Abstract
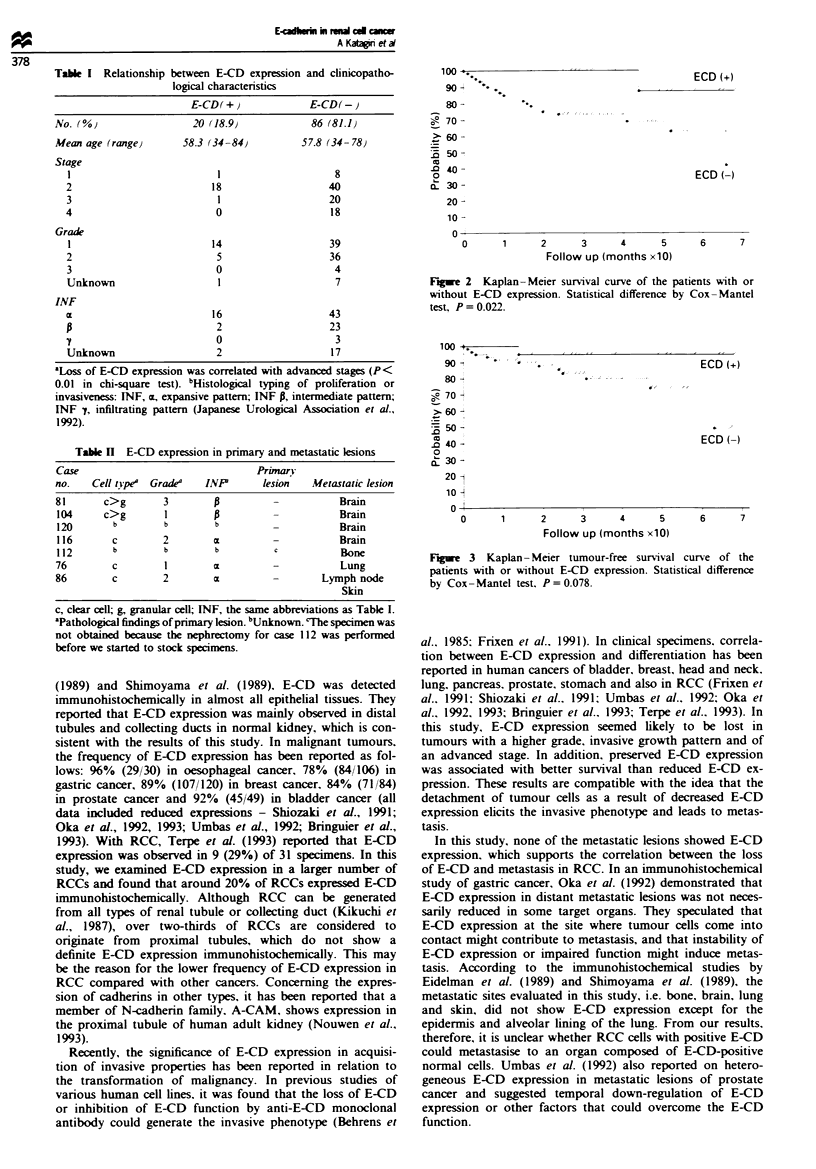
Decreased expression of E-cadherin (E-CD), a homotypic intercellular adhesion molecule, is considered to elicit detachment of tumour cells from primary lesions, which is the first stage of metastasis. Since renal cell cancer (RCC) shows a relatively high frequency of metastasis, we focused our interest on E-CD expression in RCC and its clinicopathological implications. We examined E-CD expression in normal kidney and RCC by immunohistochemical staining. In normal kidney, E-CD expression was localised in distal tubules and collecting ducts. In RCC, 20 of 106 primary lesions (18.9%) expressed E-CD, whereas none showed positive staining for eight metastatic lesions. There was a statistically significant correlation between loss of E-CD expression and advanced stages of RCC. Kaplan-Meier analysis showed better prognosis in the group with preserved E-CD expression than without E-CD expression (Cox-Mantel test, P = 0.022, the average follow-up was 32 months or until death). This study suggests that the patients with decreased E-CD expression may be associated with metastasis, resulting in poor prognosis. However, frequency of E-CD expression in RCC is lower than in other cancers, which may be derived from the localised distribution of E-CD expression in normal kidney.
Full text
PDF
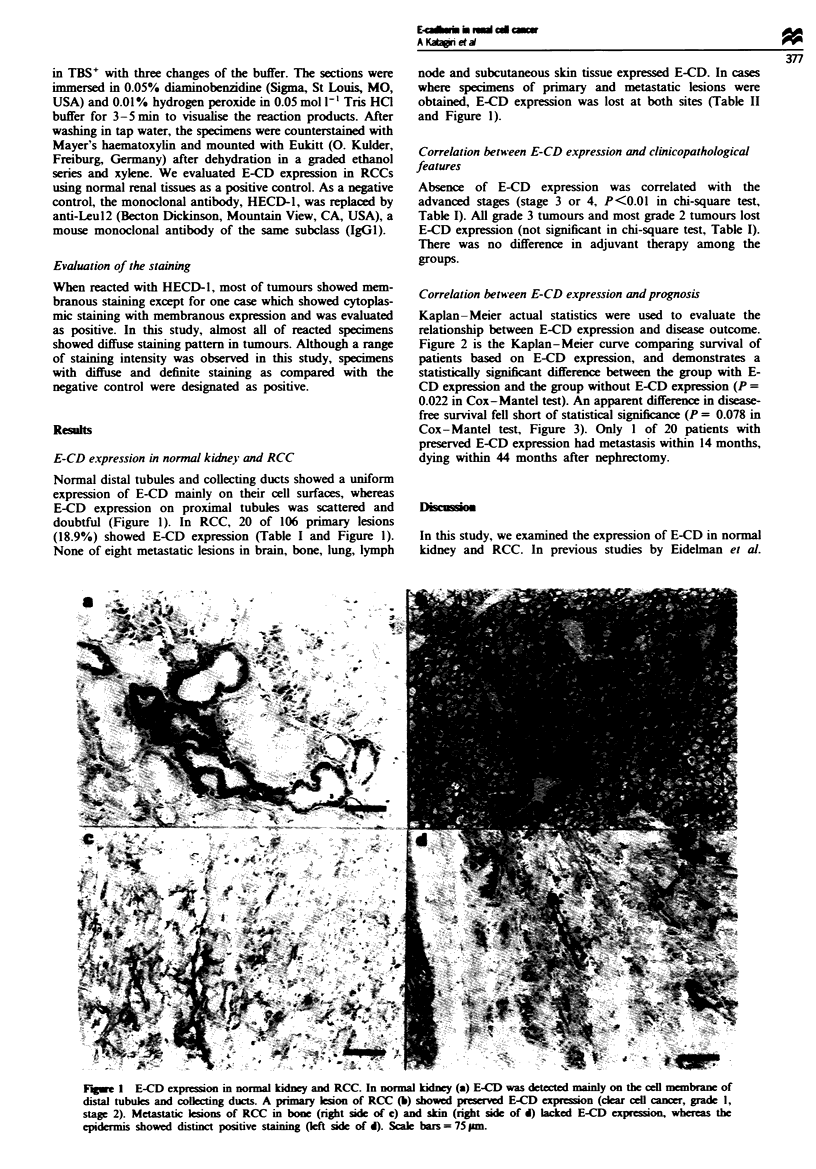

Images in this article
Selected References
These references are in PubMed. This may not be the complete list of references from this article.
- Behrens J., Birchmeier W., Goodman S. L., Imhof B. A. Dissociation of Madin-Darby canine kidney epithelial cells by the monoclonal antibody anti-arc-1: mechanistic aspects and identification of the antigen as a component related to uvomorulin. J Cell Biol. 1985 Oct;101(4):1307–1315. doi: 10.1083/jcb.101.4.1307. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Behrens J., Vakaet L., Friis R., Winterhager E., Van Roy F., Mareel M. M., Birchmeier W. Loss of epithelial differentiation and gain of invasiveness correlates with tyrosine phosphorylation of the E-cadherin/beta-catenin complex in cells transformed with a temperature-sensitive v-SRC gene. J Cell Biol. 1993 Feb;120(3):757–766. doi: 10.1083/jcb.120.3.757. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Bringuier P. P., Umbas R., Schaafsma H. E., Karthaus H. F., Debruyne F. M., Schalken J. A. Decreased E-cadherin immunoreactivity correlates with poor survival in patients with bladder tumors. Cancer Res. 1993 Jul 15;53(14):3241–3245. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Eidelman S., Damsky C. H., Wheelock M. J., Damjanov I. Expression of the cell-cell adhesion glycoprotein cell-CAM 120/80 in normal human tissues and tumors. Am J Pathol. 1989 Jul;135(1):101–110. [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Frixen U. H., Behrens J., Sachs M., Eberle G., Voss B., Warda A., Löchner D., Birchmeier W. E-cadherin-mediated cell-cell adhesion prevents invasiveness of human carcinoma cells. J Cell Biol. 1991 Apr;113(1):173–185. doi: 10.1083/jcb.113.1.173. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Hirano S., Kimoto N., Shimoyama Y., Hirohashi S., Takeichi M. Identification of a neural alpha-catenin as a key regulator of cadherin function and multicellular organization. Cell. 1992 Jul 24;70(2):293–301. doi: 10.1016/0092-8674(92)90103-j. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Katagiri A., Tomita Y., Nishiyama T., Kimura M., Sato S. Immunohistochemical detection of P-glycoprotein and GSTP1-1 in testis cancer. Br J Cancer. 1993 Jul;68(1):125–129. doi: 10.1038/bjc.1993.299. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Nouwen E. J., Dauwe S., van der Biest I., De Broe M. E. Stage- and segment-specific expression of cell-adhesion molecules N-CAM, A-CAM, and L-CAM in the kidney. Kidney Int. 1993 Jul;44(1):147–158. doi: 10.1038/ki.1993.225. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Oka H., Shiozaki H., Kobayashi K., Inoue M., Tahara H., Kobayashi T., Takatsuka Y., Matsuyoshi N., Hirano S., Takeichi M. Expression of E-cadherin cell adhesion molecules in human breast cancer tissues and its relationship to metastasis. Cancer Res. 1993 Apr 1;53(7):1696–1701. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Oka H., Shiozaki H., Kobayashi K., Tahara H., Tamura S., Miyata M., Doki Y., Iihara K., Matsuyoshi N., Hirano S. Immunohistochemical evaluation of E-cadherin adhesion molecule expression in human gastric cancer. Virchows Arch A Pathol Anat Histopathol. 1992;421(2):149–156. doi: 10.1007/BF01607048. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Shimoyama Y., Hirohashi S., Hirano S., Noguchi M., Shimosato Y., Takeichi M., Abe O. Cadherin cell-adhesion molecules in human epithelial tissues and carcinomas. Cancer Res. 1989 Apr 15;49(8):2128–2133. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Shiozaki H., Tahara H., Oka H., Miyata M., Kobayashi K., Tamura S., Iihara K., Doki Y., Hirano S., Takeichi M. Expression of immunoreactive E-cadherin adhesion molecules in human cancers. Am J Pathol. 1991 Jul;139(1):17–23. [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Takeichi M. Cadherin cell adhesion receptors as a morphogenetic regulator. Science. 1991 Mar 22;251(5000):1451–1455. doi: 10.1126/science.2006419. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Terpe H. J., Tajrobehkar K., Günthert U., Altmannsberger M. Expression of cell adhesion molecules alpha-2, alpha-5 and alpha-6 integrin, E-cadherin, N-CAM and CD-44 in renal cell carcinomas. An immunohistochemical study. Virchows Arch A Pathol Anat Histopathol. 1993;422(3):219–224. doi: 10.1007/BF01621805. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Umbas R., Schalken J. A., Aalders T. W., Carter B. S., Karthaus H. F., Schaafsma H. E., Debruyne F. M., Isaacs W. B. Expression of the cellular adhesion molecule E-cadherin is reduced or absent in high-grade prostate cancer. Cancer Res. 1992 Sep 15;52(18):5104–5109. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]



