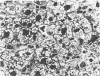
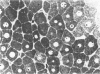
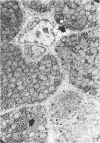
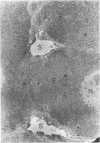
Full text
PDF
















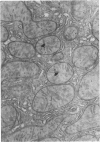
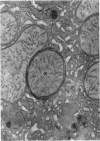
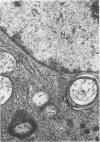
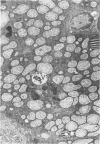
Images in this article
Selected References
These references are in PubMed. This may not be the complete list of references from this article.
- Bressler R., Corredor C., Brendel K. Hypoglycin and hypoglycin-like compounds. Pharmacol Rev. 1969 Jun;21(2):105–130. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Entman M., Bressler R. The mechanism of action of hypoglycin on long-chain fatty acid oxidation. Mol Pharmacol. 1967 Jul;3(4):333–340. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- FENG P. C., KEAN E. A. Influence of diet on the acute toxicity of hypoglycin-A in rats. Br J Nutr. 1955;9(4):368–372. doi: 10.1079/bjn19550052. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- HASSALL C. H., REYLE K. Hypoglycin A,B: biologically active polypeptides from Blighia sapida. Nature. 1954 Feb 20;173(4399):356–357. doi: 10.1038/173356b0. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- HILL K. R., BRAS G., CLEARKIN K. P. Acute toxic hypoglycaemia occurring in the vomiting sickness of Jamaica; morbid anatomical aspects. West Indian Med J. 1955 Jun;4(2):91–104. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- JELLIFFE D. B., STUART K. L. Acute toxic hypoglycaemia in the vomiting sickness of Jamaica. Br Med J. 1954 Jan 9;1(4853):75–77. doi: 10.1136/bmj.1.4853.75. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- LARDY H. A., PRESSMAN B. C. Effect of surface active agents on the latent ATPase of mitochondria. Biochim Biophys Acta. 1956 Sep;21(3):458–466. doi: 10.1016/0006-3002(56)90182-2. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- LEHNINGER A. L., REMMERT L. F. An endogenous uncoupling and swelling agent in liver mitochondria and its enzymic formation. J Biol Chem. 1959 Sep;234:2459–2464. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- LEHNINGER A. L. Reversal of various types of mitochondrial swelling by adenosine triphosphate. J Biol Chem. 1959 Sep;234:2465–2471. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- REYNOLDS E. S. The use of lead citrate at high pH as an electron-opaque stain in electron microscopy. J Cell Biol. 1963 Apr;17:208–212. doi: 10.1083/jcb.17.1.208. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Senior A. E., Robson B., Sherratt H. S. Biochemical effects of the hypoglycaemic compound pent--4-enoic acid and related non-hypoglycaemic fatty acids. Biochem J. 1968 Dec;110(3):511–519. doi: 10.1042/bj1100511. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Senior A. E., Sherratt H. S. Biochemical effects of the hypoglycaemic compound pent-4-enoic acid and related non-hypoglycaemic fatty acids. Carbohydrate metabolism. Biochem J. 1968 Dec;110(3):521–527. doi: 10.1042/bj1100521. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Senior A. E., Sherratt H. S. Biochemical effects of the hypoglycaemic compound pent-4-enoic acid and related non-hypoglycaemic fatty acids. Oxidative phosphorylation and mitochondrial oxidation of pyruvate, 3-hydroxybutyrate and tricarboxylic acid-cycle intermediates. Biochem J. 1968 Dec;110(3):499–509. doi: 10.1042/bj1100499. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- TRUMP B. F., SMUCKLER E. A., BENDITT E. P. A method for staining epoxy sections for light microscopy. J Ultrastruct Res. 1961 Aug;5:343–348. doi: 10.1016/s0022-5320(61)80011-7. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- VON HOLT C., LEPPLA W. Die Konstitution von Hypoglycin A und B. Hoppe Seylers Z Physiol Chem. 1958;313:276–290. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Von Holt C. Methylenecyclopropaneacetic acid, a metabolite of hypoglycin. Biochim Biophys Acta. 1966 Aug 3;125(1):1–10. doi: 10.1016/0005-2760(66)90138-x. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Von Holt C., Von Holt M., Böhm H. Metabolic effects of hypoglycin and methylenecyclopropaneacetic acid. Biochim Biophys Acta. 1966 Aug 3;125(1):11–21. doi: 10.1016/0005-2760(66)90139-1. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]