Abstract
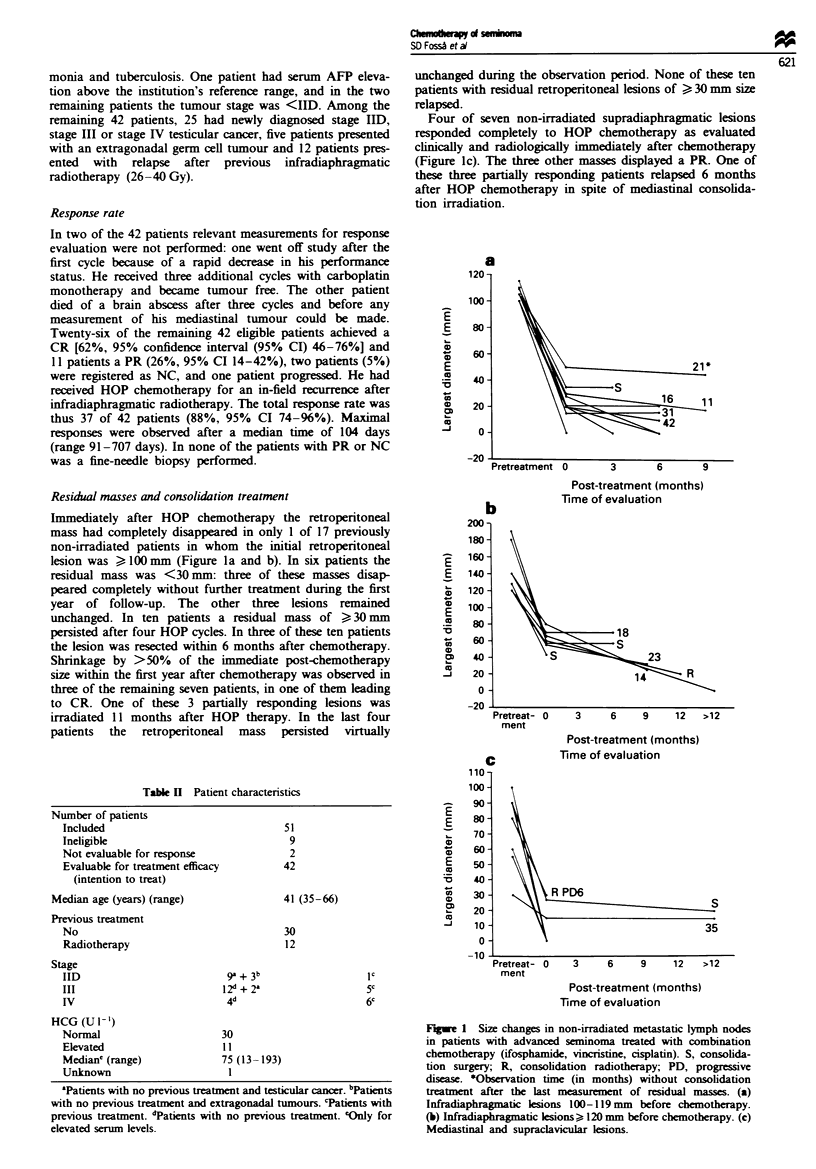
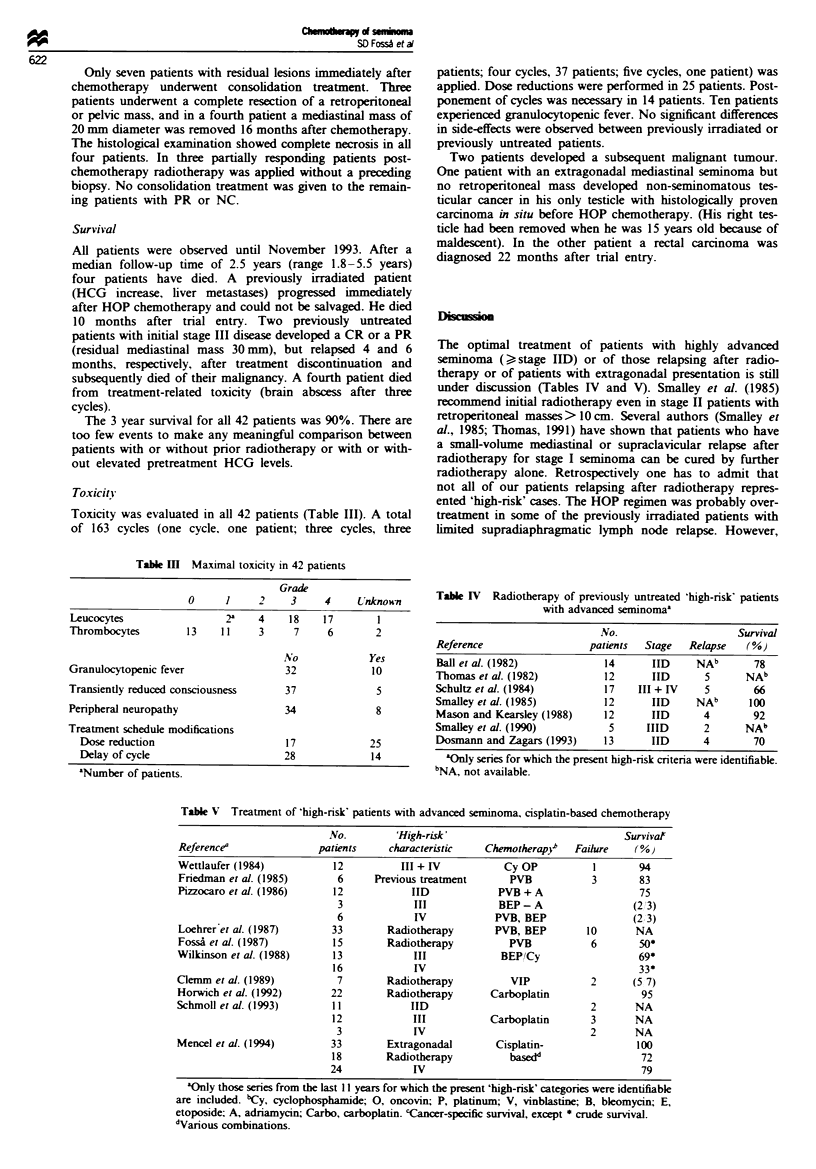
The aims of the trial were to establish the response rate and determine the toxicity of combination chemotherapy with ifosphamide, vincristine and cisplatin (HOP regimen) in advanced metastatic seminoma and to study the role of post-chemotherapy consolidation treatment. Patients with bulky metastatic non-alpha-fetoprotein-producing seminomas were eligible for this phase II study [serum human chorionic gonadotropin < 200 U l-1 (< 40 ng l-1)] if they presented with abdominal masses > or = 10 cm or had extra-gonadal seminoma or had relapsed after previous radiotherapy. The HOP regimen consisted of four 3-weekly cycles of the following drug combination: ifosphamide (days 1-5, 1.2 mg m-2 day-1), vincristine (day 1, 2 mg) and cisplatin (days 1-5, 20 mg m-2 day-1). Residual masses persisting 6 months after chemotherapy could be considered for consolidation surgery or radiotherapy. Maximal response to the HOP chemotherapy (evaluated at any time) was based on the WHO criteria. The median observation time was 2.5 years (range 1.8-5.5 years). Thirteen institutions treated 42 eligible patients within the study (testicular cancer stage > or = IID, 25; extragonadal, 5; relapse after previous radiotherapy, 12). Two patients were not evaluable for response owing to premature treatment discontinuation. Maximal response was as follows: complete remission (CR), 26 (65%); partial remission (PR) 11 (28%); no change (NC), 2 (5%); progressive disease (PD), 1 (3%). Four patients have died, three from their malignancy (two without previous irradiation and one with prior radiotherapy). The fourth patient died of treatment-related toxicity. The 3 year survival for all 42 eligible patients was 90%. Dose reduction and treatment postponement were necessary in 25 and 14 patients respectively. Ten patients experienced granulocytic fever. Previously irradiated patients tolerated chemotherapy as well as non-irradiated patients. Immediately after HOP chemotherapy a mass persisted in 16 of 17 patients with retroperitoneal masses of > or = 100 mm at presentation. Three of these residual lesions were resected within the following 6 months showing complete necrosis. Four lesions dissolved spontaneously during the first year of follow-up. Nine lesions persisted for > or = 1 year (one after consolidation radiotherapy) without leading to relapse. Four of seven patients with mediastinal lesions achieved CR and three a PR after HOP chemotherapy. The HOP chemotherapy regimen is highly effective in patients with advanced metastatic seminoma or those relapsing after previous radiotherapy, but is associated with a high risk of toxicity, in particular myelotoxicity.
Full text
PDF



Selected References
These references are in PubMed. This may not be the complete list of references from this article.
- Ball D., Barrett A., Peckham M. J. The management of metastatic seminoma testis. Cancer. 1982 Dec 1;50(11):2289–2294. doi: 10.1002/1097-0142(19821201)50:11<2289::aid-cncr2820501112>3.0.co;2-x. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Bosl G. J., Geller N. L., Bajorin D., Leitner S. P., Yagoda A., Golbey R. B., Scher H., Vogelzang N. J., Auman J., Carey R. A randomized trial of etoposide + cisplatin versus vinblastine + bleomycin + cisplatin + cyclophosphamide + dactinomycin in patients with good-prognosis germ cell tumors. J Clin Oncol. 1988 Aug;6(8):1231–1238. doi: 10.1200/JCO.1988.6.8.1231. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Clemm C., Hartenstein R., Willich N., Ledderose G., Wilmanns W. Combination chemotherapy with vinblastine, ifosfamide and cisplatin in bulky seminoma. Acta Oncol. 1989;28(2):231–235. doi: 10.3109/02841868909111253. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Dosmann M. A., Zagars G. K. Post-orchiectomy radiotherapy for stages I and II testicular seminoma. Int J Radiat Oncol Biol Phys. 1993 Jun 15;26(3):381–390. doi: 10.1016/0360-3016(93)90954-t. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Einhorn L. H., Williams S. D., Loehrer P. J., Birch R., Drasga R., Omura G., Greco F. A. Evaluation of optimal duration of chemotherapy in favorable-prognosis disseminated germ cell tumors: a Southeastern Cancer Study Group protocol. J Clin Oncol. 1989 Mar;7(3):387–391. doi: 10.1200/JCO.1989.7.3.387. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Ellison M. F., Mostofi F. K., Flanigan R. C. Treatment of the residual retroperitoneal mass after chemotherapy for advanced seminoma. J Urol. 1988 Sep;140(3):618–620. doi: 10.1016/s0022-5347(17)41739-3. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Fosså S. D., Borge L., Aass N., Johannessen N. B., Stenwig A. E., Kaalhus O. The treatment of advanced metastatic seminoma: experience in 55 cases. J Clin Oncol. 1987 Jul;5(7):1071–1077. doi: 10.1200/JCO.1987.5.7.1071. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Friedman E. L., Garnick M. B., Stomper P. C., Mauch P. M., Harrington D. P., Richie J. P. Therapeutic guidelines and results in advanced seminoma. J Clin Oncol. 1985 Oct;3(10):1325–1332. doi: 10.1200/JCO.1985.3.10.1325. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Horwich A., Dearnaley D. P., A'Hern R., Mason M., Thomas G., Jay G., Nicholls J. The activity of single-agent carboplatin in advanced seminoma. Eur J Cancer. 1992;28A(8-9):1307–1310. doi: 10.1016/0959-8049(92)90505-v. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Lehne G., Lote K. Pulmonary toxicity of cytotoxic and immunosuppressive agents. A review. Acta Oncol. 1990;29(2):113–124. doi: 10.3109/02841869009126530. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Loehrer P. J., Sr, Birch R., Williams S. D., Greco F. A., Einhorn L. H. Chemotherapy of metastatic seminoma: the Southeastern Cancer Study Group experience. J Clin Oncol. 1987 Aug;5(8):1212–1220. doi: 10.1200/JCO.1987.5.8.1212. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Mackenzie A. R. The chemotherapy of metastatic seminoma. J Urol. 1966 Nov;96(5):790–793. doi: 10.1016/S0022-5347(17)63351-2. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Mason B. R., Kearsley J. H. Radiotherapy for stage 2 testicular seminoma: the prognostic influence of tumor bulk. J Clin Oncol. 1988 Dec;6(12):1856–1862. doi: 10.1200/JCO.1988.6.12.1856. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Mencel P. J., Motzer R. J., Mazumdar M., Vlamis V., Bajorin D. F., Bosl G. J. Advanced seminoma: treatment results, survival, and prognostic factors in 142 patients. J Clin Oncol. 1994 Jan;12(1):120–126. doi: 10.1200/JCO.1994.12.1.120. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Motzer R. J., Bosl G. J., Geller N. L., Penenberg D., Yagoda A., Golbey R., Whitmore W. F., Jr, Fair W. R., Sogani P., Herr H. Advanced seminoma: the role of chemotherapy and adjunctive surgery. Ann Intern Med. 1988 Apr;108(4):513–518. doi: 10.7326/0003-4819-108-4-513. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Motzer R., Bosl G., Heelan R., Fair W., Whitmore W., Sogani P., Herr H., Morse M. Residual mass: an indication for further therapy in patients with advanced seminoma following systemic chemotherapy. J Clin Oncol. 1987 Jul;5(7):1064–1070. doi: 10.1200/JCO.1987.5.7.1064. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Peckham M. J., McElwain T. J., Barrett A., Hendry W. F. Combined management of malignant teratoma of the testis. Lancet. 1979 Aug 11;2(8137):267–270. doi: 10.1016/s0140-6736(79)90288-5. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Pizzocaro G., Salvioni R., Piva L., Zanoni F., Milani A., Faustini M. Cisplatin combination chemotherapy in advanced seminoma. Cancer. 1986 Oct 15;58(8):1625–1629. doi: 10.1002/1097-0142(19861015)58:8<1625::aid-cncr2820580807>3.0.co;2-b. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Schmoll H. J., Harstrick A., Bokemeyer C., Dieckmann K. P., Clemm C., Berdel W. E., Souchon R., Schöber C., Wilke H., Poliwoda H. Single-agent carboplatinum for advanced seminoma. A phase II study. Cancer. 1993 Jul 1;72(1):237–243. doi: 10.1002/1097-0142(19930701)72:1<237::aid-cncr2820720142>3.0.co;2-l. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Schultz S. M., Einhorn L. H., Conces D. J., Jr, Williams S. D., Loehrer P. J. Management of postchemotherapy residual mass in patients with advanced seminoma: Indiana University experience. J Clin Oncol. 1989 Oct;7(10):1497–1503. doi: 10.1200/JCO.1989.7.10.1497. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Smalley S. R., Earle J. D., Evans R. G., Richardson R. L. Modern radiotherapy results with bulky stages II and III seminoma. J Urol. 1990 Sep;144(3):685–689. doi: 10.1016/s0022-5347(17)39555-1. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Smalley S. R., Evans R. G., Richardson R. L., Farrow G. M., Earle J. D. Radiotherapy as initial treatment for bulky stage II testicular seminomas. J Clin Oncol. 1985 Oct;3(10):1333–1338. doi: 10.1200/JCO.1985.3.10.1333. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Stoter G., Sylvester R., Sleijfer D. T., ten Bokkel Huinink W. W., Kaye S. B., Jones W. G., van Oosterom A. T., Vendrik C. P., Spaander P., de Pauw M. Multivariate analysis of prognostic factors in patients with disseminated nonseminomatous testicular cancer: results from a European Organization for Research on Treatment of Cancer Multiinstitutional Phase III Study. Cancer Res. 1987 May 15;47(10):2714–2718. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Thomas G. M., Rider W. D., Dembo A. J., Cummings B. J., Gospodarowicz M., Hawkins N. V., Herman J. G., Keen C. W. Seminoma of the testis: results of treatment and patterns of failure after radiation therapy. Int J Radiat Oncol Biol Phys. 1982 Feb;8(2):165–174. doi: 10.1016/0360-3016(82)90509-0. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Wettlaufer J. N. The management of advanced seminoma. Semin Urol. 1984 Nov;2(4):257–263. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Wilkinson P. M., Read G., Magee B. The treatment of advanced seminoma with chemotherapy and radiotherapy. Br J Cancer. 1988 Jan;57(1):100–104. doi: 10.1038/bjc.1988.18. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]


