Abstract
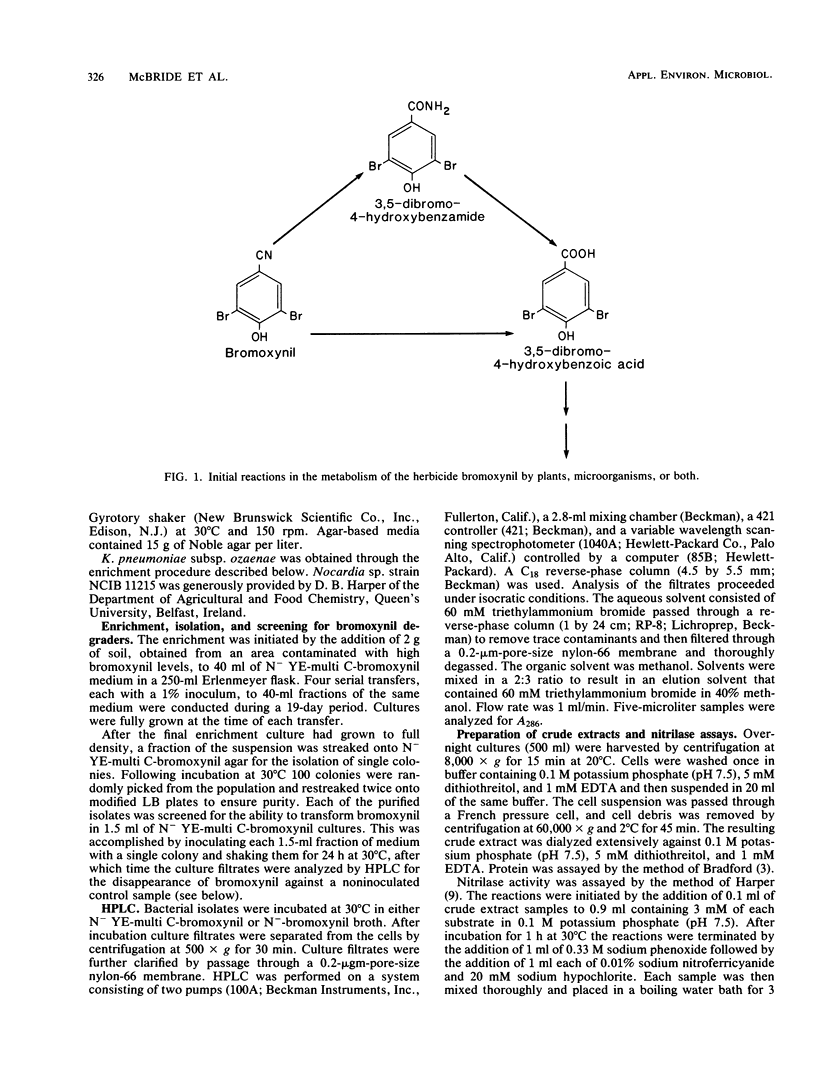
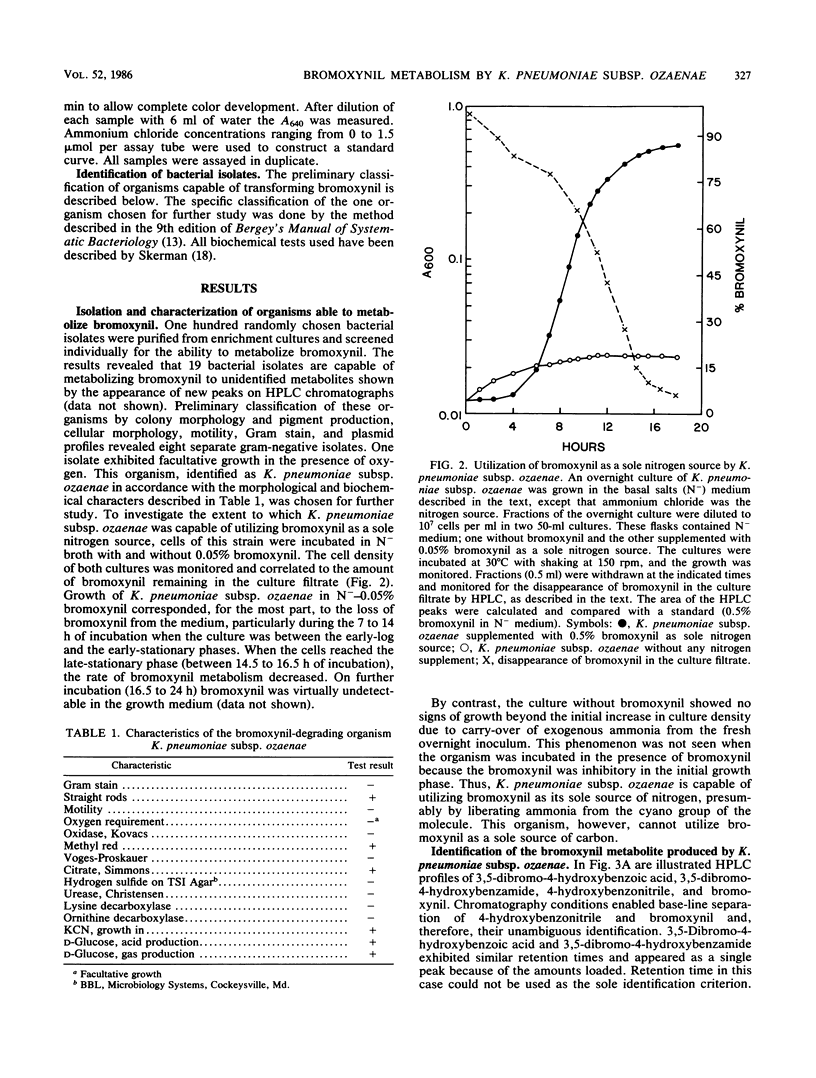
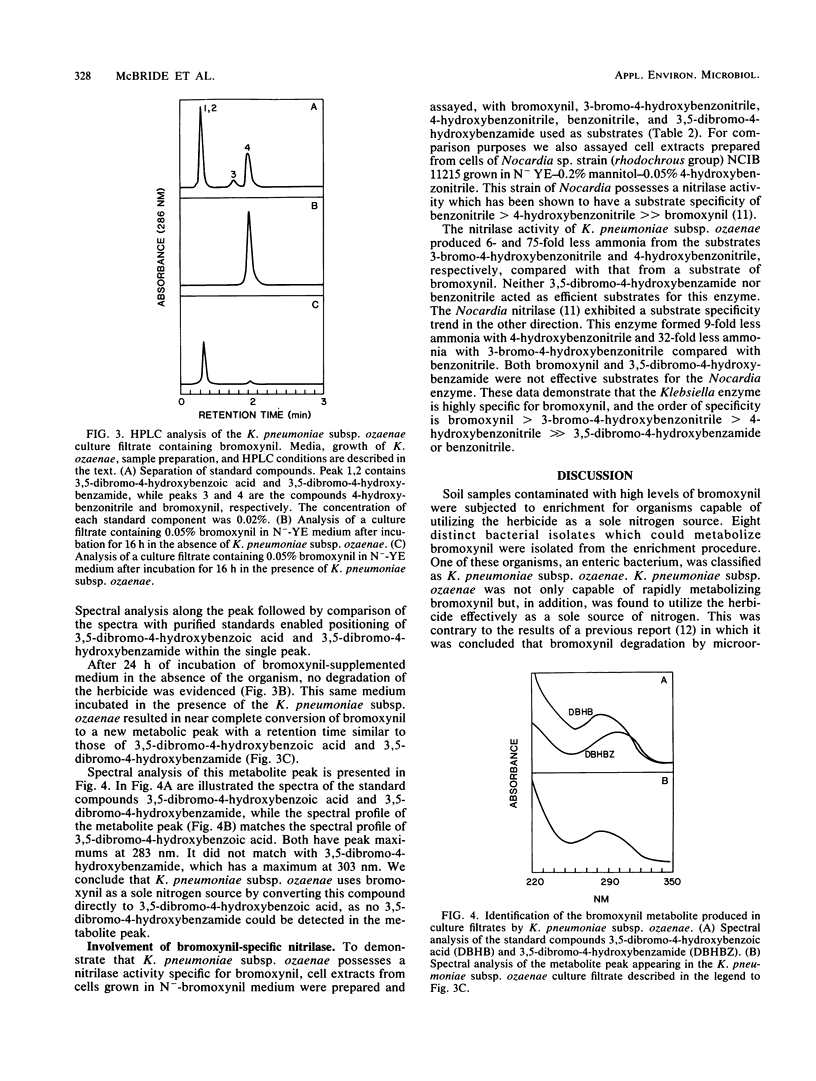
Enrichment of soil samples for organisms able to utilize the herbicide bromoxynil (3,5-dibromo-4-hydroxybenzonitrile) as a nitrogen source yielded bacterial isolates capable of rapidly metabolizing this compound. One isolate, identified as Klebsiella pneumoniae subsp. ozaenae, could completely convert 0.05% bromoxynil to 3,5-dibromo-4-hydroxybenzoic acid and use the liberated ammonia as a sole nitrogen source. Assays of cell extracts of this organism for the ability to produce ammonia from bromoxynil revealed the presence of a nitrilase (EC 3.5.51) activity. The enzyme could not utilize 3,5-dibromo-4-hydroxybenzamide as a substrate, and no 3,5-dibromo-4-hydroxybenzamide could be detected as a product of bromoxynil transformation. Comparison of related aromatic nitriles as substrates demonstrated that the Klebsiella enzyme is highly specific for bromoxynil.
Full text
PDF


Selected References
These references are in PubMed. This may not be the complete list of references from this article.
- Amy P. S., Schulke J. W., Frazier L. M., Seidler R. J. Characterization of aquatic bacteria and cloning of genes specifying partial degradation of 2,4-dichlorophenoxyacetic acid. Appl Environ Microbiol. 1985 May;49(5):1237–1245. doi: 10.1128/aem.49.5.1237-1245.1985. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Bandyopadhyay A. K., Nagasawa T., Asano Y., Fujishiro K., Tani Y., Yamada H. Purification and Characterization of Benzonitrilases from Arthrobacter sp. Strain J-1. Appl Environ Microbiol. 1986 Feb;51(2):302–306. doi: 10.1128/aem.51.2.302-306.1986. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Bradford M. M. A rapid and sensitive method for the quantitation of microgram quantities of protein utilizing the principle of protein-dye binding. Anal Biochem. 1976 May 7;72:248–254. doi: 10.1016/0003-2697(76)90527-3. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Ghosal D., You I. S., Chatterjee D. K., Chakrabarty A. M. Microbial degradation of halogenated compounds. Science. 1985 Apr 12;228(4696):135–142. doi: 10.1126/science.228.4696.135. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Harper D. B. Characterization of a nitrilase from Nocardia sp. (Rhodochrous group) N.C.I.B. 11215, using p-hydroxybenzonitrile as sole carbon source. Int J Biochem. 1985;17(6):677–683. doi: 10.1016/0020-711x(85)90364-7. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Harper D. B. Fungal degradation of aromatic nitriles. Enzymology of C-N cleavage by Fusarium solani. Biochem J. 1977 Dec 1;167(3):685–692. doi: 10.1042/bj1670685. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Harper D. B. Microbial metabolism of aromatic nitriles. Enzymology of C-N cleavage by Nocardia sp. (Rhodochrous group) N.C.I.B. 11216. Biochem J. 1977 Aug 1;165(2):309–319. doi: 10.1042/bj1650309. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Hsu J. C., Camper N. D. Isolation of ioxynil degraders from soil-enrichment cultures. Can J Microbiol. 1976 Apr;22(4):537–543. doi: 10.1139/m76-080. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Smith A. E., Cullimore D. R. The in vitro degradation of the herbicide bromoxynil. Can J Microbiol. 1974 May;20(5):773–776. doi: 10.1139/m74-119. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- THIMANN K. V., MAHADEVAN S. NITRILASE. I. OCCURRENCE, PREPARATION, AND GENERAL PROPERTIES OF THE ENZYME. Arch Biochem Biophys. 1964 Apr;105:133–141. doi: 10.1016/0003-9861(64)90244-9. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- THIMANN K. V., MAHADEVAN S. NITRILASE. I. OCCURRENCE, PREPARATION, AND GENERAL PROPERTIES OF THE ENZYME. Arch Biochem Biophys. 1964 Apr;105:133–141. doi: 10.1016/0003-9861(64)90244-9. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]


