Abstract
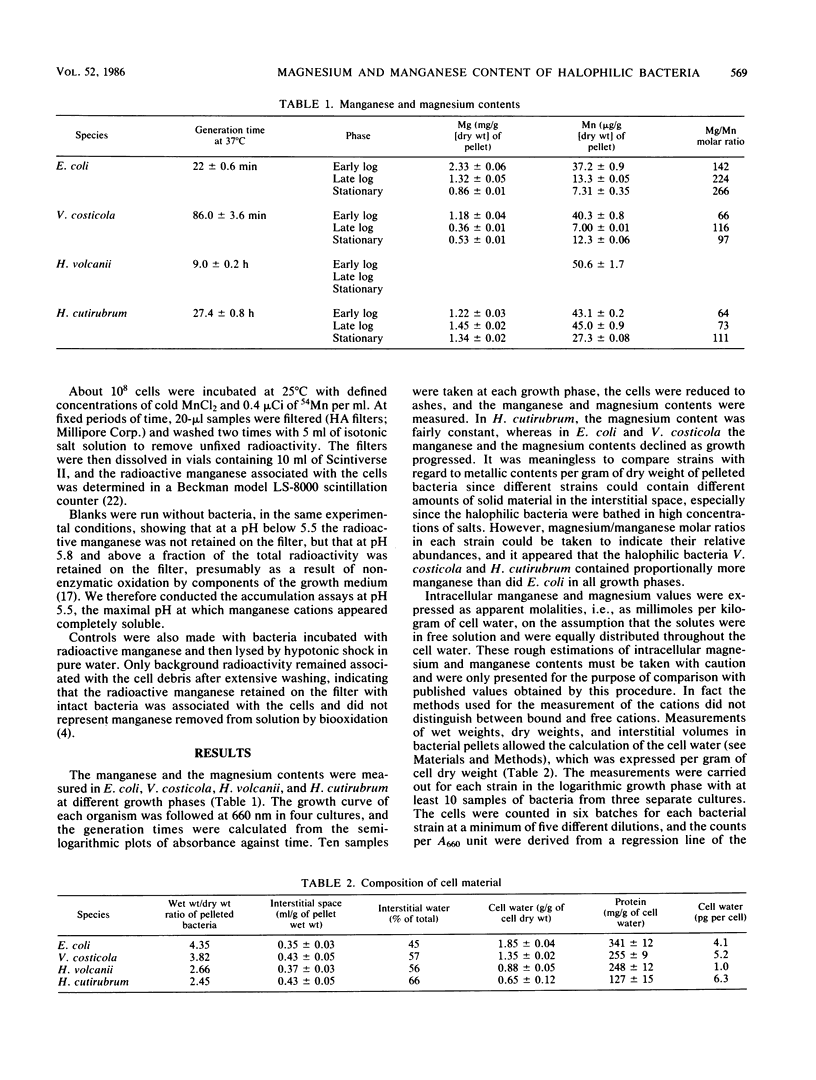
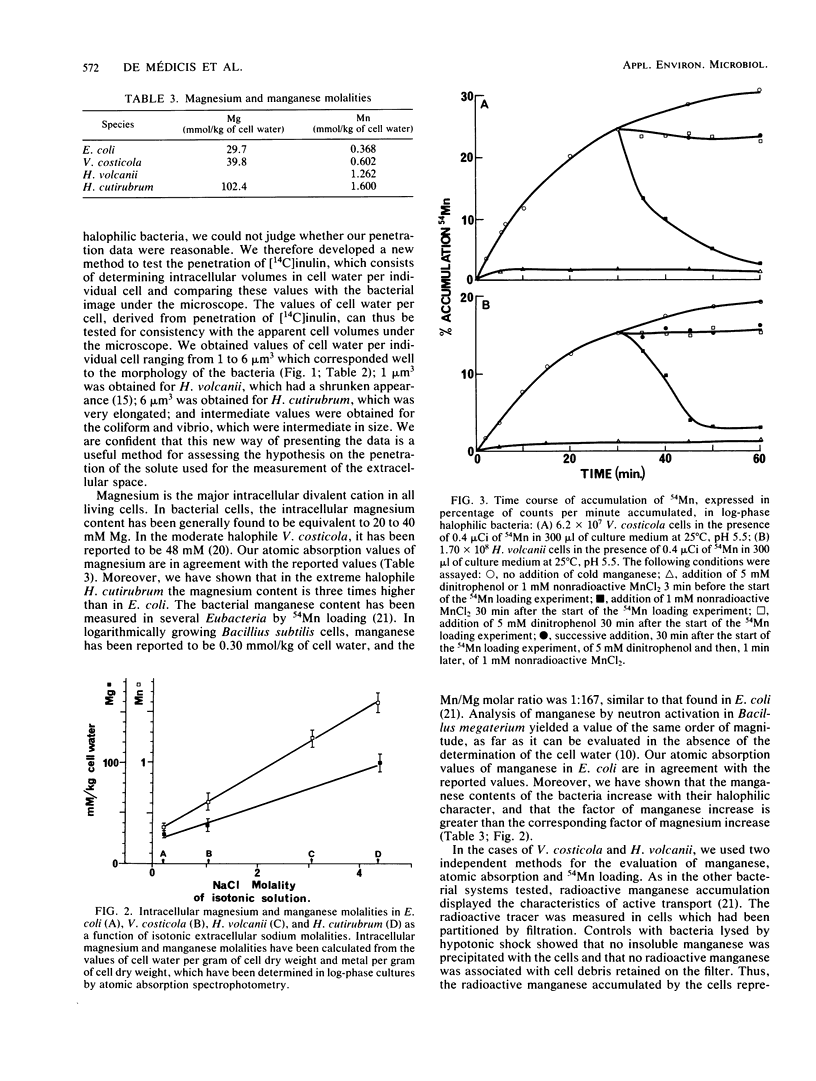
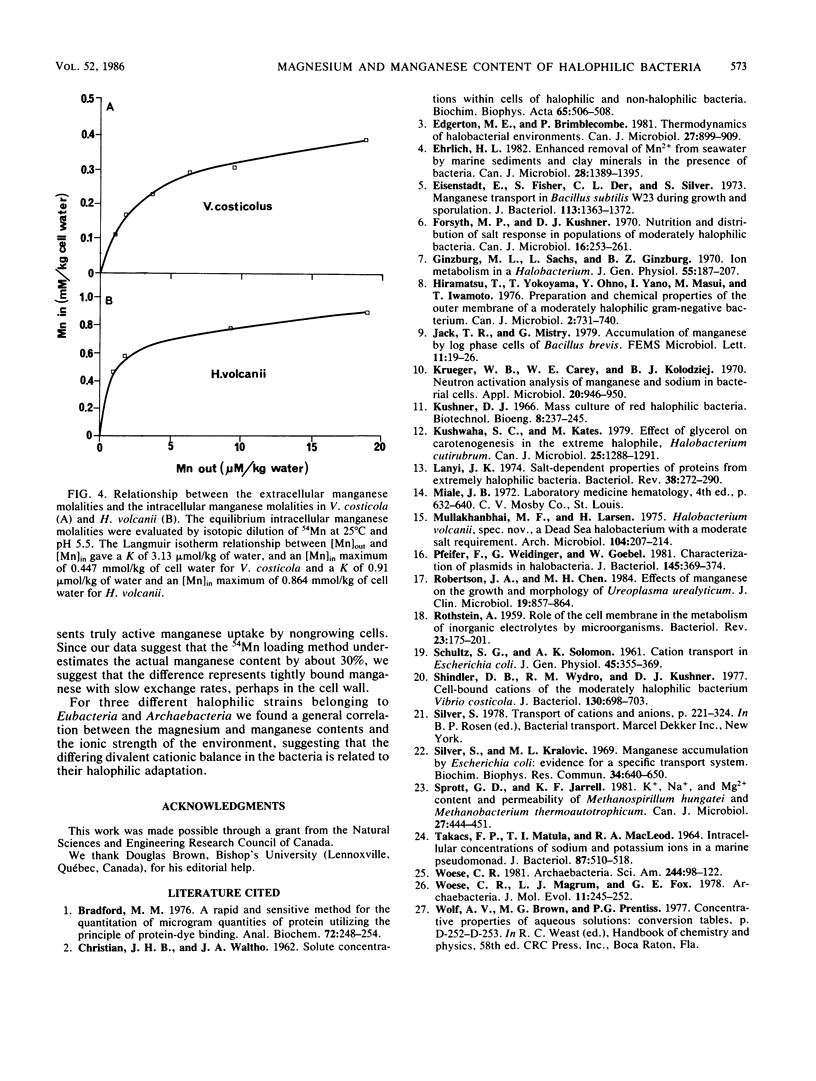
Magnesium and manganese contents were measured by atomic absorption spectrophotometry in bacteria of several halophilic levels, in Vibrio costicola, a moderately halophilic eubacterium growing in 1 M NaCl, Halobacterium volcanii, a halophilic archaebacterium growing in 2.5 M NaCl, Halobacterium cutirubrum, an extremely halophilic archaebacterium growing in 4 M NaCl, and Escherichia coli, a nonhalophilic eubacterium growing in 0.17 M NaCl. Magnesium and manganese contents varied with the growth phase, being maximal at the early log phase. Magnesium and manganese molalities in cell water were shown to increase with the halophilic character of the logarithmically growing bacteria, from 30 mmol of Mg per kg of cell water and 0.37 mmol of Mn per kg of cell water for E. coli to 102 mmol of Mg per kg of cell water and 1.6 mmol of Mn per kg of cell water for H. cutirubrum. The intracellular concentrations of manganese were determined independently by a radioactive tracer technique in V. costicola and H. volcanii. The values obtained by 54Mn loading represented about 70% of the values obtained by atomic absorption. The increase of magnesium and manganese contents associated with the halophilic character of the bacteria suggests that manganese and magnesium play a role in haloadaptation.
Full text
PDF



Images in this article
Selected References
These references are in PubMed. This may not be the complete list of references from this article.
- Bradford M. M. A rapid and sensitive method for the quantitation of microgram quantities of protein utilizing the principle of protein-dye binding. Anal Biochem. 1976 May 7;72:248–254. doi: 10.1016/0003-2697(76)90527-3. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- CHRISTIAN J. H., WALTHO J. A. Solute concentrations within cells of halophilic and non-halophilic bacteria. Biochim Biophys Acta. 1962 Dec 17;65:506–508. doi: 10.1016/0006-3002(62)90453-5. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Edgerton M. E., Brimblecombe P. Thermodynamics of halobacterial environments. Can J Microbiol. 1981 Sep;27(9):899–909. doi: 10.1139/m81-142. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Eisenstadt E., Fisher S., Der C. L., Silver S. Manganese transport in Bacillus subtilis W23 during growth and sporulation. J Bacteriol. 1973 Mar;113(3):1363–1372. doi: 10.1128/jb.113.3.1363-1372.1973. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Forsyth M. P., Kushner D. J. Nutrition and distribution of salt response in populations of moderately halophilic bacteria. Can J Microbiol. 1970 Apr;16(4):253–261. doi: 10.1139/m70-047. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Ginzburg M., Sachs L., Ginzburg B. Z. Ion metabolism in a Halobacterium. I. Influence of age of culture on intracellular concentrations. J Gen Physiol. 1970 Feb;55(2):187–207. doi: 10.1085/jgp.55.2.187. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Hiramatsu T., Yokoyama T., Ohno Y., Yano I., Masui M. Preparation and chemical properties of the outer membrane of a moderately halophilic gram-negative bacterium. Can J Microbiol. 1976 May;22(5):731–740. doi: 10.1139/m76-106. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Krueger W. B., Carey W. E., Kolodziej B. J. Neutron activation analysis of manganese and sodium in bacterial cells. Appl Microbiol. 1970 Dec;20(6):946–950. doi: 10.1128/am.20.6.946-950.1970. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Kushwaha S. C., Kates M. Effect of glycerol on carotenogenesis in the extreme halophile, Halobacterium cutirubrum. Can J Microbiol. 1979 Nov;25(11):1288–1291. doi: 10.1139/m79-203. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Lanyi J. K. Salt-dependent properties of proteins from extremely halophilic bacteria. Bacteriol Rev. 1974 Sep;38(3):272–290. doi: 10.1128/br.38.3.272-290.1974. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Mullakhanbhai M. F., Larsen H. Halobacterium volcanii spec. nov., a Dead Sea halobacterium with a moderate salt requirement. Arch Microbiol. 1975 Aug 28;104(3):207–214. doi: 10.1007/BF00447326. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Pfeifer F., Weidinger G., Goebel W. Characterization of plasmids in halobacteria. J Bacteriol. 1981 Jan;145(1):369–374. doi: 10.1128/jb.145.1.369-374.1981. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- ROTHSTEIN A. Role of the cell membrane in the metabolism of inorganic electrolytes by microorganisms. Bacteriol Rev. 1959 Dec;23(4):175–201. doi: 10.1128/br.23.4.175-201.1959. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Robertson J. A., Chen M. H. Effects of manganese on the growth and morphology of Ureaplasma urealyticum. J Clin Microbiol. 1984 Jun;19(6):857–864. doi: 10.1128/jcm.19.6.857-864.1984. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- SCHULTZ S. G., SOLOMON A. K. Cation transport in Escherichia coli. I. Intracellular Na and K concentrations and net cation movement. J Gen Physiol. 1961 Nov;45:355–369. doi: 10.1085/jgp.45.2.355. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Shindler D. B., Wydro R. M., Kushner D. J. Cell-bound cations of the moderately halophilic bacterium Vibrio costicola. J Bacteriol. 1977 May;130(2):698–703. doi: 10.1128/jb.130.2.698-703.1977. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Silver S., Kralovic M. L. Manganese accumulation by Escherichia coli: evidence for a specific transport system. Biochem Biophys Res Commun. 1969 Mar 10;34(5):640–645. doi: 10.1016/0006-291x(69)90786-4. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Sprott G. D., Jarrell K. F. K+, Na+, and Mg2+ content and permeability of Methanospirillum hungatei and Methanobacterium thermoautotrophicum. Can J Microbiol. 1981 Apr;27(4):444–451. doi: 10.1139/m81-067. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- TAKACS F. P., MATULA T. I., MACLEOD R. A. NUTRITION AND METABOLISM OF MARINE BACTERIA. XIII. INTRACELLULAR CONCENTRATIONS OF SODIUM AND POTASSIUM IONS IN A MARINE PSEUDOMONAD. J Bacteriol. 1964 Mar;87:510–518. doi: 10.1128/jb.87.3.510-518.1964. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Woese C. R., Magrum L. J., Fox G. E. Archaebacteria. J Mol Evol. 1978 Aug 2;11(3):245–251. doi: 10.1007/BF01734485. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]




