Abstract
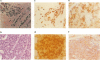
We established a panel of 17 xenografts from primary human breast carcinomas. We examined which characteristics of the original tumours and the xenografts facilitate growth in animals. Tumours expressing medium or strong immunoreactivity for p53 protein had significantly (P < 0.05) higher incidence (92%) of in vivo tumour take than those showing weak or negative immunoreactivity (9.1%). No such association was observed between either c-erbB-2 or epidermal growth factor receptor (EGFR) expression in the original tumours and their in vivo tumour take. Following subcutaneous (s.c.) transplantation of original breast tumours or established xenografts, 7/17 tumours showed metastatic disease spread to distant sites (mainly lungs). This study suggests that selective growth of highly aggressive tumours occurs during in vivo propagation of malignant tumours, and these tumours will be of particular interest in evaluating various chemotherapeutic agents for breast cancer management.
Full text
PDF



Images in this article
Selected References
These references are in PubMed. This may not be the complete list of references from this article.
- Barsky S. H., Rao C. N., Williams J. E., Liotta L. A. Laminin molecular domains which alter metastasis in a murine model. J Clin Invest. 1984 Sep;74(3):843–848. doi: 10.1172/JCI111501. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- D'Souza B., Berdichevsky F., Kyprianou N., Taylor-Papadimitriou J. Collagen-induced morphogenesis and expression of the alpha 2-integrin subunit is inhibited in c-erbB2-transfected human mammary epithelial cells. Oncogene. 1993 Jul;8(7):1797–1806. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Folkman J. Anti-angiogenesis: new concept for therapy of solid tumors. Ann Surg. 1972 Mar;175(3):409–416. doi: 10.1097/00000658-197203000-00014. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Fridman R., Giaccone G., Kanemoto T., Martin G. R., Gazdar A. F., Mulshine J. L. Reconstituted basement membrane (matrigel) and laminin can enhance the tumorigenicity and the drug resistance of small cell lung cancer cell lines. Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A. 1990 Sep;87(17):6698–6702. doi: 10.1073/pnas.87.17.6698. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Fridman R., Kibbey M. C., Royce L. S., Zain M., Sweeney M., Jicha D. L., Yannelli J. R., Martin G. R., Kleinman H. K. Enhanced tumor growth of both primary and established human and murine tumor cells in athymic mice after coinjection with Matrigel. J Natl Cancer Inst. 1991 Jun 5;83(11):769–774. doi: 10.1093/jnci/83.11.769. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Furcht L. T. Critical factors controlling angiogenesis: cell products, cell matrix, and growth factors. Lab Invest. 1986 Nov;55(5):505–509. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Gasparini G., Weidner N., Bevilacqua P., Maluta S., Dalla Palma P., Caffo O., Barbareschi M., Boracchi P., Marubini E., Pozza F. Tumor microvessel density, p53 expression, tumor size, and peritumoral lymphatic vessel invasion are relevant prognostic markers in node-negative breast carcinoma. J Clin Oncol. 1994 Mar;12(3):454–466. doi: 10.1200/JCO.1994.12.3.454. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Gimbrone M. A., Jr, Leapman S. B., Cotran R. S., Folkman J. Tumor dormancy in vivo by prevention of neovascularization. J Exp Med. 1972 Aug 1;136(2):261–276. doi: 10.1084/jem.136.2.261. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Giovanella B. C., Fogh J. The nude mouse in cancer research. Adv Cancer Res. 1985;44:69–120. doi: 10.1016/s0065-230x(08)60026-3. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Giovanella B. C., Vardeman D. M., Williams L. J., Taylor D. J., de Ipolyi P. D., Greeff P. J., Stehlin J. S., Ullrich A., Cailleau R., Slamon D. J. Heterotransplantation of human breast carcinomas in nude mice. Correlation between successful heterotransplants, poor prognosis and amplification of the HER-2/neu oncogene. Int J Cancer. 1991 Jan 2;47(1):66–71. doi: 10.1002/ijc.2910470113. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Hurst J., Maniar N., Tombarkiewicz J., Lucas F., Roberson C., Steplewski Z., James W., Perras J. A novel model of a metastatic human breast tumour xenograft line. Br J Cancer. 1993 Aug;68(2):274–276. doi: 10.1038/bjc.1993.327. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Kallioniemi O. P., Holli K., Visakorpi T., Koivula T., Helin H. H., Isola J. J. Association of c-erbB-2 protein over-expression with high rate of cell proliferation, increased risk of visceral metastasis and poor long-term survival in breast cancer. Int J Cancer. 1991 Nov 11;49(5):650–655. doi: 10.1002/ijc.2910490504. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Kopp A., von Laffert C., Jonat W. Immunhistochemischer Nachweis von EGF-Rezeptoren in Mammakarzinomen. Geburtshilfe Frauenheilkd. 1993 Jul;53(7):461–466. doi: 10.1055/s-2007-1022914. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Liotta L. A., Rao C. N., Wewer U. M. Biochemical interactions of tumor cells with the basement membrane. Annu Rev Biochem. 1986;55:1037–1057. doi: 10.1146/annurev.bi.55.070186.005133. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Mehta R. R., Bratescu L., Graves J. M., Hart G. D., Shilkaitis A., Green A., Beattie C. W., Das Gupta T. K. Human breast carcinoma cell lines: ultrastructural, genotypic, and immunocytochemical characterization. Anticancer Res. 1992 May-Jun;12(3):683–692. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Mehta R. R., Graves J. M., Hart G. D., Shilkaitis A., Das Gupta T. K. Growth and metastasis of human breast carcinomas with Matrigel in athymic mice. Breast Cancer Res Treat. 1993;25(1):65–71. doi: 10.1007/BF00662402. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Passaniti A., Taylor R. M., Pili R., Guo Y., Long P. V., Haney J. A., Pauly R. R., Grant D. S., Martin G. R. A simple, quantitative method for assessing angiogenesis and antiangiogenic agents using reconstituted basement membrane, heparin, and fibroblast growth factor. Lab Invest. 1992 Oct;67(4):519–528. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Pretlow T. G., Delmoro C. M., Dilley G. G., Spadafora C. G., Pretlow T. P. Transplantation of human prostatic carcinoma into nude mice in Matrigel. Cancer Res. 1991 Jul 15;51(14):3814–3817. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Rae-Venter B., Reid L. M. Growth of human breast carcinomas in nude mice and subsequent establishment in tissue culture. Cancer Res. 1980 Jan;40(1):95–100. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Sabiston P., Adams M. E., Ho Y. A. Automation of 1,9-dimethylmethylene blue dye-binding assay for sulfated glycosaminoglycans with application to cartilage microcultures. Anal Biochem. 1985 Sep;149(2):543–548. doi: 10.1016/0003-2697(85)90611-6. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Sakamoto N., Iwahana M., Tanaka N. G., Osada Y. Inhibition of angiogenesis and tumor growth by a synthetic laminin peptide, CDPGYIGSR-NH2. Cancer Res. 1991 Feb 1;51(3):903–906. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Silvestrini R., Benini E., Daidone M. G., Veneroni S., Boracchi P., Cappelletti V., Di Fronzo G., Veronesi U. p53 as an independent prognostic marker in lymph node-negative breast cancer patients. J Natl Cancer Inst. 1993 Jun 16;85(12):965–970. doi: 10.1093/jnci/85.12.965. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Taylor W. R., Egan S. E., Mowat M., Greenberg A. H., Wright J. A. Evidence for synergistic interactions between ras, myc and a mutant form of p53 in cellular transformation and tumor dissemination. Oncogene. 1992 Jul;7(7):1383–1390. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Terranova V. P., Williams J. E., Liotta L. A., Martin G. R. Modulation of the metastatic activity of melanoma cells by laminin and fibronectin. Science. 1984 Nov 23;226(4677):982–985. doi: 10.1126/science.6505678. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Thor A. D., Schwartz L. H., Koerner F. C., Edgerton S. M., Skates S. J., Yin S., McKenzie S. J., Panicali D. L., Marks P. J., Fingert H. J. Analysis of c-erbB-2 expression in breast carcinomas with clinical follow-up. Cancer Res. 1989 Dec 15;49(24 Pt 1):7147–7152. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Wolman S. R., Feiner H. D., Schinella R. A., Gimotty P., Ownby H., Maloney T., Dawson P. J. A retrospective analysis of breast cancer based on outcome differences. Hum Pathol. 1991 May;22(5):475–480. doi: 10.1016/0046-8177(91)90134-b. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Yamamura K., Kibbey M. C., Jun S. H., Kleinman H. K. Effect of Matrigel and laminin peptide YIGSR on tumor growth and metastasis. Semin Cancer Biol. 1993 Aug;4(4):259–265. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Yu D., Hamada J., Zhang H., Nicolson G. L., Hung M. C. Mechanisms of c-erbB2/neu oncogene-induced metastasis and repression of metastatic properties by adenovirus 5 E1A gene products. Oncogene. 1992 Nov;7(11):2263–2270. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]