Abstract
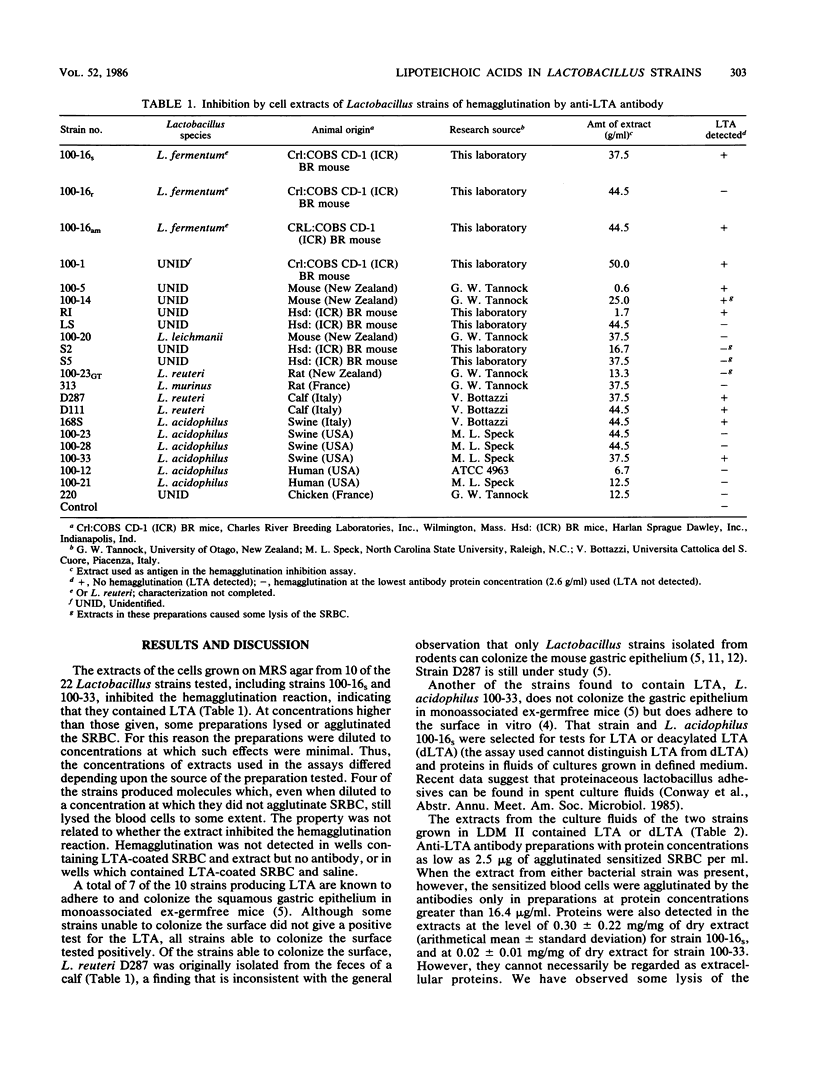
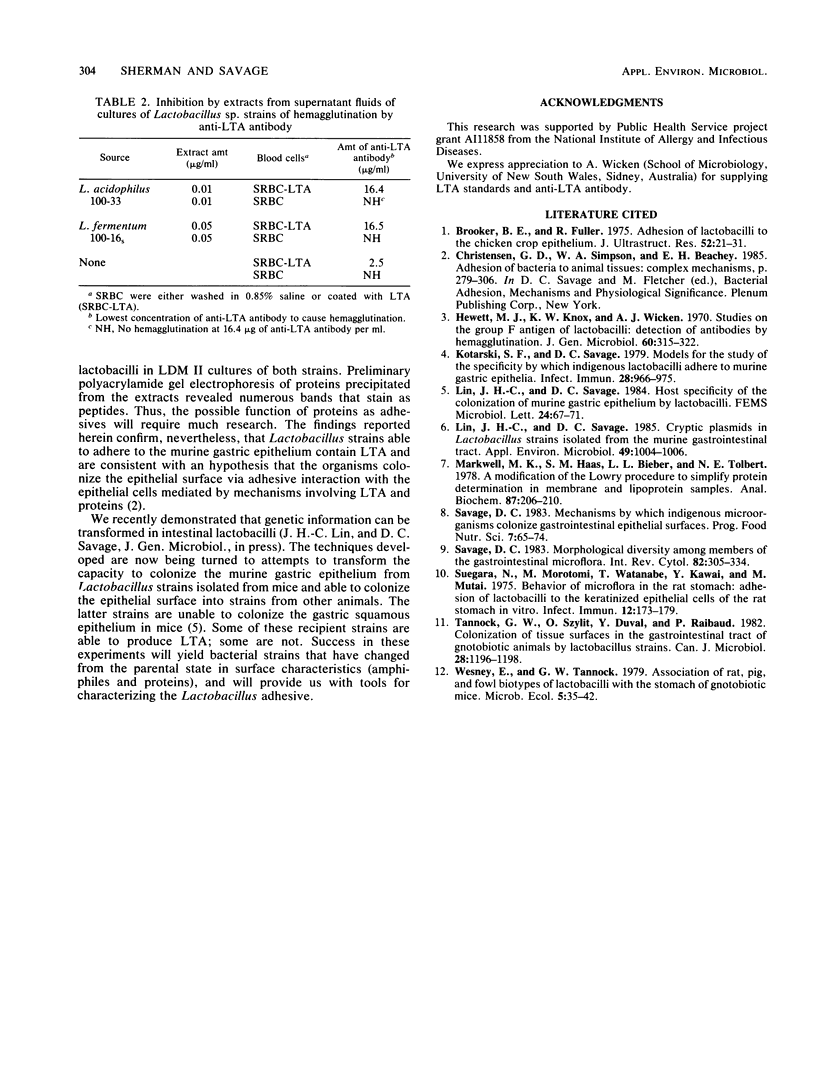
Extracts of cells of 22 strains of Lactobacillus species, and of fluids from cultures in a defined medium of two of the strains, were assayed by hemagglutination inhibition for lipoteichoic acids. A total of 10 of the preparations gave positive tests for the acids, including those from eight strains known to adhere to the keratinized squamous epithelium of the mouse stomach. These findings are consistent with an hypothesis that lactobacilli colonize the epithelial surface via adhesive interaction with the keratinized cells mediated by macromolecular complexes containing lipoteichoic acids.
Full text
PDF
Selected References
These references are in PubMed. This may not be the complete list of references from this article.
- Brooker B. E., Fuller R. Adhesion of Lactobacilli to the chicken crop epithelium. J Ultrastruct Res. 1975 Jul;52(1):21–31. doi: 10.1016/s0022-5320(75)80019-0. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Hewett M. J., Knox K. W., Wicken A. J. Studies on the group F antigen of lactobacilli: detection of antibodies by haemagglutination. J Gen Microbiol. 1970 Mar;60(3):315–322. doi: 10.1099/00221287-60-3-315. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Kotarski S. F., Savage D. C. Models for study of the specificity by which indigenous lactobacilli adhere to murine gastric epithelia. Infect Immun. 1979 Dec;26(3):966–975. doi: 10.1128/iai.26.3.966-975.1979. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Lin J. H., Savage D. C. Cryptic plasmids in Lactobacillus strains isolated from the murine gastrointestinal tract. Appl Environ Microbiol. 1985 Apr;49(4):1004–1006. doi: 10.1128/aem.49.4.1004-1006.1985. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Markwell M. A., Haas S. M., Bieber L. L., Tolbert N. E. A modification of the Lowry procedure to simplify protein determination in membrane and lipoprotein samples. Anal Biochem. 1978 Jun 15;87(1):206–210. doi: 10.1016/0003-2697(78)90586-9. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Savage D. C. Mechanisms by which indigenous microorganisms colonize gastrointestinal epithelial surfaces. Prog Food Nutr Sci. 1983;7(3-4):65–74. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Savage D. C. Morphological diversity among members of the gastrointestinal microflora. Int Rev Cytol. 1983;82:305–334. doi: 10.1016/s0074-7696(08)60827-x. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Suegara N., Morotomi M., Watanabe T., Kawal Y., Mutai M. Behavior of microflora in the rat stomach: adhesion of lactobacilli to the keratinized epithelial cells of the rat stomach in vitro. Infect Immun. 1975 Jul;12(1):173–179. doi: 10.1128/iai.12.1.173-179.1975. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Tannock G. W., Szylit O., Duval Y., Raibaud P. Colonization of tissue surfaces in the gastrointestinal tract of gnotobiotic animals by lactobacillus strains. Can J Microbiol. 1982 Oct;28(10):1196–1198. doi: 10.1139/m82-177. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]



