Abstract
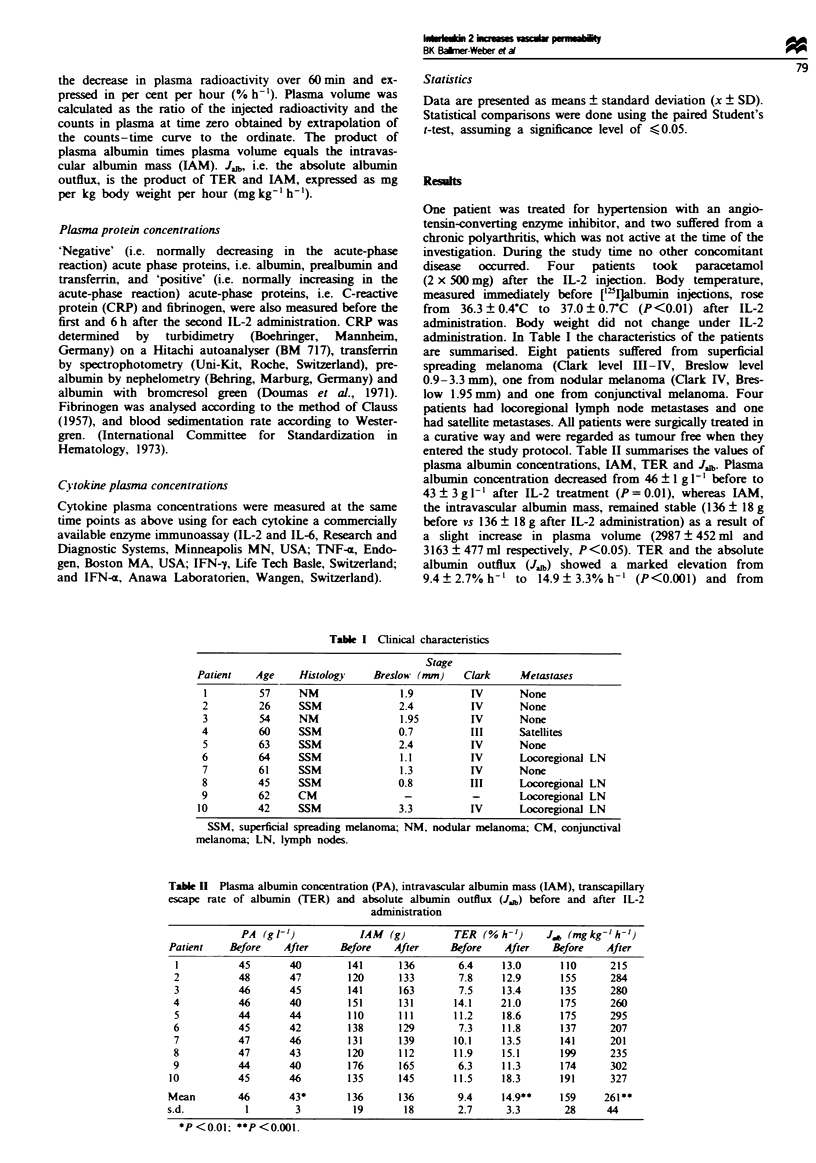
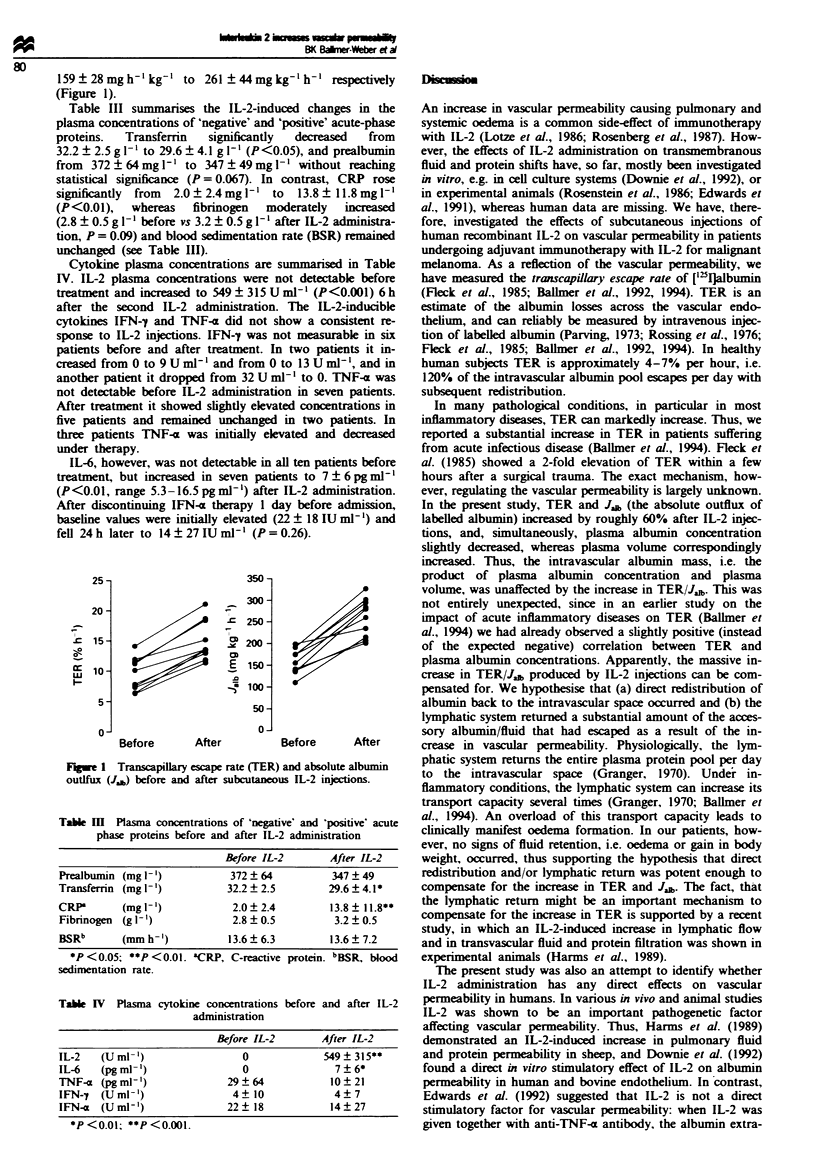
Interleukin 2 (IL-2) exhibits anti-tumour activity. High-dose IL-2 regimens are limited by side-effects such as pulmonary oedema and a systemic vascular leak. The mechanisms by which IL-2 mediates transvascular fluid and protein losses in humans are largely unknown. We have, therefore, measured the transcapillary escape rate (TER) of albumin as a reflection of the vascular permeability by injecting [125I]albumin (5 microCi i.v.). In ten melanoma patients pretreated with interferon alpha (IFN-alpha) TER of albumin was measured before and after IL-2 injections (1.5 x 10(6) Cetus-U. s.c. daily for 4 days). The TER of albumin increased from 9.4 +/- 2.7% h-1 before to 14.9 +/- 3.3% h-1 (P < 0.001) after IL-2 injections and the absolute outflux of albumin (Jalb) from 159 +/- 28 mg kg-1 h-1 to 261 +/- 44 mg kg-1 h-1 (P < 0.001), whereas the intravascular albumin pool remained stable (136 +/- 19 g vs 136 +/- 18 g). IL-2 and IL-6 were not detectable in the plasma prior to IL-2 injections and increased to 549 +/- 315 U ml-1 (P < 0.001) and 7 +/- 6 pg ml-1 (P < 0.01), respectively, after IL-2 administration. In conclusion, IL-2 increases the vascular permeability in humans, without affecting the intravascular albumin pool. This suggests that mechanisms such as the lymphatic return can compensate for the severe transendothelial fluid/albumin losses.
Full text
PDF


Selected References
These references are in PubMed. This may not be the complete list of references from this article.
- Ballmer P. E., Ochsenbein A. F., Schütz-Hofmann S. Transcapillary escape rate of albumin positively correlates with plasma albumin concentration in acute but not in chronic inflammatory disease. Metabolism. 1994 Jun;43(6):697–705. doi: 10.1016/0026-0495(94)90117-1. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Ballmer P. E., Walshe D., McNurlan M. A., Watson H., Brunt P. W., Garlick P. J. Albumin synthesis rates in cirrhosis: correlation with Child-Turcotte classification. Hepatology. 1993 Aug;18(2):292–297. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Ballmer P. E., Weber B. K., Roy-Chaudhury P., McNurlan M. A., Watson H., Power D. A., Garlick P. J. Elevation of albumin synthesis rates in nephrotic patients measured with [1-13C]leucine. Kidney Int. 1992 Jan;41(1):132–138. doi: 10.1038/ki.1992.17. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Baumann H., Gauldie J. Regulation of hepatic acute phase plasma protein genes by hepatocyte stimulating factors and other mediators of inflammation. Mol Biol Med. 1990 Apr;7(2):147–159. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- CLAUSS A. Gerinnungsphysiologische Schnellmethode zur Bestimmung des Fibrinogens. Acta Haematol. 1957 Apr;17(4):237–246. doi: 10.1159/000205234. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Doumas B. T., Watson W. A., Biggs H. G. Albumin standards and the measurement of serum albumin with bromcresol green. Clin Chim Acta. 1971 Jan;31(1):87–96. doi: 10.1016/0009-8981(71)90365-2. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Downie G. H., Ryan U. S., Hayes B. A., Friedman M. Interleukin-2 directly increases albumin permeability of bovine and human vascular endothelium in vitro. Am J Respir Cell Mol Biol. 1992 Jul;7(1):58–65. doi: 10.1165/ajrcmb/7.1.58. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Economou J. S., Hoban M., Lee J. D., Essner R., Swisher S., McBride W., Hoon D. B., Morton D. L. Production of tumor necrosis factor alpha and interferon gamma in interleukin-2-treated melanoma patients: correlation with clinical toxicity. Cancer Immunol Immunother. 1991;34(1):49–52. doi: 10.1007/BF01741324. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Edwards M. J., Abney D. L., Heniford B. T., Miller F. N. Passive immunization against tumor necrosis factor inhibits interleukin-2-induced microvascular alterations and reduces toxicity. Surgery. 1992 Aug;112(2):480–486. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Edwards M. J., Schuschke D. A., Abney D. L., Miller F. N. Interleukin-2 acutely induces protein leakage from the microcirculation. J Surg Res. 1991 Jun;50(6):609–615. doi: 10.1016/0022-4804(91)90050-v. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Fairman R. P., Glauser F. L., Merchant R. E., Bechard D., Fowler A. A. Increase of rat pulmonary microvascular permeability to albumin by recombinant interleukin-2. Cancer Res. 1987 Jul 1;47(13):3528–3532. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Fleck A., Raines G., Hawker F., Trotter J., Wallace P. I., Ledingham I. M., Calman K. C. Increased vascular permeability: a major cause of hypoalbuminaemia in disease and injury. Lancet. 1985 Apr 6;1(8432):781–784. doi: 10.1016/s0140-6736(85)91447-3. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Fraker D. L., Langstein H. N., Norton J. A. Passive immunization against tumor necrosis factor partially abrogates interleukin 2 toxicity. J Exp Med. 1989 Sep 1;170(3):1015–1020. doi: 10.1084/jem.170.3.1015. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Gauldie J., Richards C., Harnish D., Lansdorp P., Baumann H. Interferon beta 2/B-cell stimulatory factor type 2 shares identity with monocyte-derived hepatocyte-stimulating factor and regulates the major acute phase protein response in liver cells. Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A. 1987 Oct;84(20):7251–7255. doi: 10.1073/pnas.84.20.7251. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Granger H. J. Role of the interstitial matrix and lymphatic pump in regulation of transcapillary fluid balance. Microvasc Res. 1979 Sep;18(2):209–216. doi: 10.1016/0026-2862(79)90029-3. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Grimm E. A., Mazumder A., Zhang H. Z., Rosenberg S. A. Lymphokine-activated killer cell phenomenon. Lysis of natural killer-resistant fresh solid tumor cells by interleukin 2-activated autologous human peripheral blood lymphocytes. J Exp Med. 1982 Jun 1;155(6):1823–1841. doi: 10.1084/jem.155.6.1823. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Harms B. A., Pahl A. C., Pohlman T. H., Conhaim R. L., Starling J. R., Storm F. K. Effects of interleukin-2 on pulmonary and systemic transvascular fluid filtration. Surgery. 1989 Aug;106(2):339–346. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Lotze M. T., Matory Y. L., Rayner A. A., Ettinghausen S. E., Vetto J. T., Seipp C. A., Rosenberg S. A. Clinical effects and toxicity of interleukin-2 in patients with cancer. Cancer. 1986 Dec 15;58(12):2764–2772. doi: 10.1002/1097-0142(19861215)58:12<2764::aid-cncr2820581235>3.0.co;2-z. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Maruo N., Morita I., Shirao M., Murota S. IL-6 increases endothelial permeability in vitro. Endocrinology. 1992 Aug;131(2):710–714. doi: 10.1210/endo.131.2.1639018. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Michie H. R., Eberlein T. J., Spriggs D. R., Manogue K. R., Cerami A., Wilmore D. W. Interleukin-2 initiates metabolic responses associated with critical illness in humans. Ann Surg. 1988 Oct;208(4):493–503. doi: 10.1097/00000658-198810000-00011. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Mier J. W., Vachino G., van der Meer J. W., Numerof R. P., Adams S., Cannon J. G., Bernheim H. A., Atkins M. B., Parkinson D. R., Dinarello C. A. Induction of circulating tumor necrosis factor (TNF alpha) as the mechanism for the febrile response to interleukin-2 (IL-2) in cancer patients. J Clin Immunol. 1988 Nov;8(6):426–436. doi: 10.1007/BF00916947. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Paciucci P. A. Immunotherapy of metastatic melanoma with interleukin-2. Mt Sinai J Med. 1992 May;59(3):238–243. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Parkinson D. R. Interleukin-2 in cancer therapy. Semin Oncol. 1988 Dec;15(6 Suppl 6):10–26. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Parving H. P., Gyntelberg F. Transcapillary escape rate of albumin and plasma volume in essential hypertension. Circ Res. 1973 May;32(5):643–651. doi: 10.1161/01.res.32.5.643. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Puri R. K., Rosenberg S. A. Combined effects of interferon alpha and interleukin 2 on the induction of a vascular leak syndrome in mice. Cancer Immunol Immunother. 1989;28(4):267–274. doi: 10.1007/BF00205236. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Rosenberg S. A., Lotze M. T., Muul L. M., Chang A. E., Avis F. P., Leitman S., Linehan W. M., Robertson C. N., Lee R. E., Rubin J. T. A progress report on the treatment of 157 patients with advanced cancer using lymphokine-activated killer cells and interleukin-2 or high-dose interleukin-2 alone. N Engl J Med. 1987 Apr 9;316(15):889–897. doi: 10.1056/NEJM198704093161501. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Rosenberg S. A., Lotze M. T., Yang J. C., Linehan W. M., Seipp C., Calabro S., Karp S. E., Sherry R. M., Steinberg S., White D. E. Combination therapy with interleukin-2 and alpha-interferon for the treatment of patients with advanced cancer. J Clin Oncol. 1989 Dec;7(12):1863–1874. doi: 10.1200/JCO.1989.7.12.1863. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Rosenberg S. A., Mulé J. J., Spiess P. J., Reichert C. M., Schwarz S. L. Regression of established pulmonary metastases and subcutaneous tumor mediated by the systemic administration of high-dose recombinant interleukin 2. J Exp Med. 1985 May 1;161(5):1169–1188. doi: 10.1084/jem.161.5.1169. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Rosenstein M., Ettinghausen S. E., Rosenberg S. A. Extravasation of intravascular fluid mediated by the systemic administration of recombinant interleukin 2. J Immunol. 1986 Sep 1;137(5):1735–1742. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Siegel J. P., Puri R. K. Interleukin-2 toxicity. J Clin Oncol. 1991 Apr;9(4):694–704. doi: 10.1200/JCO.1991.9.4.694. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Vlasveld L. T., Rankin E. M., Hekman A., Rodenhuis S., Beijnen J. H., Hilton A. M., Dubbelman A. C., Vyth-Dreese F. A., Melief C. J. A phase I study of prolonged continuous infusion of low dose recombinant interleukin-2 in melanoma and renal cell cancer. Part I: Clinical aspects. Br J Cancer. 1992 May;65(5):744–750. doi: 10.1038/bjc.1992.157. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]



