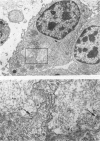
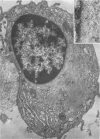
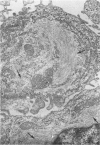
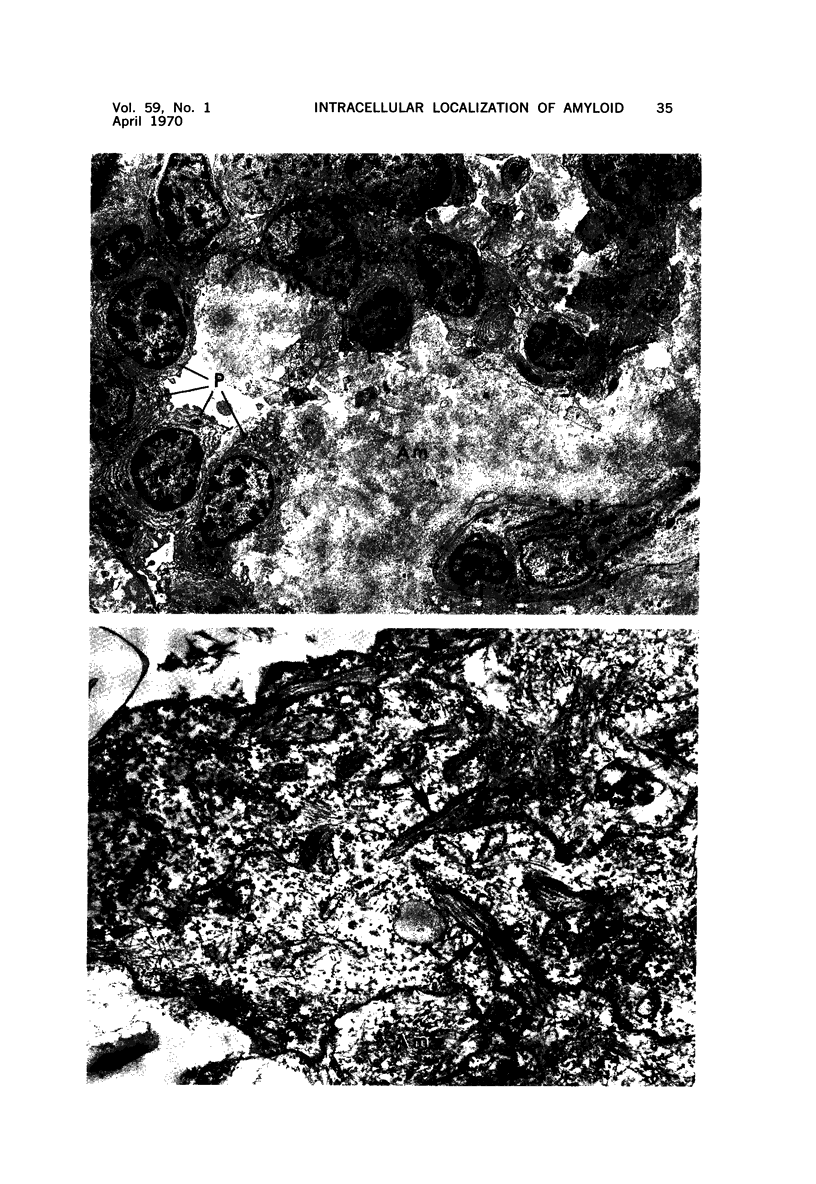
Full text
PDF

















Images in this article
Selected References
These references are in PubMed. This may not be the complete list of references from this article.
- BATTAGLIA S. [Electronoptic studies on liver amyloid in mice]. Beitr Pathol Anat. 1962 Jun;126:300–320. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- BATTAGLIA S. [On amyloid genesis]. Klin Wochenschr. 1961 Aug 1;39:795–798. doi: 10.1007/BF01482097. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Ben-Ishay Z., Zlotnick A. The cellular origin of amyloid. Electron microscopid study in a case of amyloidosis. Isr J Med Sci. 1968 Sep-Oct;4(5):987–994. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Boeré H., Ruinen L., Scholten J. H. Electron microscopic studies on the fibrillar component of human splenic amyloid. J Lab Clin Med. 1965 Dec;66(6):943–951. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- CAESAR R. [The fine structure of the spleen and liver in experimental amyloidosis]. Z Zellforsch Mikrosk Anat. 1960;52:653–673. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- COHEN A. S., CALKINS E. A study of the fine structure of the kidney in casein-induced amyloidosis in rabbits. J Exp Med. 1960 Sep 1;112:479–490. doi: 10.1084/jem.112.3.479. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- COHEN A. S., CALKINS E. Electron microscopic observations on a fibrous component in amyloid of diverse origins. Nature. 1959 Apr 25;183(4669):1202–1203. doi: 10.1038/1831202a0. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- COONS A. H., KAPLAN M. H. Localization of antigen in tissue cells; improvements in a method for the detection of antigen by means of fluorescent antibody. J Exp Med. 1950 Jan 1;91(1):1–13. doi: 10.1084/jem.91.1.1. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Cathcart E. S., Cohen A. S. The relation between isolated human amyloid fibrils and human gamma-globulin and its subunits. J Immunol. 1966 Feb;96(2):239–244. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Cohen A. S., Gross E., Shirahama T. The light and electron microscopic autoradiographic demonstration of local amyloid formation in spleen explants. Am J Pathol. 1965 Dec;47(6):1079–1111. [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Cohen A. S. The constitution and genesis of amyloid. Int Rev Exp Pathol. 1965;4:159–243. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- DIXON F. J., VAZQUEZ J. J. Immunohistochemical analysis of amyloid by the fluorescence technique. J Exp Med. 1956 Nov 1;104(5):727–736. doi: 10.1084/jem.104.5.727. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- GODMAN G. C., LANE N. ON THE SITE OF SULFATION IN THE CHONDROCYTE. J Cell Biol. 1964 Jun;21:353–366. doi: 10.1083/jcb.21.3.353. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- GOLDSTEIN G., SLIZYS I. S., CHASE M. W. Studies on fluorescent antibody staining. I. Non-specific fluorescence with fluorescein-coupled sheep anti-rabbit globulins. J Exp Med. 1961 Jul 1;114:89–110. doi: 10.1084/jem.114.1.89. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- GUEFT B., GHIDONI J. J. THE SITE OF FORMATION AND ULTRASTRUCTURE OF AMYLOID. Am J Pathol. 1963 Nov;43:837–854. [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Gafni J., Merker H. J., Shibolet S., Sohar E., Heller H. On the origin of amyloid. Study of an amyloid tumor in multiple myeloma. Ann Intern Med. 1966 Nov;65(5):1031–1043. doi: 10.7326/0003-4819-65-5-1031. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- HEEFNER W. A., SORENSON G. D. Experimental amyloidosis. I. Light and electron microscopic observation of spleen and lymph nodes. Lab Invest. 1962 Aug;11:585–593. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- HJORT G. H., CHRISTENSEN H. E. Electron-microscopic investigations on secondary renal amyloidosis. Acta Rheumatol Scand. 1961;7:65–68. doi: 10.3109/rhe1.1961.7.issue-1-4.15. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- HOROWITZ R. E., STUYVESANT V. W., WIGMORE W., TATTER D. FIBRINOGEN AS A COMPONENT OF AMYLOID. Arch Pathol. 1965 Mar;79:238–244. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Klatskin G. Nonspecific green birefringence in Congo red-stained tissues. Am J Pathol. 1969 Jul;56(1):1–13. [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- LACHMANN P. J., MULLER-EBERHARD H. J., KUNKEL H. G., PARONETTO F. The localization of in vivo bound complement in tissue section. J Exp Med. 1962 Jan 1;115:63–82. doi: 10.1084/jem.115.1.63. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- LANE N., CARO L., OTERO VILARDEBO L. R., GODMAN G. C. ON THE SITE OF SULFATION IN COLONIC GOBLET CELLS. J Cell Biol. 1964 Jun;21:339–351. doi: 10.1083/jcb.21.3.339. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- LUFT J. H. Improvements in epoxy resin embedding methods. J Biophys Biochem Cytol. 1961 Feb;9:409–414. doi: 10.1083/jcb.9.2.409. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- MILLONIG G. A modified procedure for lead staining of thin sections. J Biophys Biochem Cytol. 1961 Dec;11:736–739. doi: 10.1083/jcb.11.3.736. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- OUCHTERLONY O. Diffusion-in-gel methods for immunological analysis. Prog Allergy. 1958;5:1–78. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- PAUL W. E., COHEN A. S. ELECTRON MICROSCOPIC STUDIES OF AMYLOID FIBRILS WITH FERRITINCONJUGATED ANTIBODY. Am J Pathol. 1963 Oct;43:721–738. [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- PETERSON M., LEBLOND C. P. SYNTHESIS OF COMPLEX CARBOHYDRATES IN THE GOLGI REGION, AS SHOWN BY RADIOAUTOGRAPHY AFTER INJECTION OF LABELED GLUCOSE. J Cell Biol. 1964 Apr;21:143–148. doi: 10.1083/jcb.21.1.143. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Pras M., Schubert M. Metachromatic properties of amyloid in solution. J Histochem Cytochem. 1969 Apr;17(4):258–265. doi: 10.1177/17.4.258. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Pras M., Schubert M., Zucker-Franklin D., Rimon A., Franklin E. C. The characterization of soluble amyloid prepared in water. J Clin Invest. 1968 Apr;47(4):924–933. doi: 10.1172/JCI105784. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Puchtler H., Sweat F. Congo red as a stain for fluorescence microscopy of amyloid. J Histochem Cytochem. 1965 Nov-Dec;13(8):693–694. doi: 10.1177/13.8.693. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Ranlov P., Wanstrup J. Ultrastructural investigations on the cellular morphogenesis of experimental mouse amyloidosis. Acta Pathol Microbiol Scand. 1967;71(4):575–591. doi: 10.1111/j.1699-0463.1967.tb05178.x. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- SABATINI D. D., BENSCH K., BARRNETT R. J. Cytochemistry and electron microscopy. The preservation of cellular ultrastructure and enzymatic activity by aldehyde fixation. J Cell Biol. 1963 Apr;17:19–58. doi: 10.1083/jcb.17.1.19. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- SPIRO D. The structural basis of proteinuria in man; electron microscopic studies of renal biopsy specimens from patients with lipid nephrosis, amyloidosis, and subacute and chronic glomerulonephritis. Am J Pathol. 1959 Jan-Feb;35(1):47–73. [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Schultz R. T., Calkins E., Milgrom F., Witebsky E. Association of gamma globulin with amyloid. Am J Pathol. 1966 Jan;48(1):1–17. [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Shibolet S., Merker H. J., Sohar E., Gafni J., Heller H. Cellular proliferation during the development of amyloid. Electron microscopic observations on the kidneys of Leishmania-infected hamsters. Br J Exp Pathol. 1967 Apr;48(2):244–249. [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- TEILUM G. Periodic acid-Schiff-positive reticulo-endothelial cells producing glycoprotein; functional significance during formation of amyloid. Am J Pathol. 1956 Sep-Oct;32(5):945–959. [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- VASSAR P. S., CULLING C. F. Fluorescent stains, with special reference to amyloid and connective tissues. Arch Pathol. 1959 Nov;68:487–498. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- ZUCKER-FRANKLIN D. MULTIPLE MYELOMA. II. STRUCTURAL FEATURES OF CELLS ASSOCIATED WITH THE PARAPROTEINEMIAS. Semin Hematol. 1964 Apr;1:165–198. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]