Abstract
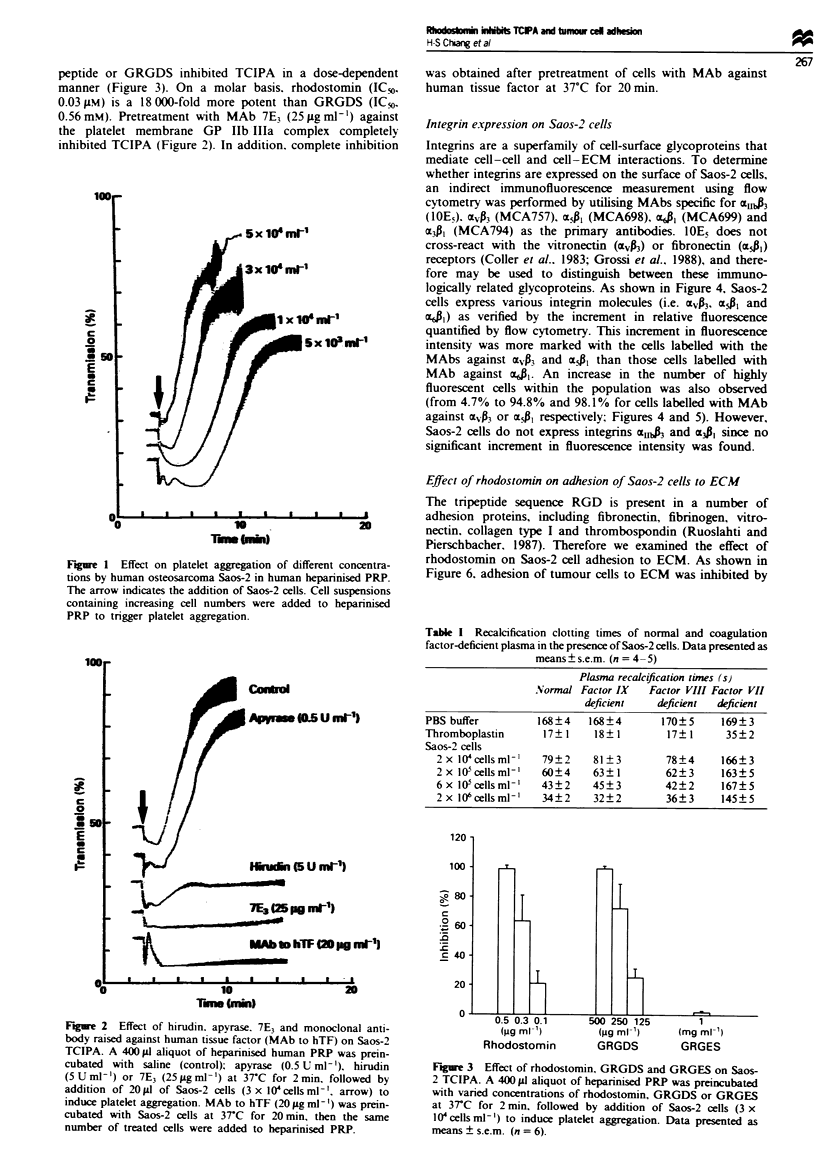
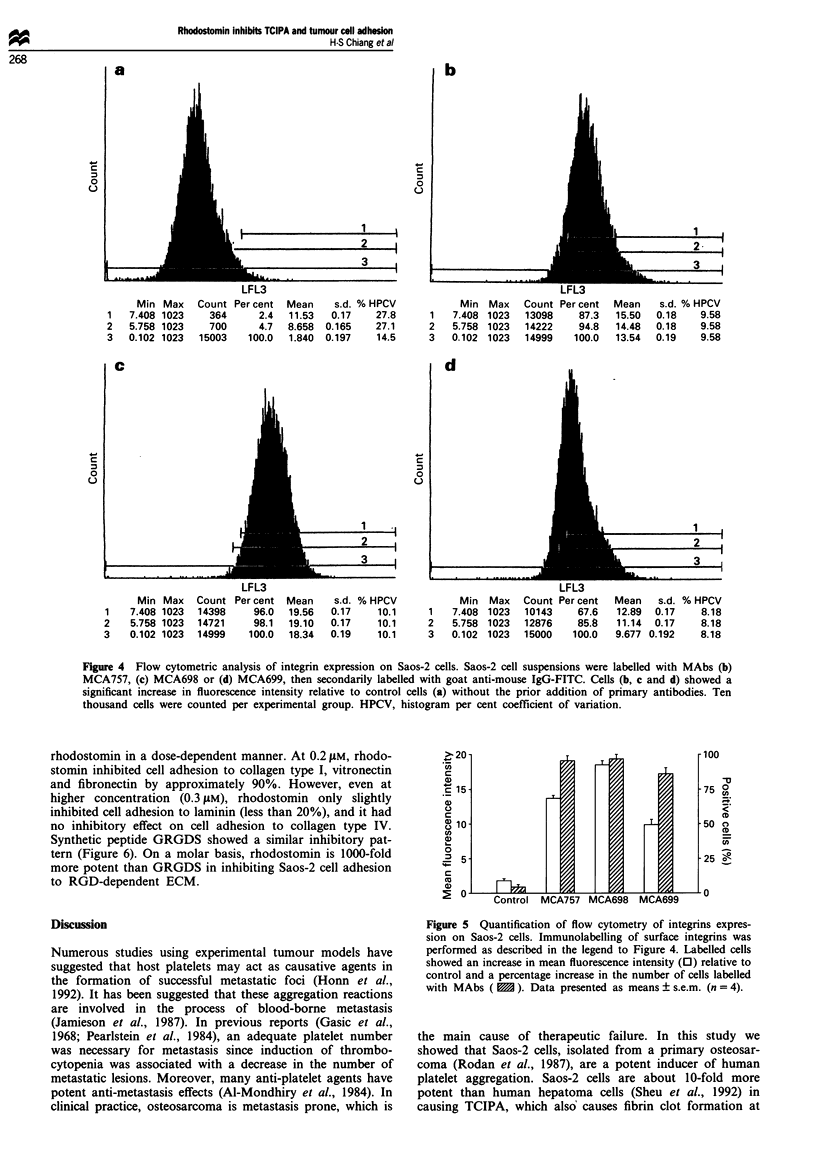
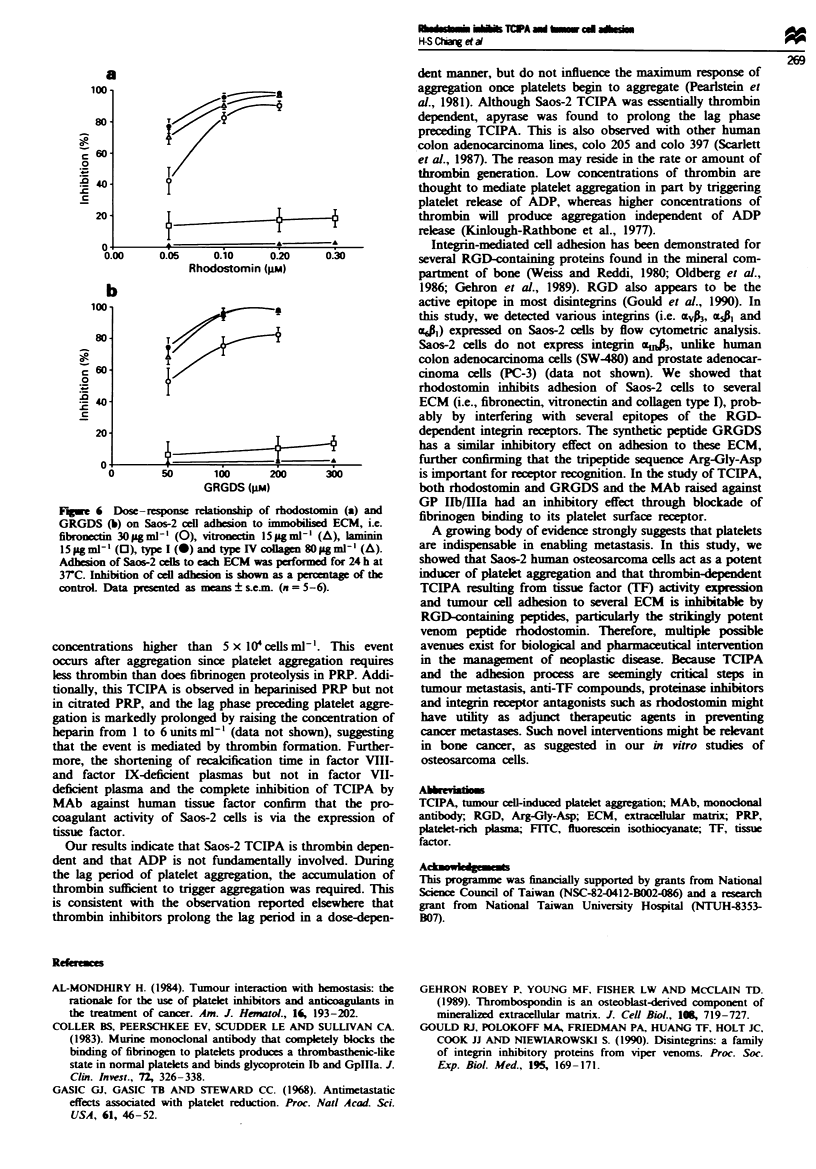
Saos-2 cells, derived from a primary human osteosarcoma, caused dose-dependent platelet aggregation in heparinised human platelet-rich plasma. Saos-2 tumour cell-induced platelet aggregation (TCIPA) was completely inhibited by hirudin but unaffected by apyrase. The cell suspension shortened the plasma recalcification times of normal, factor VIII-deficient and factor IX-deficient human plasmas in a dose-dependent manner. However, the cell suspension did not affect the recalcification time of factor VII-deficient plasma. Moreover, a monoclonal antibody (MAb) against human tissue factor completely abolished TCIPA. Flow cytometric analysis using anti-integrin MAbs as the primary binding ligands demonstrated that the integrin receptors alpha v beta 3, alpha 5 beta 1 and alpha 6 beta 1 were present of Saos-2 cells, which might mediate tumour cell adhesion to extracellular matrix. Rhodostomin, an Arg-Gly-Asp (RGD)-containing snake venom peptide which antagonises the binding of fibrinogen to platelet membrane glycoprotein IIb/IIIa, prevented Saos-2 TCIPA as well as tumour cell adhesion to vitronectin, fibronectin and collagen type I. Likewise, the synthetic peptide Gly-Arg-Gly-Asp-Ser (GRGDS) showed a similar effect. On a molar basis, rhodostomin was about 18,000 and 1000 times, respectively, more potent than GRGDS in inhibiting TCIPA and tumour cell adhesion.
Full text
PDF


Selected References
These references are in PubMed. This may not be the complete list of references from this article.
- Al-Mondhiry H. Tumor interaction with hemostasis: the rationale for the use of platelet inhibitors and anticoagulants in the treatment of cancer. Am J Hematol. 1984 Feb;16(2):193–202. doi: 10.1002/ajh.2830160213. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Coller B. S., Peerschke E. I., Scudder L. E., Sullivan C. A. A murine monoclonal antibody that completely blocks the binding of fibrinogen to platelets produces a thrombasthenic-like state in normal platelets and binds to glycoproteins IIb and/or IIIa. J Clin Invest. 1983 Jul;72(1):325–338. doi: 10.1172/JCI110973. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Gasic G. J., Gasic T. B., Stewart C. C. Antimetastatic effects associated with platelet reduction. Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A. 1968 Sep;61(1):46–52. doi: 10.1073/pnas.61.1.46. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Gould R. J., Polokoff M. A., Friedman P. A., Huang T. F., Holt J. C., Cook J. J., Niewiarowski S. Disintegrins: a family of integrin inhibitory proteins from viper venoms. Proc Soc Exp Biol Med. 1990 Nov;195(2):168–171. doi: 10.3181/00379727-195-43129b. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Grossi I. M., Fitzgerald L. A., Umbarger L. A., Nelson K. K., Diglio C. A., Taylor J. D., Honn K. V. Bidirectional control of membrane expression and/or activation of the tumor cell IRGpIIb/IIIa receptor and tumor cell adhesion by lipoxygenase products of arachidonic acid and linoleic acid. Cancer Res. 1989 Feb 15;49(4):1029–1037. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Grossi I. M., Hatfield J. S., Fitzgerald L. A., Newcombe M., Taylor J. D., Honn K. V. Role of tumor cell glycoproteins immunologically related to glycoproteins Ib and IIb/IIIa in tumor cell-platelet and tumor cell-matrix interactions. FASEB J. 1988 May;2(8):2385–2395. doi: 10.1096/fasebj.2.8.2452113. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Honn K. V., Tang D. G., Chen Y. Q. Platelets and cancer metastasis: more than an epiphenomenon. Semin Thromb Hemost. 1992;18(4):392–415. doi: 10.1055/s-2007-1002578. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Huang T. F., Holt J. C., Kirby E. P., Niewiarowski S. Trigramin: primary structure and its inhibition of von Willebrand factor binding to glycoprotein IIb/IIIa complex on human platelets. Biochemistry. 1989 Jan 24;28(2):661–666. doi: 10.1021/bi00428a037. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Huang T. F., Holt J. C., Lukasiewicz H., Niewiarowski S. Trigramin. A low molecular weight peptide inhibiting fibrinogen interaction with platelet receptors expressed on glycoprotein IIb-IIIa complex. J Biol Chem. 1987 Nov 25;262(33):16157–16163. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Huang T. F., Liu C. Z., Ouyang C. H., Teng C. M. Halysin, an antiplatelet Arg-Gly-Asp-containing snake venom peptide, as fibrinogen receptor antagonist. Biochem Pharmacol. 1991 Aug 22;42(6):1209–1219. doi: 10.1016/0006-2952(91)90256-5. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Huang T. F., Wang W. J., Teng C. M., Ouyang C. Mechanism of action of the antiplatelet peptide, arietin, from Bitis arietans venom. Biochim Biophys Acta. 1991 May 24;1074(1):144–150. doi: 10.1016/0304-4165(91)90053-j. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Huang T. F., Wu Y. J., Ouyang C. Characterization of a potent platelet aggregation inhibitor from Agkistrodon rhodostoma snake venom. Biochim Biophys Acta. 1987 Sep 11;925(3):248–257. doi: 10.1016/0304-4165(87)90189-9. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Hynes R. O. Integrins: a family of cell surface receptors. Cell. 1987 Feb 27;48(4):549–554. doi: 10.1016/0092-8674(87)90233-9. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Kinlough-Rathbone R. L., Packham M. A., Reimers H. J., Cazenave J. P., Mustard J. F. Mechanisms of platelet shape change, aggregation, and release induced by collagen, thrombin, or A23,187. J Lab Clin Med. 1977 Oct;90(4):707–719. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Oldberg A., Franzén A., Heinegård D. Cloning and sequence analysis of rat bone sialoprotein (osteopontin) cDNA reveals an Arg-Gly-Asp cell-binding sequence. Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A. 1986 Dec;83(23):8819–8823. doi: 10.1073/pnas.83.23.8819. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Pearlstein E., Ambrogio C., Gasic G., Karpatkin S. Inhibition of the platelet-aggregating activity of two human adenocarcinomas of the colon and an anaplastic murine tumor with a specific thrombin inhibitor, dansylarginine N-(3-ethyl-1,5-pentanediyl)amide. Cancer Res. 1981 Nov;41(11 Pt 1):4535–4539. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Pearlstein E., Ambrogio C., Karpatkin S. Effect of antiplatelet antibody on the development of pulmonary metastases following injection of CT26 colon adenocarcinoma, Lewis lung carcinoma, and B16 amelanotic melanoma tumor cells into mice. Cancer Res. 1984 Sep;44(9):3884–3887. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Pearlstein E., Salk P. L., Yogeeswaran G., Karpatkin S. Correlation between spontaneous metastatic potential, platelet-aggregating activity of cell surface extracts, and cell surface sialylation in 10 metastatic-variant derivatives of a rat renal sarcoma cell line. Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A. 1980 Jul;77(7):4336–4339. doi: 10.1073/pnas.77.7.4336. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Pierschbacher M. D., Ruoslahti E. Cell attachment activity of fibronectin can be duplicated by small synthetic fragments of the molecule. Nature. 1984 May 3;309(5963):30–33. doi: 10.1038/309030a0. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Robey P. G., Young M. F., Fisher L. W., McClain T. D. Thrombospondin is an osteoblast-derived component of mineralized extracellular matrix. J Cell Biol. 1989 Feb;108(2):719–727. doi: 10.1083/jcb.108.2.719. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Rodan S. B., Imai Y., Thiede M. A., Wesolowski G., Thompson D., Bar-Shavit Z., Shull S., Mann K., Rodan G. A. Characterization of a human osteosarcoma cell line (Saos-2) with osteoblastic properties. Cancer Res. 1987 Sep 15;47(18):4961–4966. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Rucinski B., Niewiarowski S., Holt J. C., Soszka T., Knudsen K. A. Batroxostatin, an Arg-Gly-Asp-containing peptide from Bothrops atrox, is a potent inhibitor of platelet aggregation and cell interaction with fibronectin. Biochim Biophys Acta. 1990 Sep 24;1054(3):257–262. doi: 10.1016/0167-4889(90)90096-v. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Ruoslahti E., Pierschbacher M. D. New perspectives in cell adhesion: RGD and integrins. Science. 1987 Oct 23;238(4826):491–497. doi: 10.1126/science.2821619. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Scarlett J. D., Thurlow P. J., Connellan J. M., Louis C. J. Plasma-dependent and -independent mechanisms of platelet aggregation induced by human tumour cell lines. Thromb Res. 1987 Jun 1;46(5):715–726. doi: 10.1016/0049-3848(87)90273-8. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Shebuski R. J., Ramjit D. R., Bencen G. H., Polokoff M. A. Characterization and platelet inhibitory activity of bitistatin, a potent arginine-glycine-aspartic acid-containing peptide from the venom of the viper Bitis arietans. J Biol Chem. 1989 Dec 25;264(36):21550–21556. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Sheu J. R., Lin C. H., Chung J. L., Teng C. M., Huang T. F. Triflavin, an Arg-Gly-Asp containing snake venom peptide, inhibits aggregation of human platelets induced by human hepatoma cell line. Thromb Res. 1992 Jun 15;66(6):679–691. doi: 10.1016/0049-3848(92)90044-b. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Vaporciyan A. A., Jones M. L., Ward P. A. Rapid analysis of leukocyte-endothelial adhesion. J Immunol Methods. 1993 Feb 26;159(1-2):93–100. doi: 10.1016/0022-1759(93)90145-w. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Weiss R. E., Reddi A. H. Synthesis and localization of fibronectin during collagenous matrix-mesenchymal cell interaction and differentiation of cartilage and bone in vivo. Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A. 1980 Apr;77(4):2074–2078. doi: 10.1073/pnas.77.4.2074. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]


