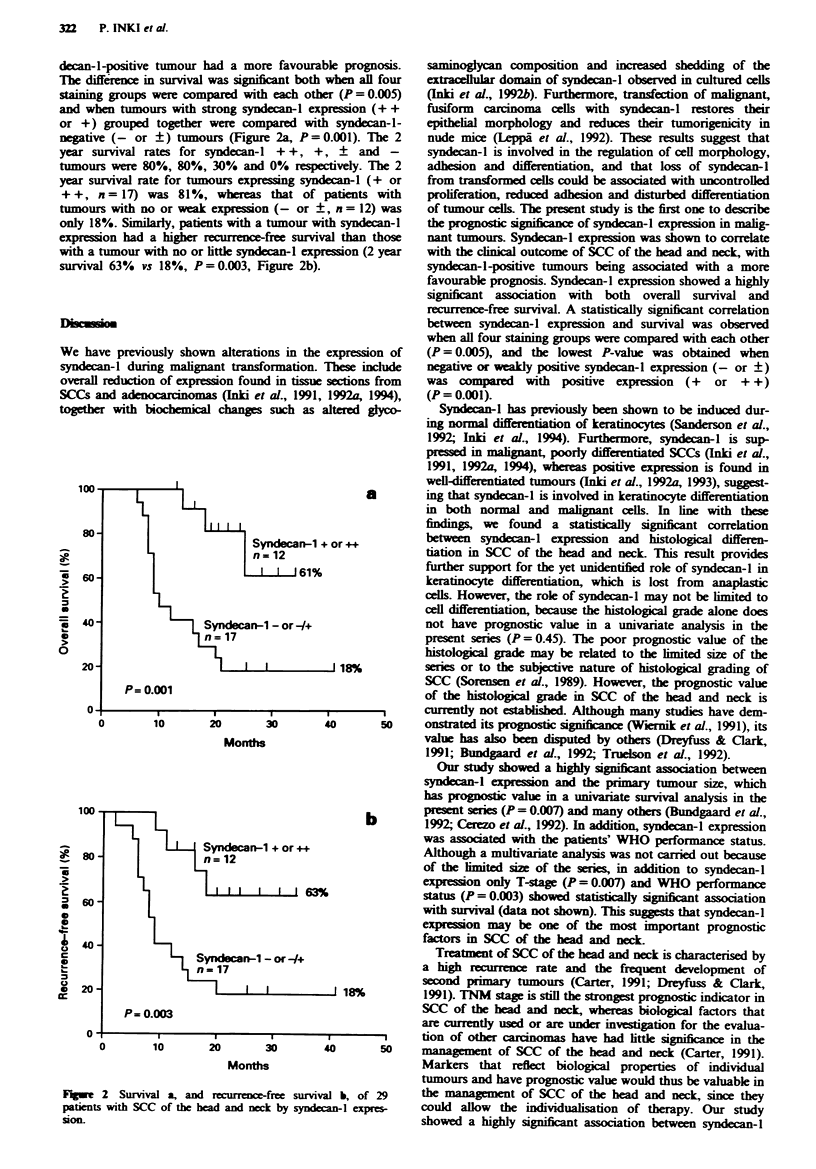
Abstract
Syndecans are a family of cell-surface heparan sulphate proteoglycans which are involved in cell-matrix interactions and growth factor binding. Syndecan-1 binds basic fibroblast growth factor (bFGF) and several components of the extracellular matrix. Syndecan-1 expression is induced during keratinocyte differentiation and reduced during the formation of squamous cell carcinomas (SCCs). The purpose of this study was to examine the association of syndecan-1 expression with prognostic factors and clinical outcome in SCC of the head and neck. Frozen sections of 29 primary SCCs were analysed for syndecan-1 expression using immunohistochemical methods. Intermediate or strong staining for syndecan-1 was associated with a smaller primary tumour size (P = 0.0005) and higher histological grade of differentiation (P = 0.006) than negative or weakly positive staining. In a univariate analysis, syndecan-1-positive tumours were associated with higher overall (P = 0.001) and recurrence-free survival (P = 0.003) than those tumours with no or little syndecan-1 expression. The results suggest that syndecan-1 could be an important prognostic factor of SCC of the head and neck. Further studies on the prognostic significance of syndecan-1 expression in SCCs are warranted.
Full text
PDF



Images in this article
Selected References
These references are in PubMed. This may not be the complete list of references from this article.
- Bernfield M., Kokenyesi R., Kato M., Hinkes M. T., Spring J., Gallo R. L., Lose E. J. Biology of the syndecans: a family of transmembrane heparan sulfate proteoglycans. Annu Rev Cell Biol. 1992;8:365–393. doi: 10.1146/annurev.cb.08.110192.002053. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Bundgaard T., Sørensen F. B., Gaihede M., Søgaard H., Overgaard J. Stereologic, histopathologic, flow cytometric, and clinical parameters in the prognostic evaluation of 74 patients with intraoral squamous cell carcinomas. Cancer. 1992 Jul 1;70(1):1–13. doi: 10.1002/1097-0142(19920701)70:1<1::aid-cncr2820700102>3.0.co;2-s. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Carter R. L. Pathology of squamous carcinomas of the head and neck. Curr Opin Oncol. 1991 Jun;3(3):507–511. doi: 10.1097/00001622-199106000-00010. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Cerezo L., Millán I., Torre A., Aragón G., Otero J. Prognostic factors for survival and tumor control in cervical lymph node metastases from head and neck cancer. A multivariate study of 492 cases. Cancer. 1992 Mar 1;69(5):1224–1234. doi: 10.1002/cncr.2820690526. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Dreyfuss A. I., Clark J. R. Analysis of prognostic factors in squamous cell carcinomas of the head and neck. Hematol Oncol Clin North Am. 1991 Aug;5(4):701–712. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Elenius K., Mättä A., Salmivirta M., Jalkanen M. Growth factors induce 3T3 cells to express bFGF-binding syndecan. J Biol Chem. 1992 Mar 25;267(9):6435–6441. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Elenius K., Salmivirta M., Inki P., Mali M., Jalkanen M. Binding of human syndecan to extracellular matrix proteins. J Biol Chem. 1990 Oct 15;265(29):17837–17843. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Folkman J., Shing Y. Control of angiogenesis by heparin and other sulfated polysaccharides. Adv Exp Med Biol. 1992;313:355–364. doi: 10.1007/978-1-4899-2444-5_34. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Gallagher J. T. The extended family of proteoglycans: social residents of the pericellular zone. Curr Opin Cell Biol. 1989 Dec;1(6):1201–1218. doi: 10.1016/s0955-0674(89)80072-9. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Hayashi K., Hayashi M., Jalkanen M., Firestone J. H., Trelstad R. L., Bernfield M. Immunocytochemistry of cell surface heparan sulfate proteoglycan in mouse tissues. A light and electron microscopic study. J Histochem Cytochem. 1987 Oct;35(10):1079–1088. doi: 10.1177/35.10.2957423. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Inki P., Kujari H., Jalkanen M. Syndecan in carcinomas produced from transformed epithelial cells in nude mice. Lab Invest. 1992 Mar;66(3):314–323. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Inki P., Larjava H., Haapasalmi K., Miettinen H. M., Grenman R., Jalkanen M. Expression of syndecan-1 is induced by differentiation and suppressed by malignant transformation of human keratinocytes. Eur J Cell Biol. 1994 Feb;63(1):43–51. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Inki P., Stenbäck F., Talve L., Jalkanen M. Immunohistochemical localization of syndecan in mouse skin tumors induced by UV irradiation. Loss of expression associated with malignant transformation. Am J Pathol. 1991 Dec;139(6):1333–1340. [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Kiefer M. C., Stephans J. C., Crawford K., Okino K., Barr P. J. Ligand-affinity cloning and structure of a cell surface heparan sulfate proteoglycan that binds basic fibroblast growth factor. Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A. 1990 Sep;87(18):6985–6989. doi: 10.1073/pnas.87.18.6985. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Leppä S., Mali M., Miettinen H. M., Jalkanen M. Syndecan expression regulates cell morphology and growth of mouse mammary epithelial tumor cells. Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A. 1992 Feb 1;89(3):932–936. doi: 10.1073/pnas.89.3.932. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Liotta L. A., Rao C. N., Wewer U. M. Biochemical interactions of tumor cells with the basement membrane. Annu Rev Biochem. 1986;55:1037–1057. doi: 10.1146/annurev.bi.55.070186.005133. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Miller A. B., Hoogstraten B., Staquet M., Winkler A. Reporting results of cancer treatment. Cancer. 1981 Jan 1;47(1):207–214. doi: 10.1002/1097-0142(19810101)47:1<207::aid-cncr2820470134>3.0.co;2-6. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Navarro P., Gómez M., Pizarro A., Gamallo C., Quintanilla M., Cano A. A role for the E-cadherin cell-cell adhesion molecule during tumor progression of mouse epidermal carcinogenesis. J Cell Biol. 1991 Oct;115(2):517–533. doi: 10.1083/jcb.115.2.517. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Ruoslahti E. Integrins. J Clin Invest. 1991 Jan;87(1):1–5. doi: 10.1172/JCI114957. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Salmivirta M., Elenius K., Vainio S., Hofer U., Chiquet-Ehrismann R., Thesleff I., Jalkanen M. Syndecan from embryonic tooth mesenchyme binds tenascin. J Biol Chem. 1991 Apr 25;266(12):7733–7739. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Salmivirta M., Heino J., Jalkanen M. Basic fibroblast growth factor-syndecan complex at cell surface or immobilized to matrix promotes cell growth. J Biol Chem. 1992 Sep 5;267(25):17606–17610. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Sanderson R. D., Hinkes M. T., Bernfield M. Syndecan-1, a cell-surface proteoglycan, changes in size and abundance when keratinocytes stratify. J Invest Dermatol. 1992 Oct;99(4):390–396. doi: 10.1111/1523-1747.ep12616103. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Saunders S., Jalkanen M., O'Farrell S., Bernfield M. Molecular cloning of syndecan, an integral membrane proteoglycan. J Cell Biol. 1989 Apr;108(4):1547–1556. doi: 10.1083/jcb.108.4.1547. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Schipper J. H., Frixen U. H., Behrens J., Unger A., Jahnke K., Birchmeier W. E-cadherin expression in squamous cell carcinomas of head and neck: inverse correlation with tumor dedifferentiation and lymph node metastasis. Cancer Res. 1991 Dec 1;51(23 Pt 1):6328–6337. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Sun X., Mosher D. F., Rapraeger A. Heparan sulfate-mediated binding of epithelial cell surface proteoglycan to thrombospondin. J Biol Chem. 1989 Feb 15;264(5):2885–2889. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Sutherland A. E., Sanderson R. D., Mayes M., Seibert M., Calarco P. G., Bernfield M., Damsky C. H. Expression of syndecan, a putative low affinity fibroblast growth factor receptor, in the early mouse embryo. Development. 1991 Sep;113(1):339–351. doi: 10.1242/dev.113.1.339. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Sørensen F. B., Bennedbaek O., Pilgaard J., Spaun E. Stereological estimation of nuclear volume and other quantitative histopathological parameters in the prognostic evaluation of supraglottic laryngeal squamous cell carcinoma. APMIS. 1989 Nov;97(11):987–995. doi: 10.1111/j.1699-0463.1989.tb00507.x. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Takeichi M. Cadherin cell adhesion receptors as a morphogenetic regulator. Science. 1991 Mar 22;251(5000):1451–1455. doi: 10.1126/science.2006419. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Thesleff I., Jalkanen M., Vainio S., Bernfield M. Cell surface proteoglycan expression correlates with epithelial-mesenchymal interaction during tooth morphogenesis. Dev Biol. 1988 Oct;129(2):565–572. doi: 10.1016/0012-1606(88)90401-0. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Truelson J. M., Fisher S. G., Beals T. E., McClatchey K. D., Wolf G. T. DNA content and histologic growth pattern correlate with prognosis in patients with advanced squamous cell carcinoma of the larynx. The Department of Veterans Affairs Cooperative Laryngeal Cancer Study Group. Cancer. 1992 Jul 1;70(1):56–62. doi: 10.1002/1097-0142(19920701)70:1<56::aid-cncr2820700110>3.0.co;2-q. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Vainio S., Lehtonen E., Jalkanen M., Bernfield M., Saxén L. Epithelial-mesenchymal interactions regulate the stage-specific expression of a cell surface proteoglycan, syndecan, in the developing kidney. Dev Biol. 1989 Aug;134(2):382–391. doi: 10.1016/0012-1606(89)90110-3. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Vainio S., Thesleff I. Sequential induction of syndecan, tenascin and cell proliferation associated with mesenchymal cell condensation during early tooth development. Differentiation. 1992 Jun;50(2):97–105. doi: 10.1111/j.1432-0436.1992.tb00490.x. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Virtanen I., Korhonen M., Kariniemi A. L., Gould V. E., Laitinen L., Ylänne J. Integrins in human cells and tumors. Cell Differ Dev. 1990 Dec 2;32(3):215–227. doi: 10.1016/0922-3371(90)90034-t. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Wiernik G., Millard P. R., Haybittle J. L. The predictive value of histological classification into degrees of differentiation of squamous cell carcinoma of the larynx and hypopharynx compared with the survival of patients. Histopathology. 1991 Nov;19(5):411–417. doi: 10.1111/j.1365-2559.1991.tb00230.x. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]