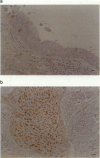
Abstract
Bronchial epithelial dysplasia is thought to be a premalignant stage in the evolution of lung cancers. Using the CM-1 polyclonal antibody, we have examined the expression of the p53 protein in a larger series of bronchial dysplasias (n = 60) than hitherto investigated. The p53 protein was detected in 14% of mild, 25% of moderate and 59% of severe dysplasias; increased p53 expression correlated with the severity of dysplasia. p53-positive dysplasias had greater PCNA indices than p53-negative dysplasias. p53 expression in dysplastic tissues was compared with that in two groups of histologically normal epithelium: 14 bronchial biopsies from non-cancer patients of which all but one were negative and 32 bronchial margins from resected carcinomas, of which 17 showed infrequent solitary cells with p53-positive nuclei in predominantly basal locations scattered throughout the epithelium. These results for resection margins were confirmed by use of a second antibody, DO-1. Sixty-nine per cent of the corresponding carcinomas were p53 positive, but in 15 cases the p53 reactivity differed from resection margins. No correlation between p53 expression and any of the clinicopathological characteristics of these tumours was found. This study supports the observation that abnormal p53 expression may be an early but not obligatory event in malignant transformation in lung.
Full text
PDF

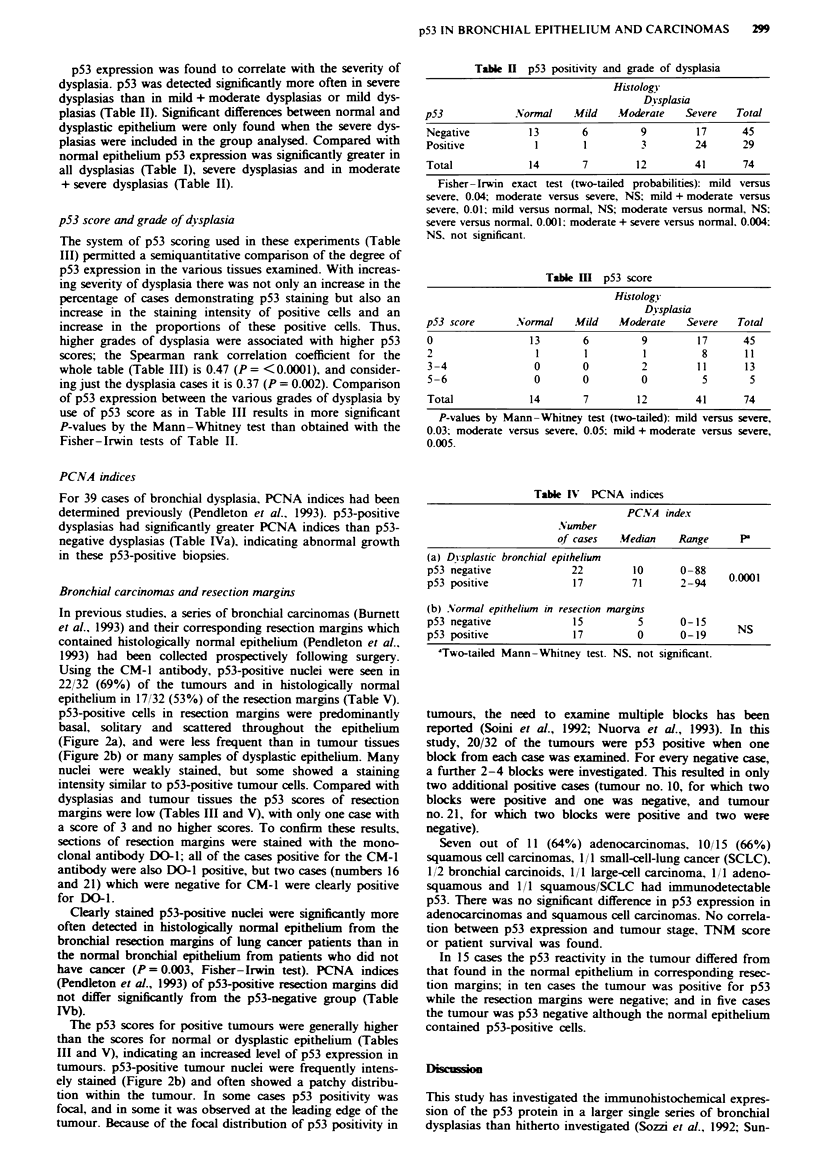



Images in this article
Selected References
These references are in PubMed. This may not be the complete list of references from this article.
- AUERBACH O., STOUT A. P., HAMMOND E. C., GARFINKEL L. Changes in bronchial epithelium in relation to sex, age, residence, smoking and pneumonia. N Engl J Med. 1962 Jul 19;267:111–119. doi: 10.1056/NEJM196207192670301. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Auerbach O., Hammond E. C., Garfinkel L. Changes in bronchial epithelium in relation to cigarette smoking, 1955-1960 vs. 1970-1977. N Engl J Med. 1979 Feb 22;300(8):381–385. doi: 10.1056/NEJM197902223000801. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Bennett W. P., Colby T. V., Travis W. D., Borkowski A., Jones R. T., Lane D. P., Metcalf R. A., Samet J. M., Takeshima Y., Gu J. R. p53 protein accumulates frequently in early bronchial neoplasia. Cancer Res. 1993 Oct 15;53(20):4817–4822. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Birrer M. J., Brown P. H. Application of molecular genetics to the early diagnosis and screening of lung cancer. Cancer Res. 1992 May 1;52(9 Suppl):2658s–2664s. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Campbell C., Quinn A. G., Angus B., Rees J. L. The relation between p53 mutation and p53 immunostaining in non-melanoma skin cancer. Br J Dermatol. 1993 Sep;129(3):235–241. doi: 10.1111/j.1365-2133.1993.tb11840.x. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Chang F., Syrjänen S., Tervahauta A., Syrjänen K. Tumourigenesis associated with the p53 tumour suppressor gene. Br J Cancer. 1993 Oct;68(4):653–661. doi: 10.1038/bjc.1993.404. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Fisher C. J., Gillett C. E., Vojtesek B., Barnes D. M., Millis R. R. Problems with p53 immunohistochemical staining: the effect of fixation and variation in the methods of evaluation. Br J Cancer. 1994 Jan;69(1):26–31. doi: 10.1038/bjc.1994.4. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Fontanini G., Bigini D., Vignati S., Macchiarini P., Pepe S., Angeletti C. A., Pingitore R., Squartini F. p53 expression in non small cell lung cancer: clinical and biological correlations. Anticancer Res. 1993 May-Jun;13(3):737–742. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Green J. A., Robertson L. J., Clark A. H. Glutathione S-transferase expression in benign and malignant ovarian tumours. Br J Cancer. 1993 Aug;68(2):235–239. doi: 10.1038/bjc.1993.321. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Horio Y., Takahashi T., Kuroishi T., Hibi K., Suyama M., Niimi T., Shimokata K., Yamakawa K., Nakamura Y., Ueda R. Prognostic significance of p53 mutations and 3p deletions in primary resected non-small cell lung cancer. Cancer Res. 1993 Jan 1;53(1):1–4. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Iggo R., Gatter K., Bartek J., Lane D., Harris A. L. Increased expression of mutant forms of p53 oncogene in primary lung cancer. Lancet. 1990 Mar 24;335(8691):675–679. doi: 10.1016/0140-6736(90)90801-b. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Isobe M., Emanuel B. S., Givol D., Oren M., Croce C. M. Localization of gene for human p53 tumour antigen to band 17p13. Nature. 1986 Mar 6;320(6057):84–85. doi: 10.1038/320084a0. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Joypaul B. V., Newman E. L., Hopwood D., Grant A., Qureshi S., Lane D. P., Cuschieri A. Expression of p53 protein in normal, dysplastic, and malignant gastric mucosa: an immunohistochemical study. J Pathol. 1993 Jul;170(3):279–283. doi: 10.1002/path.1711700310. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Kamel D., Päkkö P., Nuorva K., Vähäkangas K., Soini Y. p53 and c-erbB-2 protein expression in adenocarcinomas and epithelial dysplasias of the gall bladder. J Pathol. 1993 May;170(1):67–72. doi: 10.1002/path.1711700111. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Lane D. P. Cancer. p53, guardian of the genome. Nature. 1992 Jul 2;358(6381):15–16. doi: 10.1038/358015a0. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Lassam N. J., From L., Kahn H. J. Overexpression of p53 is a late event in the development of malignant melanoma. Cancer Res. 1993 May 15;53(10 Suppl):2235–2238. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Lehman T. A., Bennett W. P., Metcalf R. A., Welsh J. A., Ecker J., Modali R. V., Ullrich S., Romano J. W., Appella E., Testa J. R. p53 mutations, ras mutations, and p53-heat shock 70 protein complexes in human lung carcinoma cell lines. Cancer Res. 1991 Aug 1;51(15):4090–4096. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Levine A. J., Momand J., Finlay C. A. The p53 tumour suppressor gene. Nature. 1991 Jun 6;351(6326):453–456. doi: 10.1038/351453a0. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Levine A. J. The tumor suppressor genes. Annu Rev Biochem. 1993;62:623–651. doi: 10.1146/annurev.bi.62.070193.003203. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Mabry M., Nelkin B. D., Falco J. P., Barr L. F., Baylin S. B. Transitions between lung cancer phenotypes--implications for tumor progression. Cancer Cells. 1991 Feb;3(2):53–58. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Marchetti A., Buttitta F., Merlo G., Diella F., Pellegrini S., Pepe S., Macchiarini P., Chella A., Angeletti C. A., Callahan R. p53 alterations in non-small cell lung cancers correlate with metastatic involvement of hilar and mediastinal lymph nodes. Cancer Res. 1993 Jun 15;53(12):2846–2851. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- McDowell E. M., McLaughlin J. S., Merenyl D. K., Kieffer R. F., Harris C. C., Trump B. F. The respiratory epithelium. V. Histogenesis of lung carcinomas in the human. J Natl Cancer Inst. 1978 Aug;61(2):587–606. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Midgley C. A., Fisher C. J., Bártek J., Vojtesek B., Lane D., Barnes D. M. Analysis of p53 expression in human tumours: an antibody raised against human p53 expressed in Escherichia coli. J Cell Sci. 1992 Jan;101(Pt 1):183–189. doi: 10.1242/jcs.101.1.183. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Minna J. D. The molecular biology of lung cancer pathogenesis. Chest. 1993 Apr;103(4 Suppl):449S–456S. doi: 10.1378/chest.103.4_supplement.449s. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Navone N. M., Troncoso P., Pisters L. L., Goodrow T. L., Palmer J. L., Nichols W. W., von Eschenbach A. C., Conti C. J. p53 protein accumulation and gene mutation in the progression of human prostate carcinoma. J Natl Cancer Inst. 1993 Oct 20;85(20):1657–1669. doi: 10.1093/jnci/85.20.1657. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Nuorva K., Soini Y., Kamel D., Autio-Harmainen H., Risteli L., Risteli J., Vähäkangas K., Päkkö P. Concurrent p53 expression in bronchial dysplasias and squamous cell lung carcinomas. Am J Pathol. 1993 Mar;142(3):725–732. [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Pendleton N., Dixon G. R., Burnett H. E., Occleston N. L., Myskow M. W., Green J. A. Expression of proliferating cell nuclear antigen (PCNA) in dysplasia of the bronchial epithelium. J Pathol. 1993 Jun;170(2):169–172. doi: 10.1002/path.1711700212. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Quinlan D. C., Davidson A. G., Summers C. L., Warden H. E., Doshi H. M. Accumulation of p53 protein correlates with a poor prognosis in human lung cancer. Cancer Res. 1992 Sep 1;52(17):4828–4831. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Richardson G. E., Johnson B. E. The biology of lung cancer. Semin Oncol. 1993 Apr;20(2):105–127. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Rodrigues N. R., Rowan A., Smith M. E., Kerr I. B., Bodmer W. F., Gannon J. V., Lane D. P. p53 mutations in colorectal cancer. Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A. 1990 Oct;87(19):7555–7559. doi: 10.1073/pnas.87.19.7555. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Rubio M. P., von Deimling A., Yandell D. W., Wiestler O. D., Gusella J. F., Louis D. N. Accumulation of wild type p53 protein in human astrocytomas. Cancer Res. 1993 Aug 1;53(15):3465–3467. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Saegusa M., Takano Y., Kishimoto H., Wakabayashi G., Nohga K., Okudaira M. Comparative analysis of p53 and c-myc expression and cell proliferation in human hepatocellular carcinomas--an enhanced immunohistochemical approach. J Cancer Res Clin Oncol. 1993;119(12):737–744. doi: 10.1007/BF01195346. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Soini Y., Päkkö P., Nuorva K., Kamel D., Lane D. P., Vähäkangas K. Comparative analysis of p53 protein immunoreactivity in prostatic, lung and breast carcinomas. Virchows Arch A Pathol Anat Histopathol. 1992;421(3):223–228. doi: 10.1007/BF01611179. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Souhami R. Lung cancer. BMJ. 1992 May 16;304(6837):1298–1301. doi: 10.1136/bmj.304.6837.1298. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Sozzi G., Miozzo M., Donghi R., Pilotti S., Cariani C. T., Pastorino U., Della Porta G., Pierotti M. A. Deletions of 17p and p53 mutations in preneoplastic lesions of the lung. Cancer Res. 1992 Nov 1;52(21):6079–6082. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Sozzi G., Miozzo M., Tagliabue E., Calderone C., Lombardi L., Pilotti S., Pastorino U., Pierotti M. A., Della Porta G. Cytogenetic abnormalities and overexpression of receptors for growth factors in normal bronchial epithelium and tumor samples of lung cancer patients. Cancer Res. 1991 Jan 1;51(1):400–404. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Sundaresan V., Ganly P., Hasleton P., Rudd R., Sinha G., Bleehen N. M., Rabbitts P. p53 and chromosome 3 abnormalities, characteristic of malignant lung tumours, are detectable in preinvasive lesions of the bronchus. Oncogene. 1992 Oct;7(10):1989–1997. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Sundaresan V., Reeve J. G., Wilson B., Bleehen N. M., Watson J. V. Flow cytometric and immunohistochemical analysis of p62c-myc oncoprotein in the bronchial epithelium of lung cancer patients. Anticancer Res. 1991 Nov-Dec;11(6):2111–2116. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Suzuki T., Takano Y. Comparative immunohistochemical studies of p53 and proliferating cell nuclear antigen expression and argyrophilic nucleolar organizer regions in pancreatic duct cell carcinomas. Jpn J Cancer Res. 1993 Oct;84(10):1072–1077. doi: 10.1111/j.1349-7006.1993.tb02803.x. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Vojtesek B., Bártek J., Midgley C. A., Lane D. P. An immunochemical analysis of the human nuclear phosphoprotein p53. New monoclonal antibodies and epitope mapping using recombinant p53. J Immunol Methods. 1992 Jul 6;151(1-2):237–244. doi: 10.1016/0022-1759(92)90122-a. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Vojtesek B., Fisher C. J., Barnes D. M., Lane D. P. Comparison between p53 staining in tissue sections and p53 proteins levels measured by an ELISA technique. Br J Cancer. 1993 Jun;67(6):1254–1258. doi: 10.1038/bjc.1993.234. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Vojtesek B., Lane D. P. Regulation of p53 protein expression in human breast cancer cell lines. J Cell Sci. 1993 Jul;105(Pt 3):607–612. doi: 10.1242/jcs.105.3.607. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Vähäkangas K. H., Samet J. M., Metcalf R. A., Welsh J. A., Bennett W. P., Lane D. P., Harris C. C. Mutations of p53 and ras genes in radon-associated lung cancer from uranium miners. Lancet. 1992 Mar 7;339(8793):576–580. doi: 10.1016/0140-6736(92)90866-2. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Wang L. D., Hong J. Y., Qiu S. L., Gao H., Yang C. S. Accumulation of p53 protein in human esophageal precancerous lesions: a possible early biomarker for carcinogenesis. Cancer Res. 1993 Apr 15;53(8):1783–1787. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Wynford-Thomas D. P53 in tumour pathology: can we trust immunocytochemistry? J Pathol. 1992 Apr;166(4):329–330. doi: 10.1002/path.1711660402. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Yonemura Y., Fushida S., Tsugawa K., Ninomiya I., Fonseca L., Yamaguchi A., Miyazaki I., Urano T., Shiku H. Correlation of p53 expression and proliferative activity in gastric cancer. Anal Cell Pathol. 1993 Sep;5(5):277–288. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]