Abstract
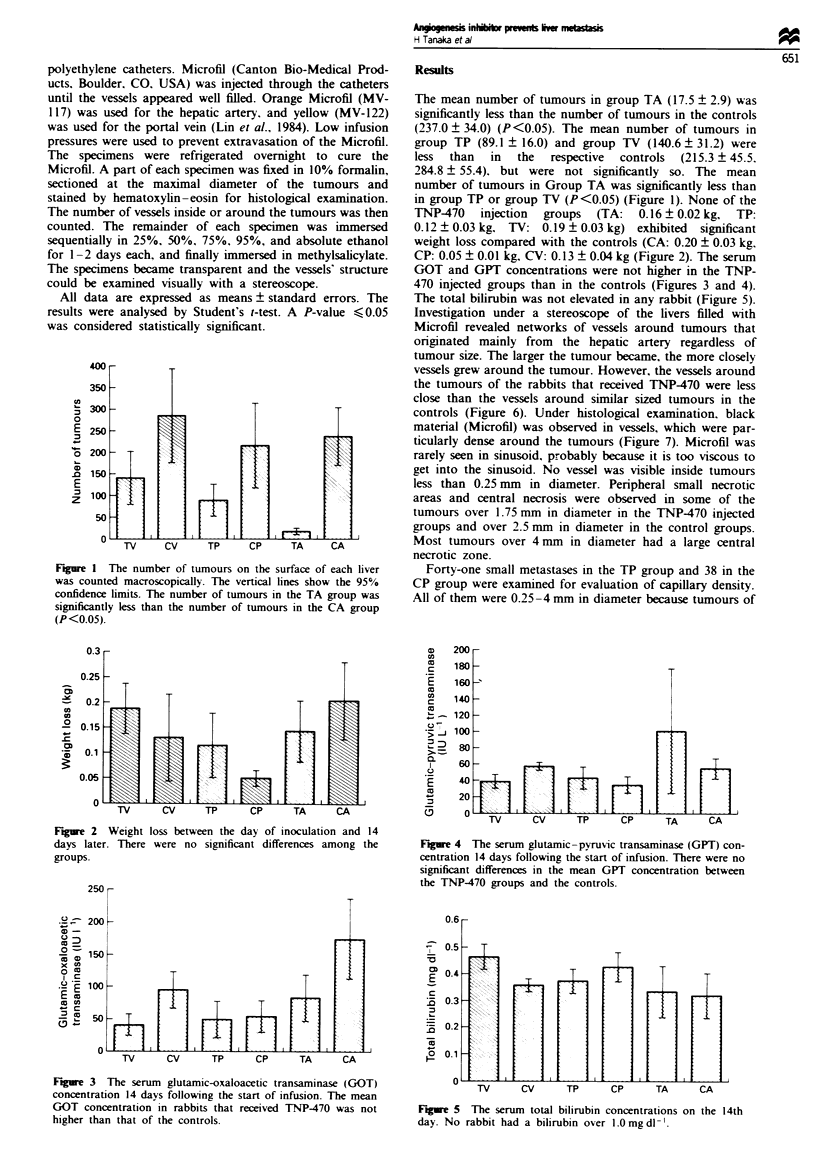
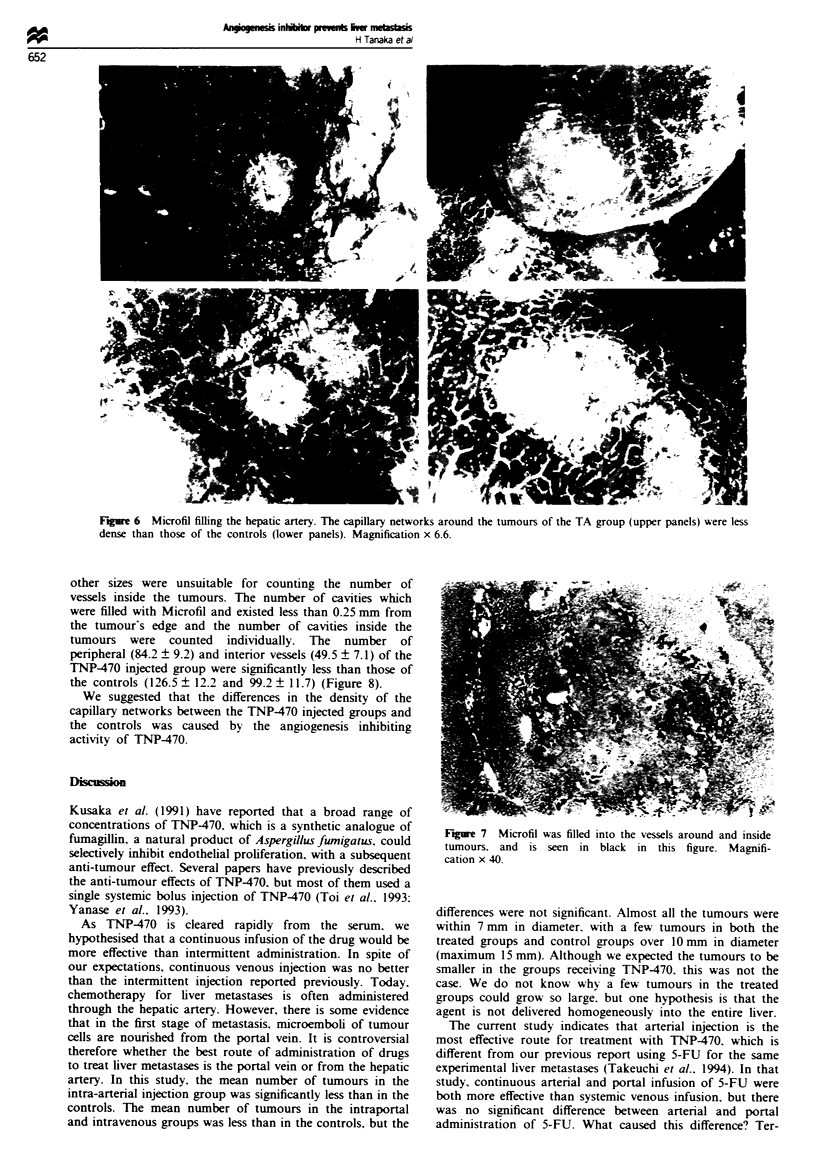
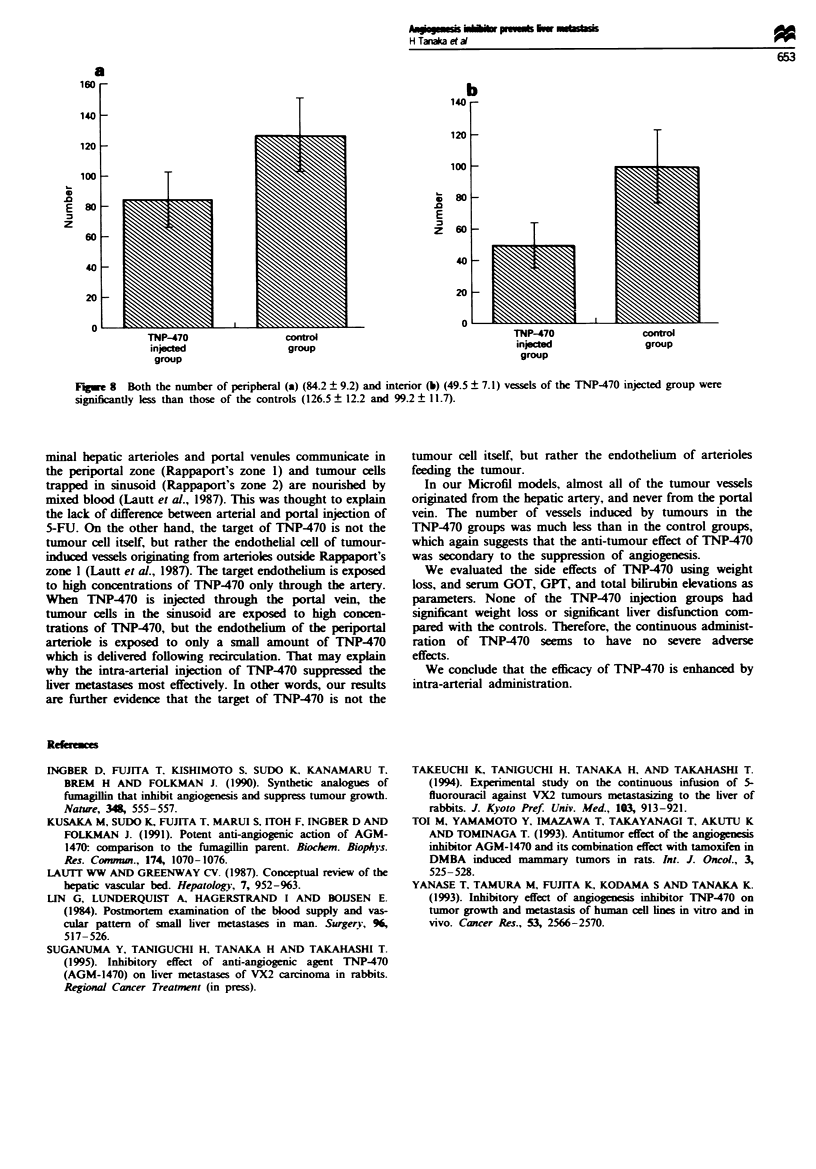
We evaluated the best route of administration of TNP-470, an angiogenesis inhibitor, by comparing the anti-tumour effects and toxicity following injection via the hepatic artery, the portal vein, or the jugular vein in a rabbit model of liver metastases. Following the injections of 1 x 10(6) VX2 carcinoma cells into the portal vein of rabbits, 50 mg of TNP-470 was injected continuously into the hepatic artery, portal vein, or jugular vein for 7 days. The number of tumours on the surface of the liver was counted 14 days following the start of the infusion, and the serum glutamic-oxaloacetic transamine (GOT), glutamic-pyruvic transaminase (GPT) and total bilirubin concentrations were examined. In addition, a coloured silicon rubber was injected into the vessels of the liver to visualise the capillary networks around the tumours and assess the degree of suppression of angiogenesis by TNP-470. The mean number of tumours following intra-arterial injection (17.5 +/- 2.9) was significantly less than the control (237.0 +/- 34.0) (P < 0.05). The mean numbers of the tumours following intraportal (89.1 +/- 16.0) and intravenous (140.6 +/- 31.2) injection were both less than the controls (215.3 +/- 45.5, 284.8 +/- 55.4 respectively), but the differences were not significant. We conclude that intra-arterial injection of TNP-470 is the most effective method for preventing liver metastases in this model.
Full text
PDF
Images in this article
Selected References
These references are in PubMed. This may not be the complete list of references from this article.
- Ingber D., Fujita T., Kishimoto S., Sudo K., Kanamaru T., Brem H., Folkman J. Synthetic analogues of fumagillin that inhibit angiogenesis and suppress tumour growth. Nature. 1990 Dec 6;348(6301):555–557. doi: 10.1038/348555a0. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Kusaka M., Sudo K., Fujita T., Marui S., Itoh F., Ingber D., Folkman J. Potent anti-angiogenic action of AGM-1470: comparison to the fumagillin parent. Biochem Biophys Res Commun. 1991 Feb 14;174(3):1070–1076. doi: 10.1016/0006-291x(91)91529-l. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Lautt W. W., Greenway C. V. Conceptual review of the hepatic vascular bed. Hepatology. 1987 Sep-Oct;7(5):952–963. doi: 10.1002/hep.1840070527. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Lin G., Lunderquist A., Hägerstrand I., Boijsen E. Postmortem examination of the blood supply and vascular pattern of small liver metastases in man. Surgery. 1984 Sep;96(3):517–526. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Yanase T., Tamura M., Fujita K., Kodama S., Tanaka K. Inhibitory effect of angiogenesis inhibitor TNP-470 on tumor growth and metastasis of human cell lines in vitro and in vivo. Cancer Res. 1993 Jun 1;53(11):2566–2570. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]