Abstract
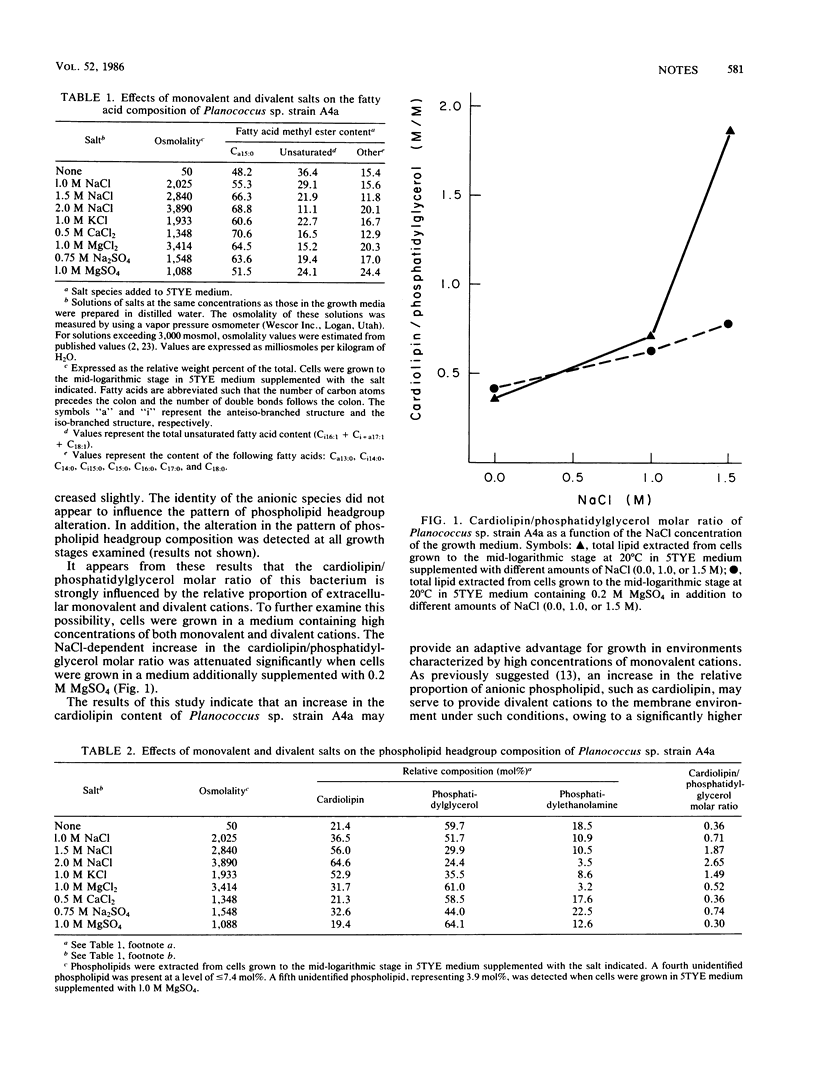
The phospholipid headgroup and fatty acid compositions of a halotolerant Planococcus sp. (strain A4a) were examined when cells were grown in the presence of high concentrations of a variety of salts. The fatty acid composition of Planococcus sp. strain A4a was altered primarily as a function of the osmolality of the growth medium. The phospholipid headgroup composition was influenced by both the osmolality of the growth medium and the nature of the cation species present. An increase in the cardiolipin/phosphatidylglycerol molar ratio was detected when cells were grown in the presence of high concentrations of monovalent cations.
Full text
PDF

Selected References
These references are in PubMed. This may not be the complete list of references from this article.
- Alphen W. V., Lugtenberg B. Influence of osmolarity of the growth medium on the outer membrane protein pattern of Escherichia coli. J Bacteriol. 1977 Aug;131(2):623–630. doi: 10.1128/jb.131.2.623-630.1977. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Hauser H., Dawson R. M. The binding of calcium at lipid-water interfaces. Eur J Biochem. 1967 Mar;1(1):61–69. doi: 10.1007/978-3-662-25813-2_11. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Kanemasa Y., Yoshioka T., Hayashi H. Alteration of the phospholipid composition of Staphylococcus aureus cultured in medium containing NaCl. Biochim Biophys Acta. 1972 Nov 30;280(3):444–450. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Kennedy E. P. Osmotic regulation and the biosynthesis of membrane-derived oligosaccharides in Escherichia coli. Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A. 1982 Feb;79(4):1092–1095. doi: 10.1073/pnas.79.4.1092. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Komaratat P., Kates M. The lipid composition of a halotolerant species of Staphylococcus epidermidis. Biochim Biophys Acta. 1975 Sep 19;398(3):464–484. doi: 10.1016/0005-2760(75)90197-6. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Laimins L. A., Rhoads D. B., Epstein W. Osmotic control of kdp operon expression in Escherichia coli. Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A. 1981 Jan;78(1):464–468. doi: 10.1073/pnas.78.1.464. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Le Rudulier D., Bouillard L. Glycine betaine, an osmotic effector in Klebsiella pneumoniae and other members of the Enterobacteriaceae. Appl Environ Microbiol. 1983 Jul;46(1):152–159. doi: 10.1128/aem.46.1.152-159.1983. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Measures J. C. Role of amino acids in osmoregulation of non-halophilic bacteria. Nature. 1975 Oct 2;257(5525):398–400. doi: 10.1038/257398a0. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Miller K. J. Effects of temperature and sodium chloride concentration on the phospholipid and fatty acid compositions of a halotolerant Planococcus sp. J Bacteriol. 1985 Apr;162(1):263–270. doi: 10.1128/jb.162.1.263-270.1985. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Miller K. J., Kennedy E. P., Reinhold V. N. Osmotic adaptation by gram-negative bacteria: possible role for periplasmic oligosaccharides. Science. 1986 Jan 3;231(4733):48–51. doi: 10.1126/science.3941890. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Mosley G. A., Card G. L., Koostra W. L. Effect of calcium and anaerobiosis on the thermostability of Bacillus stearothermophilus. Can J Microbiol. 1976 Apr;22(4):468–474. doi: 10.1139/m76-073. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Munro G. F., Hercules K., Morgan J., Sauerbier W. Dependence of the putrescine content of Escherichia coli on the osmotic strength of the medium. J Biol Chem. 1972 Feb 25;247(4):1272–1280. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Ohno Y., Yano I., Hiramatsu T., Masui M. Lipids and fatty acids of a moderately halophilic bacterium, No. 101. Biochim Biophys Acta. 1976 Mar 26;424(3):337–350. doi: 10.1016/0005-2760(76)90024-2. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Ohno Y., Yano I., Masui M. Effect of NaCl concentration and temperature on the phospholipid and fatty acid compositions of a moderately halophilic bacterium, Pseudomonas halosaccharolytica. J Biochem. 1979 Feb;85(2):413–421. doi: 10.1093/oxfordjournals.jbchem.a132348. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Tempest D. W., Meers J. L., Brown C. M. Influence of environment on the content and composition of microbial free amino acid pools. J Gen Microbiol. 1970 Dec;64(2):171–185. doi: 10.1099/00221287-64-2-171. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Vreeland R. H., Anderson R., Murray R. G. Cell wall and phospholipid composition and their contribution to the salt tolerance of Halomonas elongata. J Bacteriol. 1984 Dec;160(3):879–883. doi: 10.1128/jb.160.3.879-883.1984. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]



