Abstract
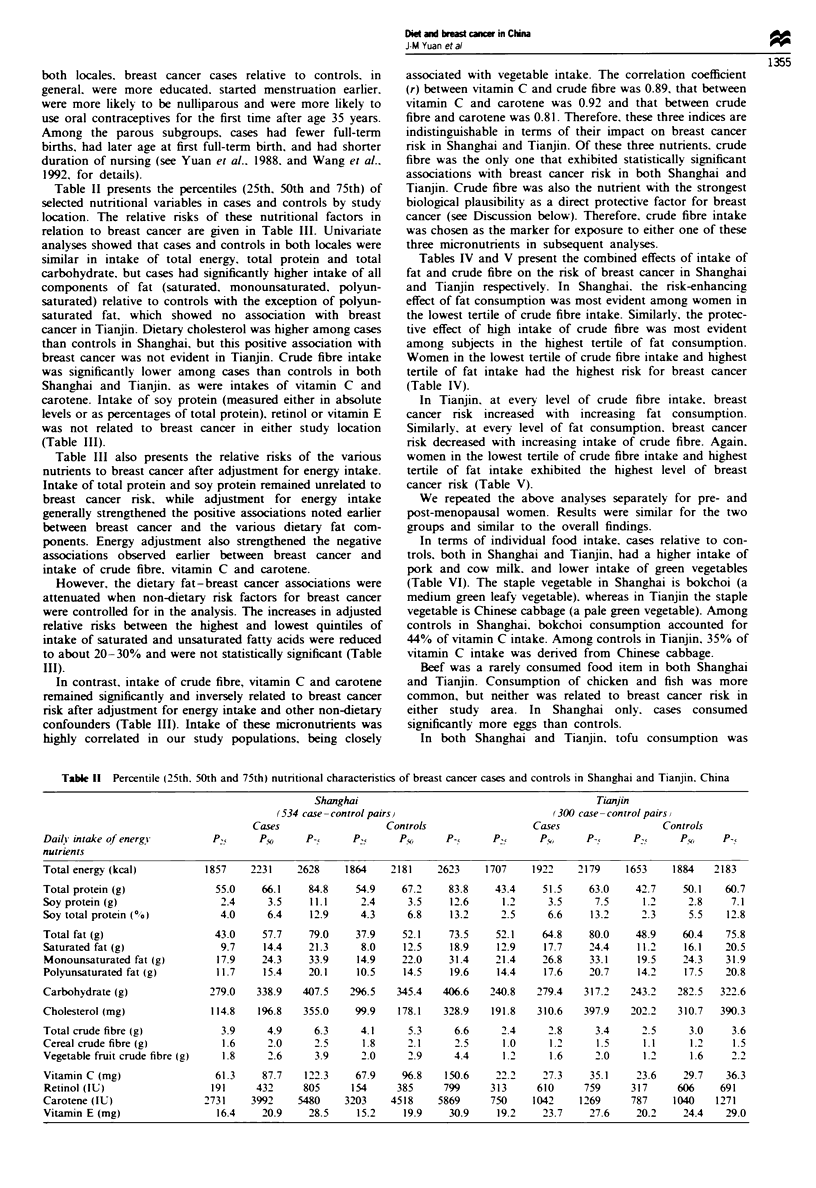
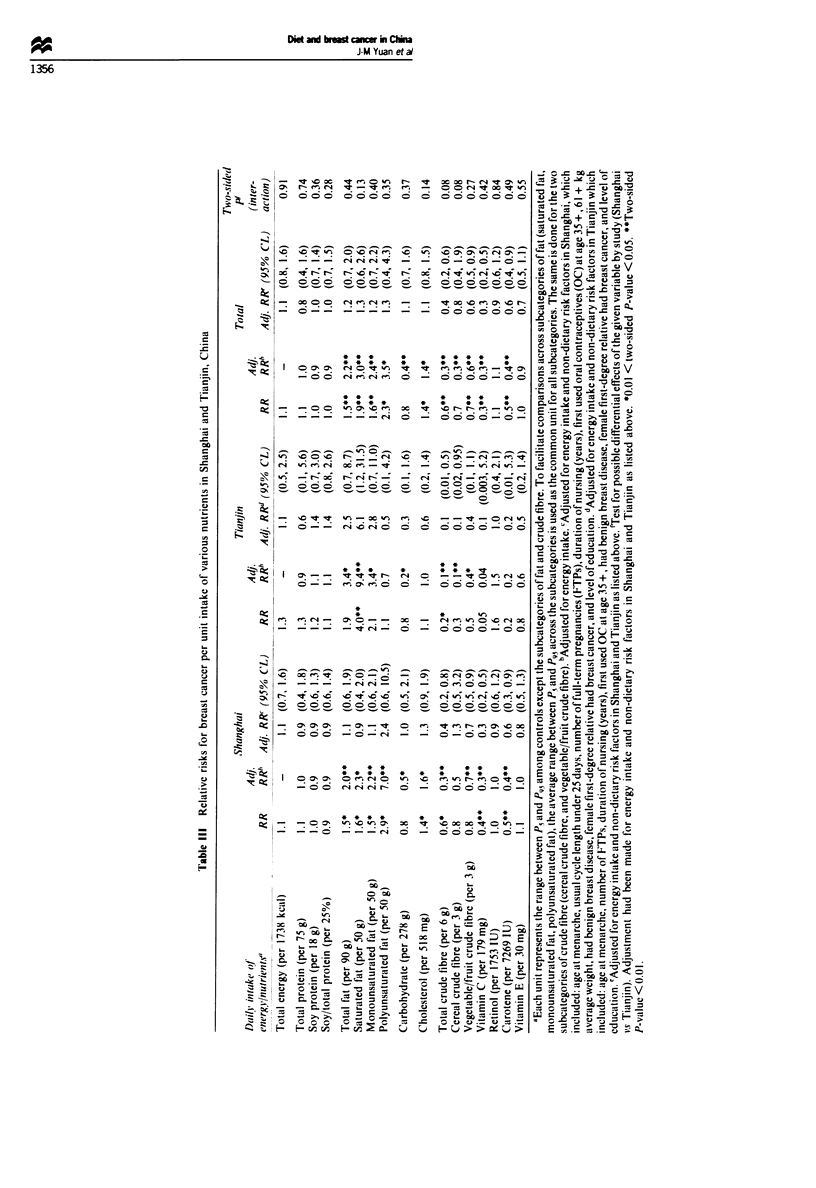
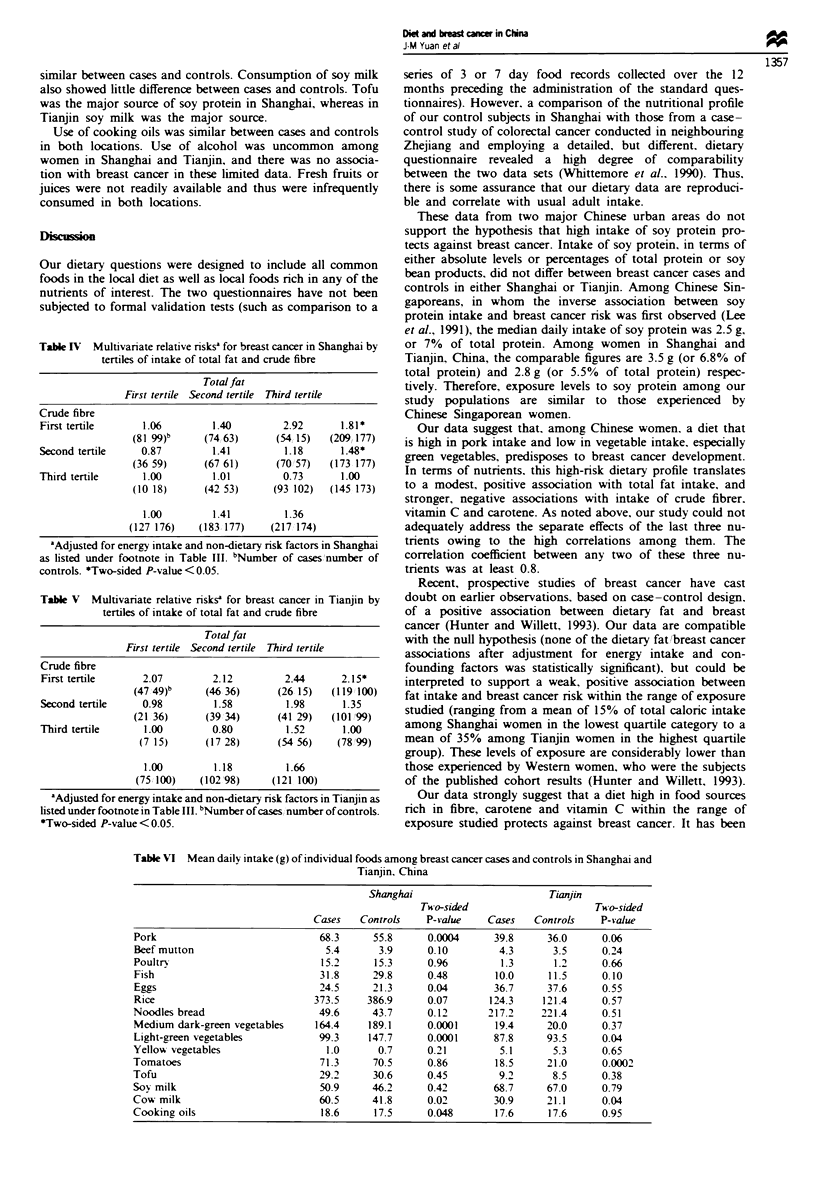
Various aspects of adult diet have been linked to breast cancer development. These include intake of fat (risk factor), and intake of fibre, soy protein and vitamins A, C and E (protective factors). Results of previous studies have been inconsistent. We examined the possible associations between breast cancer and various indices of nutrient and food intake in two Chinese populations who are at relatively low risk for breast cancer (one-fifth the rate in US white women). Two case-control studies of breast cancer were conducted in the cities of Shanghai and Tianjin, China. In Shanghai, 534 women aged 20-69 years with histologically confirmed breast cancer were recruited, whereas in Tianjin 300 women aged 20-55 years with histologically confirmed breast cancer were interviewed. All controls were community controls who were individually matched to the cases by sex and age (case-control ratio = 1:1). All interviews were conducted in person. Findings from the two studies were similar, although the diets in Shanghai and Tianjin were different in many respects. Cases and controls were similar in their consumption of soy protein, measured either in absolute levels or as percentages of total protein. Overall, all components of dietary fat (saturated fat, monounsaturated fat, polyunsaturated fat) showed a modest, non-significant association with breast cancer after adjustment for energy intake and other non-dietary risk factors for breast cancer. Intake of crude fibre, carotene and vitamin C, on the other hand, exhibited strong, statistically significant inverse associations with breast cancer risk. The last three indices were highly correlated, rendering it impossible to disentangle their individual effects; they were closely associated with intake of green vegetables in the two study populations. Vitamin E intake was unrelated to breast cancer risk in Shanghai and Tianjin. In the multivariate logistic regression model which included all non-dietary risk factors for breast cancer and energy intake, Shanghai women in the lowest tertile of crude fibre intake and highest tertile of fat intake had a 2.9-fold increased risk for breast cancer relative to those in the highest tertile of crude fibre intake and lowest tertile of fat intake. The comparable relative risk in Tianjin women was 2.4. Our data indicate a strong protective effect against breast cancer development with intake of foods rich in fibre, vitamin C and carotene. Our results are also compatible with dietary fat having a modest, positive effect on breast cancer risk within the range of exposure experienced by women in China.(ABSTRACT TRUNCATED AT 250 WORDS)
Full text
PDF


Selected References
These references are in PubMed. This may not be the complete list of references from this article.
- Graham S., Zielezny M., Marshall J., Priore R., Freudenheim J., Brasure J., Haughey B., Nasca P., Zdeb M. Diet in the epidemiology of postmenopausal breast cancer in the New York State Cohort. Am J Epidemiol. 1992 Dec 1;136(11):1327–1337. doi: 10.1093/oxfordjournals.aje.a116445. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Henderson B. E., Ross R. K., Pike M. C. Toward the primary prevention of cancer. Science. 1991 Nov 22;254(5035):1131–1138. doi: 10.1126/science.1957166. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Howe G. R. High-fat diets and breast cancer risk. The epidemiologic evidence. JAMA. 1992 Oct 21;268(15):2080–2081. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Howe G. R., Hirohata T., Hislop T. G., Iscovich J. M., Yuan J. M., Katsouyanni K., Lubin F., Marubini E., Modan B., Rohan T. Dietary factors and risk of breast cancer: combined analysis of 12 case-control studies. J Natl Cancer Inst. 1990 Apr 4;82(7):561–569. doi: 10.1093/jnci/82.7.561. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Hunter D. J., Manson J. E., Colditz G. A., Stampfer M. J., Rosner B., Hennekens C. H., Speizer F. E., Willett W. C. A prospective study of the intake of vitamins C, E, and A and the risk of breast cancer. N Engl J Med. 1993 Jul 22;329(4):234–240. doi: 10.1056/NEJM199307223290403. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Hunter D. J., Willett W. C. Diet, body size, and breast cancer. Epidemiol Rev. 1993;15(1):110–132. doi: 10.1093/oxfordjournals.epirev.a036096. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Lee H. P., Gourley L., Duffy S. W., Estéve J., Lee J., Day N. E. Dietary effects on breast-cancer risk in Singapore. Lancet. 1991 May 18;337(8751):1197–1200. doi: 10.1016/0140-6736(91)92867-2. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Rohan T. E., Howe G. R., Friedenreich C. M., Jain M., Miller A. B. Dietary fiber, vitamins A, C, and E, and risk of breast cancer: a cohort study. Cancer Causes Control. 1993 Jan;4(1):29–37. doi: 10.1007/BF00051711. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Sharpe R. M., Skakkebaek N. E. Are oestrogens involved in falling sperm counts and disorders of the male reproductive tract? Lancet. 1993 May 29;341(8857):1392–1395. doi: 10.1016/0140-6736(93)90953-e. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Wang Q. S., Ross R. K., Yu M. C., Ning J. P., Henderson B. E., Kimm H. T. A case-control study of breast cancer in Tianjin, China. Cancer Epidemiol Biomarkers Prev. 1992 Sep-Oct;1(6):435–439. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Whittemore A. S., Wu-Williams A. H., Lee M., Zheng S., Gallagher R. P., Jiao D. A., Zhou L., Wang X. H., Chen K., Jung D. Diet, physical activity, and colorectal cancer among Chinese in North America and China. J Natl Cancer Inst. 1990 Jun 6;82(11):915–926. doi: 10.1093/jnci/82.11.915. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Willett W. C., Hunter D. J., Stampfer M. J., Colditz G., Manson J. E., Spiegelman D., Rosner B., Hennekens C. H., Speizer F. E. Dietary fat and fiber in relation to risk of breast cancer. An 8-year follow-up. JAMA. 1992 Oct 21;268(15):2037–2044. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Yuan J. M., Yu M. C., Ross R. K., Gao Y. T., Henderson B. E. Risk factors for breast cancer in Chinese women in Shanghai. Cancer Res. 1988 Apr 1;48(7):1949–1953. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Zaridze D., Lifanova Y., Maximovitch D., Day N. E., Duffy S. W. Diet, alcohol consumption and reproductive factors in a case-control study of breast cancer in Moscow. Int J Cancer. 1991 Jun 19;48(4):493–501. doi: 10.1002/ijc.2910480404. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]


