Abstract
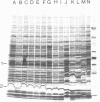
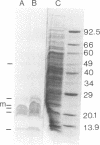
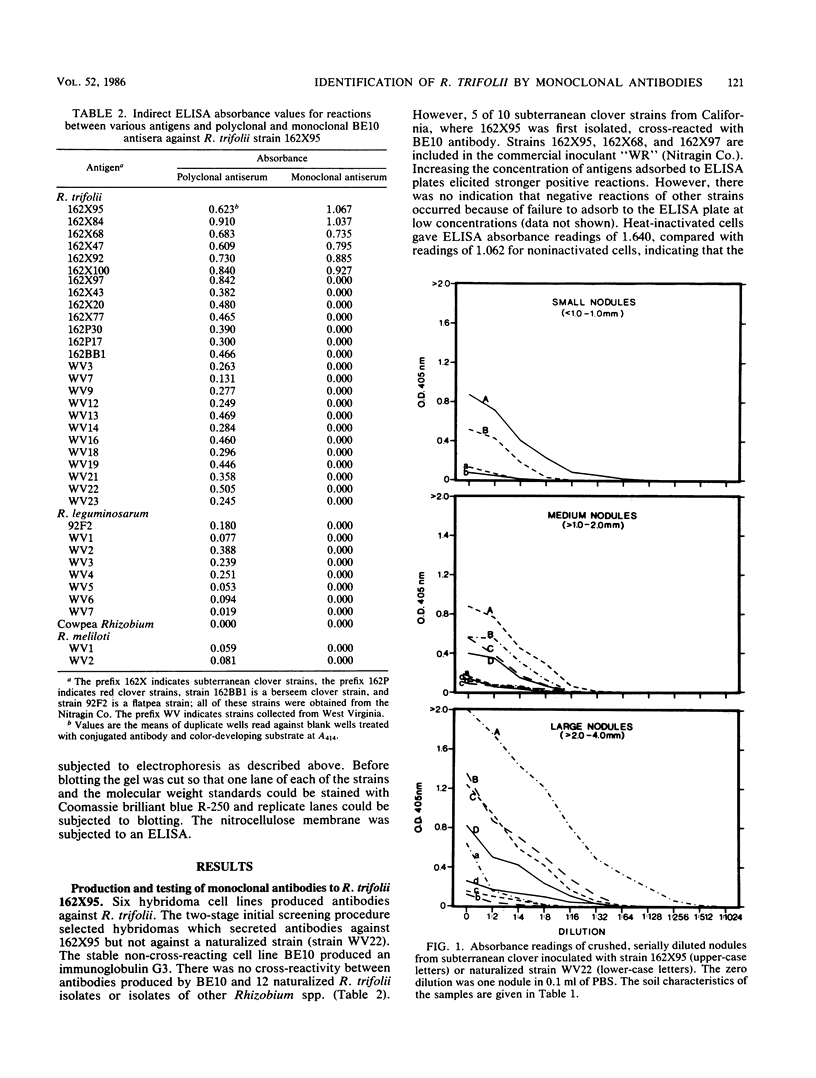
We produced a monoclonal antibody against Rhizobium trifolii 162×95. This antibody in cell culture supernatant was used in an indirect enzyme-linked immunosorbent assay to differentiate strain 162×95 from naturalized strains in the Appalachian region. Nodules crushed in 0.1 to 0.2 ml of phosphate-buffered saline and used to charge enzyme-linked immunosorbent assay plates gave strong absorbance readings. Heat-inactivated and noninactivated portions of 162×95 cultures were strongly reactive, indicating that the antigen is probably a carbohydrate. Of 10 strains from California, where 162×95 was isolated, 6 strongly cross-reacted with the antibody. The cellular protein patterns in a sodium dodecyl sulfate-polyacrylamide gradient gel of cross-reactive strains were essentially identical. A Western blot analysis indicated that the antibody was against a 19.8-kilodalton band. The Western blot analysis also revealed that the polyvalent antiserum contained other strongly reacting antibodies with molecular weights of approximately 20,000, indicating the possibility that other monoclonal antibodies to detect strain 162×95 may be produced. However, the available antibody has been shown to be useful for short-term experiments. Based upon protein profiles and immunological reactions, there are 4 or 5 California strains rather than 10.
Full text
PDF

Images in this article
Selected References
These references are in PubMed. This may not be the complete list of references from this article.
- Berger J. A., May S. N., Berger L. R., Bohlool B. B. Colorimetric enzyme-linked immunosorbent assay for the identification of strains of Rhizobium in culture and in the nodules of lentils. Appl Environ Microbiol. 1979 Mar;37(3):642–646. doi: 10.1128/aem.37.3.642-646.1979. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Burnette W. N. "Western blotting": electrophoretic transfer of proteins from sodium dodecyl sulfate--polyacrylamide gels to unmodified nitrocellulose and radiographic detection with antibody and radioiodinated protein A. Anal Biochem. 1981 Apr;112(2):195–203. doi: 10.1016/0003-2697(81)90281-5. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Fuhrmann J., Wollum A. G. Simplified Enzyme-Linked Immunosorbent Assay for Routine Identification of Rhizobium japonicum Antigens. Appl Environ Microbiol. 1985 Apr;49(4):1010–1013. doi: 10.1128/aem.49.4.1010-1013.1985. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Noel K. D., Brill W. J. Diversity and Dynamics of Indigenous Rhizobium japonicum Populations. Appl Environ Microbiol. 1980 Nov;40(5):931–938. doi: 10.1128/aem.40.5.931-938.1980. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Oakley B. R., Kirsch D. R., Morris N. R. A simplified ultrasensitive silver stain for detecting proteins in polyacrylamide gels. Anal Biochem. 1980 Jul 1;105(2):361–363. doi: 10.1016/0003-2697(80)90470-4. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]