knee biopsies of lesions of less than one year's duration. AMA Arch Pathol. 1955 Feb;59(2):129–150. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- RAWSON A. J., ABELSON N. M., HOLLANDER J. L. STUDIES ON THE PATHOGENESIS OF RHEUMATOID JOINT INFLAMMATION. II. INTRACYTOPLASMIC PARTICULATE COMPLEXES IN RHEUMATOID SYNOVIAL FLUIDS. Ann Intern Med. 1965 Feb;62:281–284. doi: 10.7326/0003-4819-62-2-281. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Rodman W. S., Williams R. C., Jr, Bilka P. J., Müller-Eberhard H. J. Immunofluorescent localization of the third and the fourth component of complement in synovial tissue from patients with rheumatoid arthritis. J Lab Clin Med. 1967 Jan;69(1):141–150. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- VENABLE J. H., COGGESHALL R. A SIMPLIFIED LEAD CITRATE STAIN FOR USE IN ELECTRON MICROSCOPY. J Cell Biol. 1965 May;25:407–408. doi: 10.1083/jcb.25.2.407. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- WAKSMAN B. H., PEARSON C. M., SHARP J. T. Studies of arthritis and other lesions induced in rats by injection of mycobacterial adjuvant. II. Evidence that the disease is a disseminated immunologic response to exogenous antigen. J Immunol. 1960 Oct;85:403–417. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Ward P. A. Neutrophil chemotactic factors and related clinical disorders. Arthritis Rheum. 1970 Mar-Apr;13(2):181–186. doi: 10.1002/art.1780130210. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Warren S. L., Marmor L., Liebes D. M., Hollins R. An active agent from human rheumatoid arthritis which is transmissible in mice. Arch Intern Med. 1969 Nov;124(5):629–634. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Williams M. H., Brostoff J., Roitt I. M. Possible role of Mycoplasma fermentans in pathogenesis of rheumatoid arthritis. Lancet. 1970 Aug 8;2(7667):277–280. doi: 10.1016/s0140-6736(70)91328-0. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]