Abstract
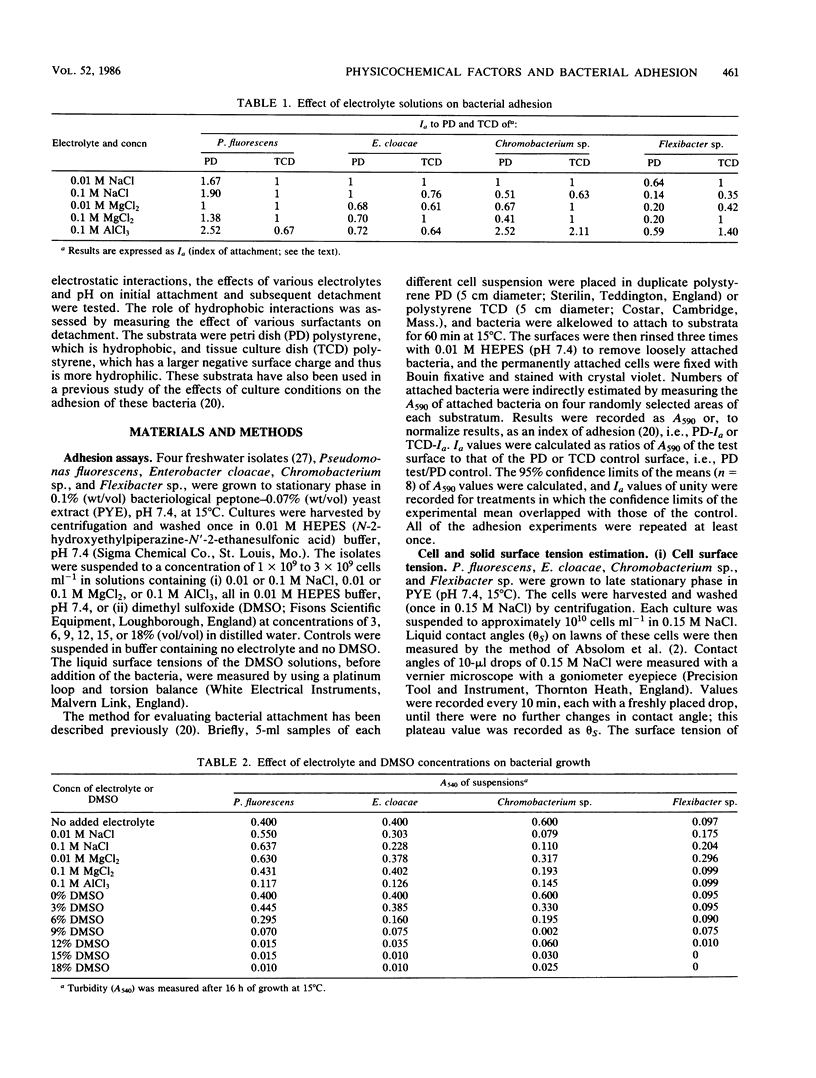
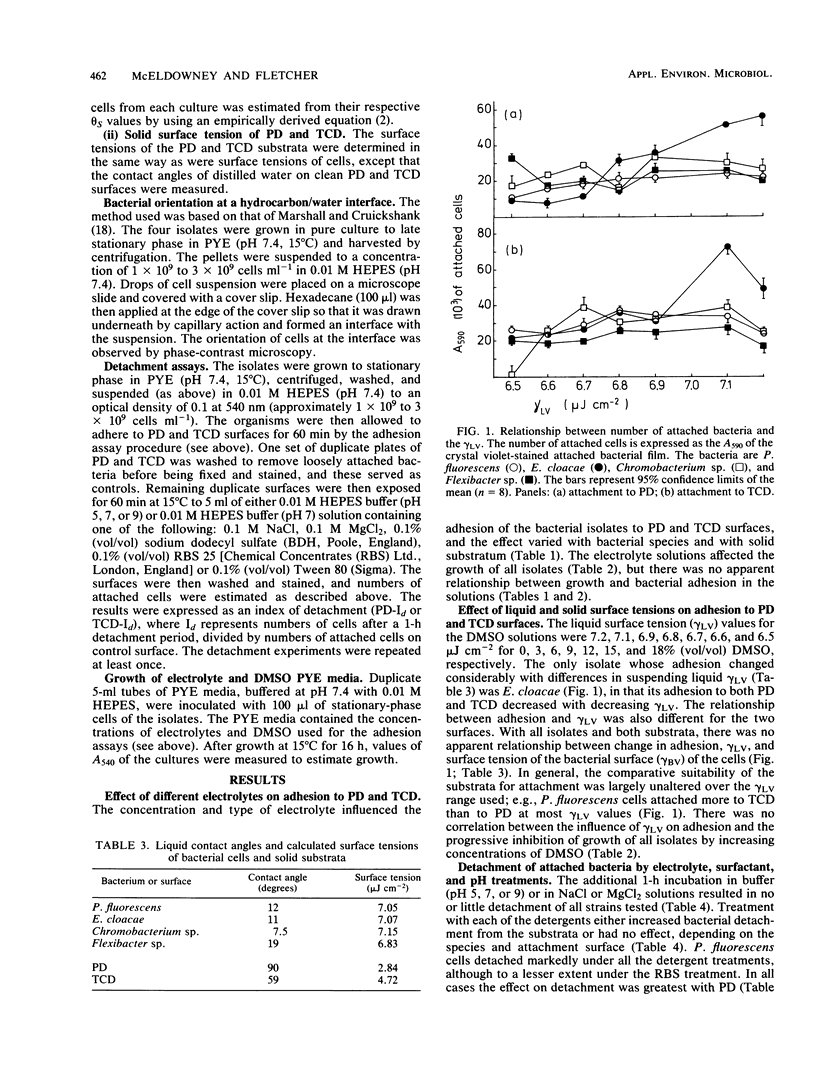
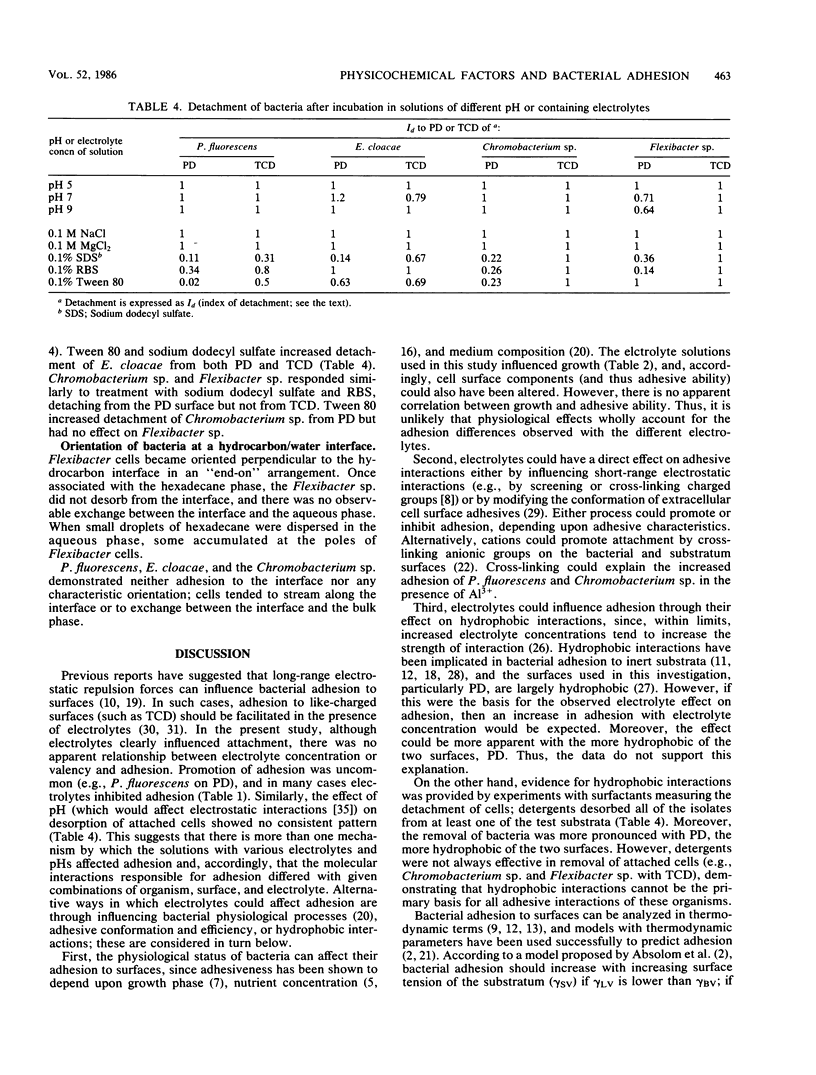
The role of electrostatic and hydrophobic interactions and solid and liquid surface tensions in the adhesion of four bacterial species (Pseudomonas fluorescens, Enterobacter cloacae, Chromobacterium sp., and Flexibacter sp.) to hydrophobic polystyrene petri dishes and to more hydrophilic polystyrene tissue culture dishes was investigated. The effect of electrostatic interactions was investigated by determining the effects of different electrolyte solutions on attachment to and of different electrolyte and pH solutions on detachment from the polystyrene substrate. The significance of solid and liquid surface tensions and hydrophobic interactions was investigated by measuring the effects of different surfactants (including a concentration series of dimethyl sulfoxide) on adhesion and detachment. Adhesion varied with bacterial species, substratum, and electrolyte type and concentration, with no apparent correlation between adhesion and electrolyte valence or concentration. The influence of different pH and detergent solutions on bacterial detachment also varied with species, substratum, pH, and detergent type; however, the greatest degree of detachment of all strains from the surfaces was produced by detergent treatment. The results suggest that adhesion cannot be attributed to any one type of adhesive interaction. There was some evidence for both electrostatic and hydrophobic interactions, but neither interaction could wholly account for the data.
Full text
PDF


Selected References
These references are in PubMed. This may not be the complete list of references from this article.
- Abbott A., Rutter P. R., Berkeley R. C. The influence of ionic strength, pH and a protein layer on the interaction between Streptococcus mutans and glass surfaces. J Gen Microbiol. 1983 Feb;129(2):439–445. doi: 10.1099/00221287-129-2-439. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Absolom D. R., Lamberti F. V., Policova Z., Zingg W., van Oss C. J., Neumann A. W. Surface thermodynamics of bacterial adhesion. Appl Environ Microbiol. 1983 Jul;46(1):90–97. doi: 10.1128/aem.46.1.90-97.1983. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Andrade J. D. Interfacial phenomena and biomaterials. Med Instrum. 1973 Mar-Apr;7(2):110–119. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Busscher H. J., Weerkamp A. H., van der Mei H. C., van Pelt A. W., de Jong H. P., Arends J. Measurement of the surface free energy of bacterial cell surfaces and its relevance for adhesion. Appl Environ Microbiol. 1984 Nov;48(5):980–983. doi: 10.1128/aem.48.5.980-983.1984. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Fletcher M., Loeb G. I. Influence of substratum characteristics on the attachment of a marine pseudomonad to solid surfaces. Appl Environ Microbiol. 1979 Jan;37(1):67–72. doi: 10.1128/aem.37.1.67-72.1979. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Gerson D. F., Scheer D. Cell surface energy, contact angles and phase partition. III. Adhesion of bacterial cells to hydrophobic surfaces. Biochim Biophys Acta. 1980 Nov 18;602(3):506–510. doi: 10.1016/0005-2736(80)90329-6. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Gordon A. S., Millero F. J. Electrolyte effects on attachment of an estuarine bacterium. Appl Environ Microbiol. 1984 Mar;47(3):495–499. doi: 10.1128/aem.47.3.495-499.1984. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- HARDEN V. P., HARRIS J. O. The isoelectric point of bacterial cells. J Bacteriol. 1953 Feb;65(2):198–202. doi: 10.1128/jb.65.2.198-202.1953. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Kjelleberg S., Hermansson M. Starvation-induced effects on bacterial surface characteristics. Appl Environ Microbiol. 1984 Sep;48(3):497–503. doi: 10.1128/aem.48.3.497-503.1984. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Marshall K. C., Cruickshank R. H. Cell surface hydrophobicity and the orientation of certain bacteria at interfaces. Arch Mikrobiol. 1973 Apr 8;91(1):29–40. doi: 10.1007/BF00409536. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Neumann A. W., Absolom D. R., van Oss C. J., Zingg W. Surface thermodynamics of leukocyte and platelet adhesion to polymer surfaces. Cell Biophys. 1979 Mar;1(1):79–92. doi: 10.1007/BF02785058. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Olsson J., Glantz P. O., Krasse B. Surface potential and adherence of oral streptococci to solid surfaces. Scand J Dent Res. 1976 Jul;84(4):240–242. doi: 10.1111/j.1600-0722.1976.tb00486.x. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Paul J. H., Jeffrey W. H. Evidence for Separate Adhesion Mechanisms for Hydrophilic and Hydrophobic Surfaces in Vibrio proteolytica. Appl Environ Microbiol. 1985 Aug;50(2):431–437. doi: 10.1128/aem.50.2.431-437.1985. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Pringle J. H., Fletcher M. Influence of substratum wettability on attachment of freshwater bacteria to solid surfaces. Appl Environ Microbiol. 1983 Mar;45(3):811–817. doi: 10.1128/aem.45.3.811-817.1983. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Rosenberg M., Judes H., Weiss E. Cell surface hydrophobicity of dental plaque microorganisms in situ. Infect Immun. 1983 Nov;42(2):831–834. doi: 10.1128/iai.42.2.831-834.1983. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Rutter P. R., Abbott A. A study of the interaction between oral streptococci and hard surfaces. J Gen Microbiol. 1978 Apr;105(2):219–226. doi: 10.1099/00221287-105-2-219. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Stanley P. M. Factors affecting the irreversible attachment of Pseudomonas aeruginosa to stainless steel. Can J Microbiol. 1983 Nov;29(11):1493–1499. doi: 10.1139/m83-230. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Tanford C. Interfacial free energy and the hydrophobic effect. Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A. 1979 Sep;76(9):4175–4176. doi: 10.1073/pnas.76.9.4175. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- van Pelt A. W., Weerkamp A. H., Uyen M. H., Busscher H. J., de Jong H. P., Arends J. Adhesion of Streptococcus sanguis CH3 to polymers with different surface free energies. Appl Environ Microbiol. 1985 May;49(5):1270–1275. doi: 10.1128/aem.49.5.1270-1275.1985. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]



