Abstract
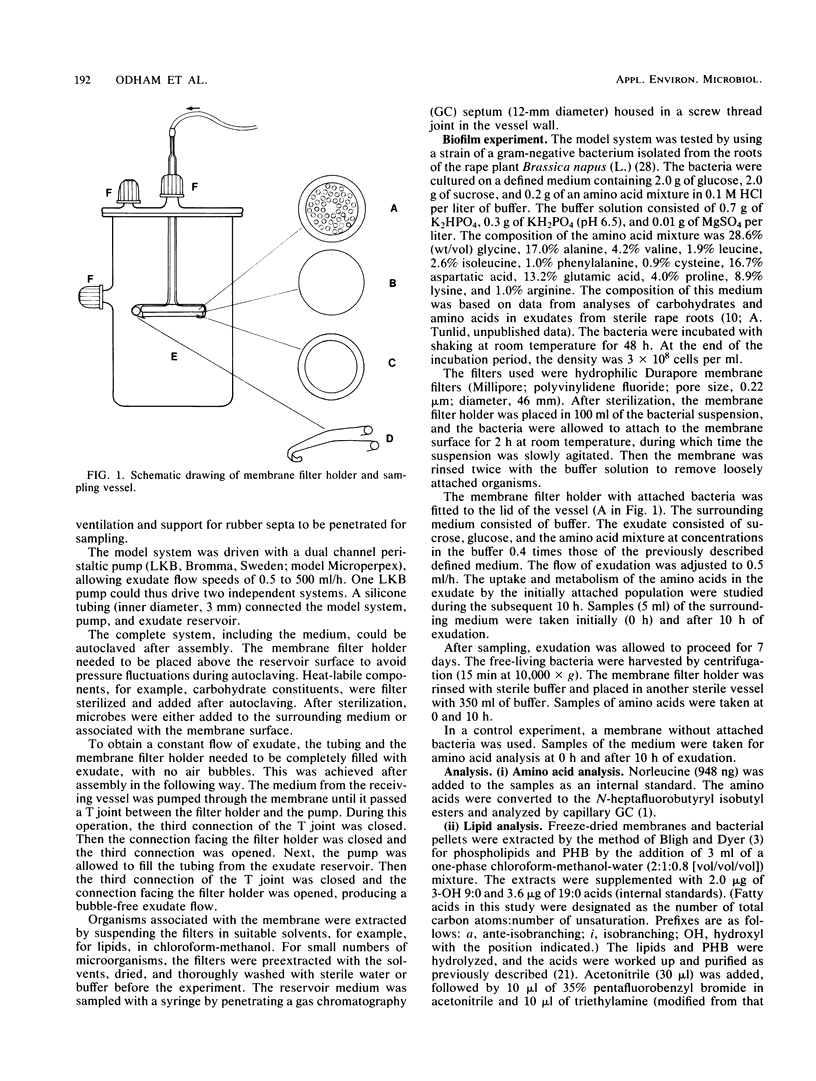
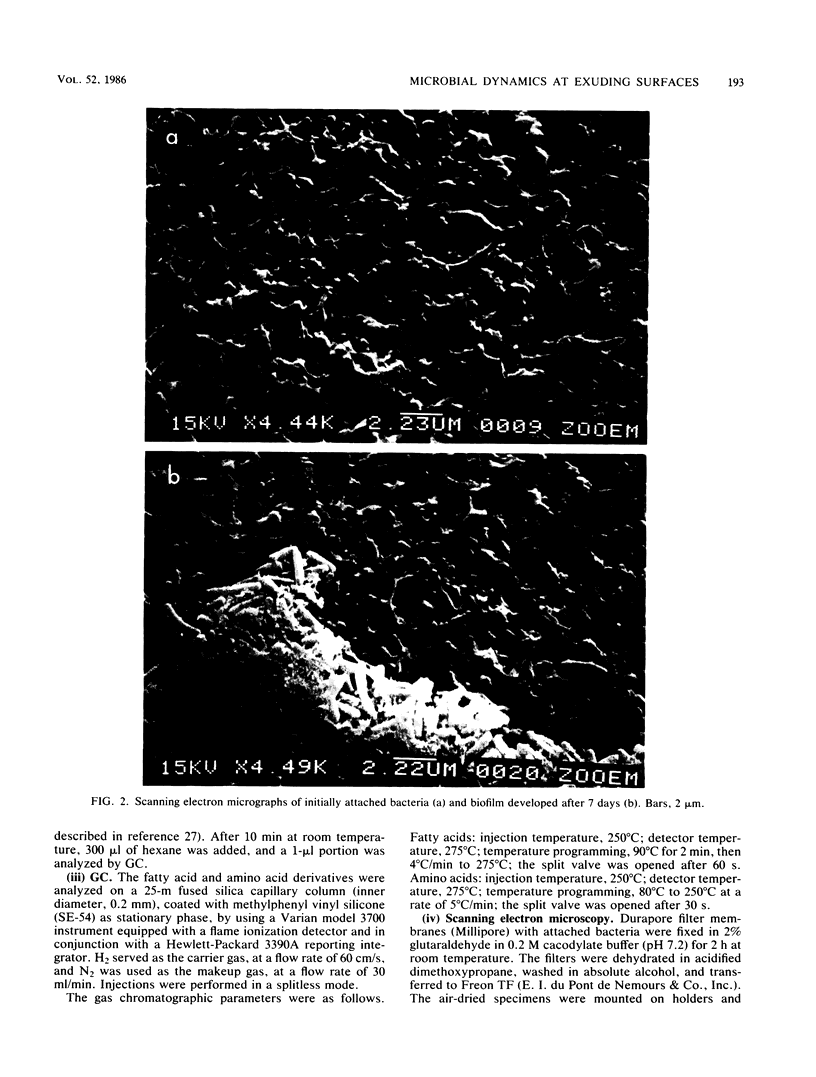
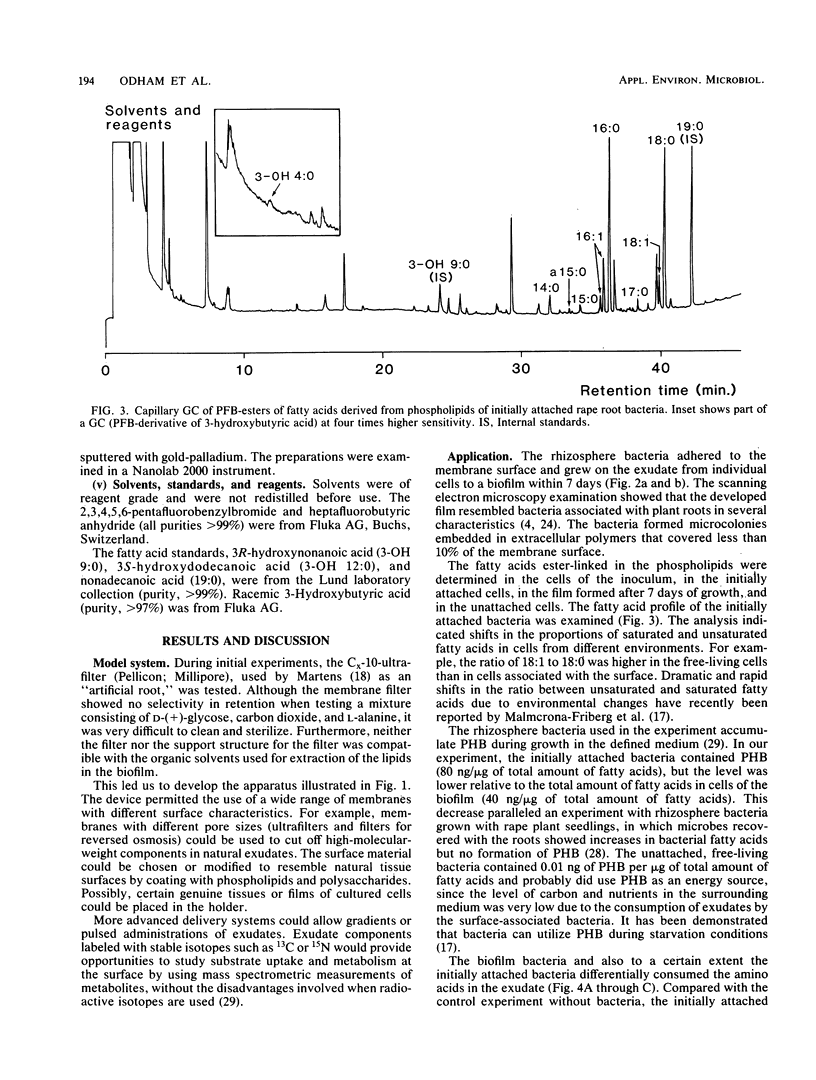
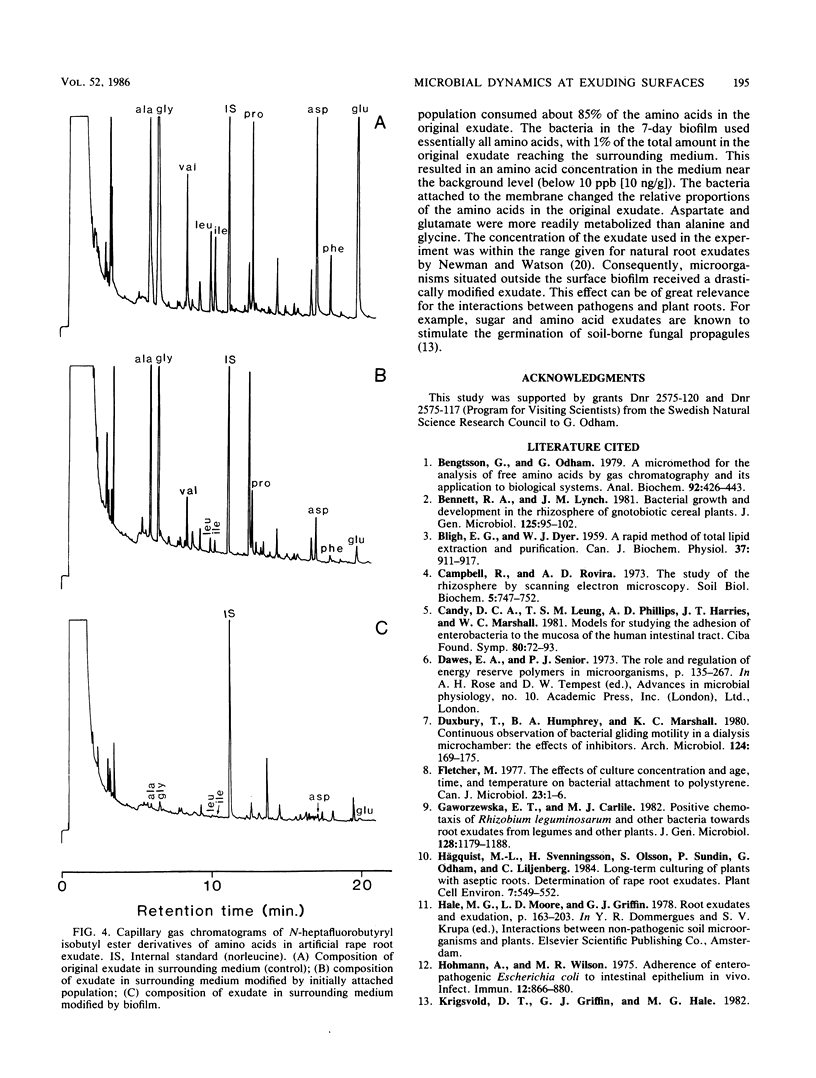
An autoclavable all-glass system for studying microbial dynamics at permeable surfaces is described. Standard hydrophobic or hydrophilic membranes (46-mm diameter) of various pore sizes were supported on a glass frit through which nutrient solutions were pumped by a peristaltic pump. The pump provided a precisely controlled flow at speeds of 0.5 to 500 ml of defined or natural cell exudates per h, which passed through the membrane into a receiving vessel. The construction allowed a choice of membranes, which could be modified. The system was tested with a bacterium, isolated from rape plant roots (Brassica napus L.), that was inoculated on a hydrophilic membrane filter and allowed to develop into a biofilm. A defined medium with a composition resembling that of natural rape root exudate was pumped through the membrane at 0.5 ml/h. Scanning electron microscopic examinations indicated that the inoculum formed microcolonies embedded in exopolymers evenly distributed over the membrane surface. The lipid composition and content of poly-beta-hydroxybutyrate in free-living and adhered cells were determined by gas chromatography. The bacterial consumption of amino acids in the exudate was also studied.
Full text
PDF

Images in this article
Selected References
These references are in PubMed. This may not be the complete list of references from this article.
- BLIGH E. G., DYER W. J. A rapid method of total lipid extraction and purification. Can J Biochem Physiol. 1959 Aug;37(8):911–917. doi: 10.1139/o59-099. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Bengtsson G., Odham G. A micromethod for the analysis of free amino acids by gas chromatography and its application to biological systems. Anal Biochem. 1979 Jan 15;92(2):426–443. doi: 10.1016/0003-2697(79)90681-x. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Candy D. C., Leung T. S., Phillips A. D., Harries J. T., Marshall W. C. Models for studying the adhesion of enterobacteria to the mucosa of the human intestinal tract. Ciba Found Symp. 1981;80:72–93. doi: 10.1002/9780470720639.ch6. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Dawes E. A., Senior P. J. The role and regulation of energy reserve polymers in micro-organisms. Adv Microb Physiol. 1973;10:135–266. doi: 10.1016/s0065-2911(08)60088-0. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Hohmann A., Wilson M. R. Adherence of enteropathogenic Escherichia coli to intestinal epithelium in vivo. Infect Immun. 1975 Oct;12(4):866–880. doi: 10.1128/iai.12.4.866-880.1975. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Lange S., Hansson H. A., Lönnroth I. Influence of bile acids on cholera toxin-induced secretion in mouse jejunum. Acta Pathol Microbiol Immunol Scand B. 1983 Aug;91(4):215–220. doi: 10.1111/j.1699-0463.1983.tb00036.x. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Ogawa T., Kotani S., Tsujimoto M., Kusumoto S., Shiba T., Kawata S., Yokogawa K. Contractile effects of bacterial cell walls, their enzymatic digests, and muramyl dipeptides on ileal strips from guinea pigs. Infect Immun. 1982 Feb;35(2):612–619. doi: 10.1128/iai.35.2.612-619.1982. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Olsson J., Krasse B. A method for studying adherence of oral streptococci to solid surfaces. Scand J Dent Res. 1976 Jan;84(1):20–28. doi: 10.1111/j.1600-0722.1976.tb00457.x. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Rutter J. M., Jones G. W. Protection against enteric disease caused by Escherichia coli--a model for vaccination with a virulence determinant? Nature. 1973 Apr 20;242(5399):531–532. doi: 10.1038/242531a0. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Sakata T., von Engelhardt W. Luminal mucin in the large intestine of mice, rats and guinea pigs. Cell Tissue Res. 1981;219(3):629–635. doi: 10.1007/BF00210000. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Tunlid A., Odham G., Findlay R. H., White D. C. Precision and sensitivity of the measurement of 15N enrichment in D-alanine from bacterial cell walls using positive/negative ion mass spectrometry. J Microbiol Methods. 1985;3:237–245. doi: 10.1016/0167-7012(85)90051-x. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]



