Abstract
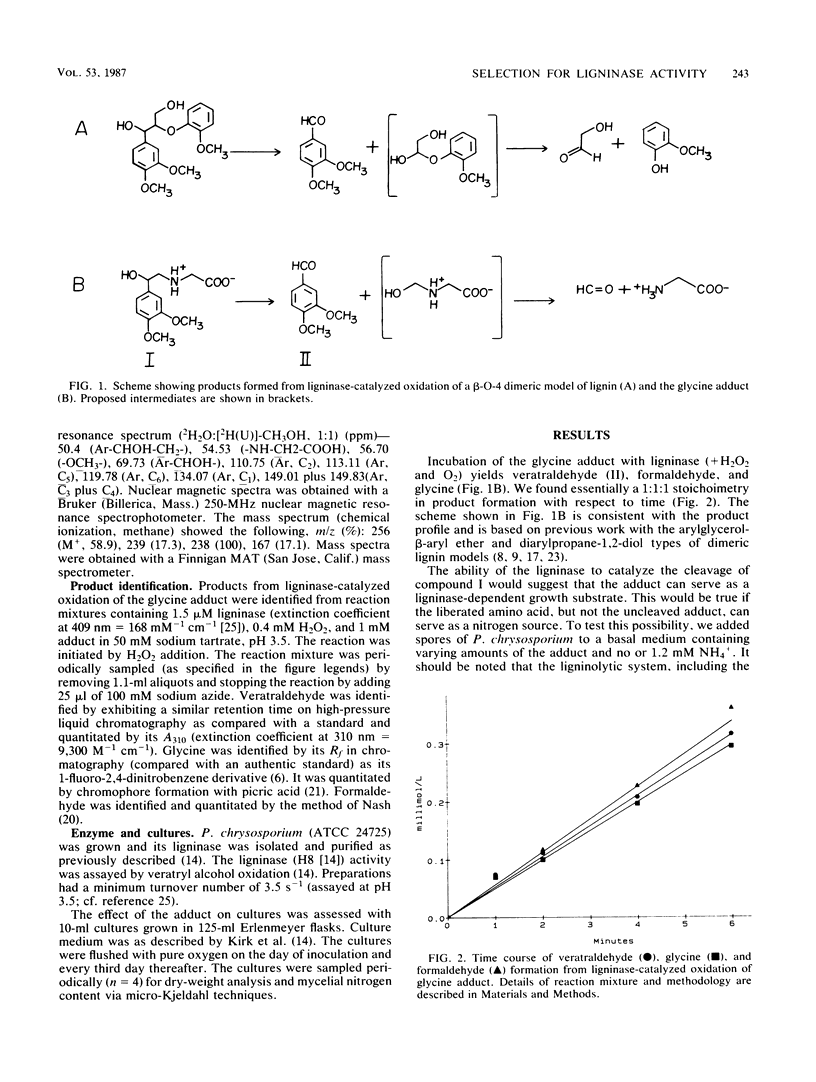
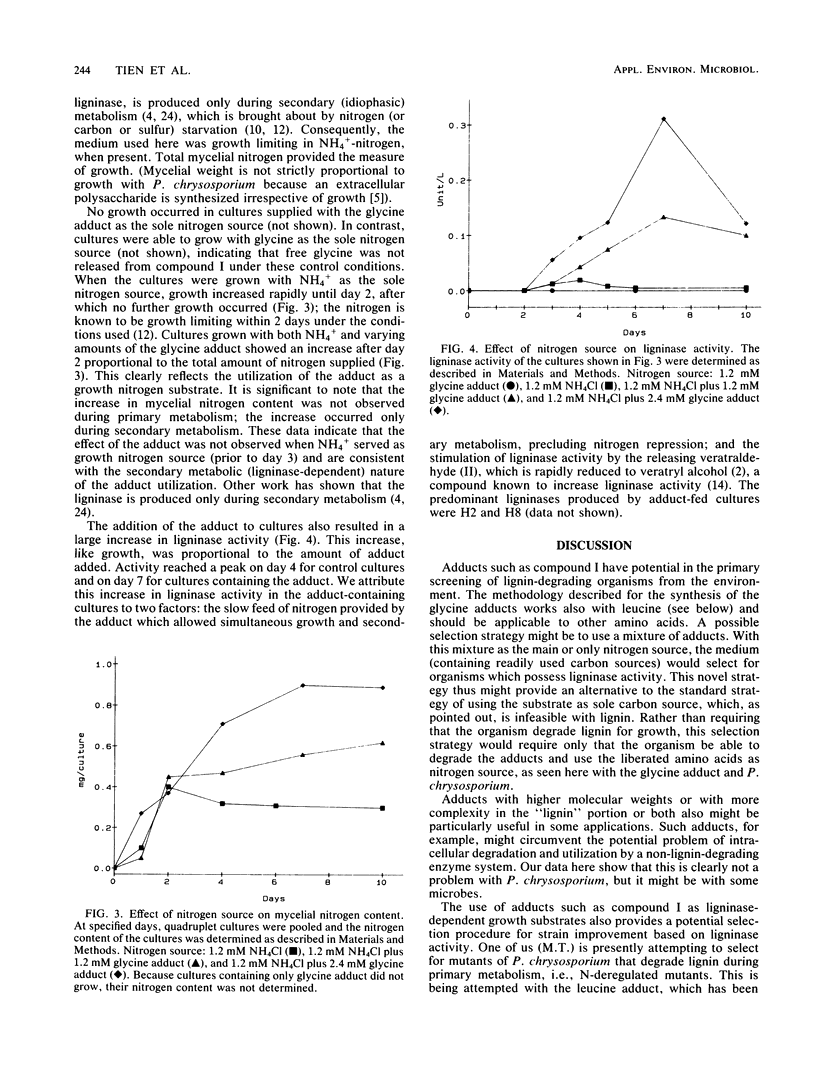
The purpose of this investigation was to test a potential strategy for the ligninase-dependent selection of lignin-degrading microorganisms. The strategy involves covalently bonding amino acids to lignin model compounds in such a way that ligninase-catalyzed cleavage of the models releases the amino acids for growth nitrogen. Here we describe the synthesis of glycine-N-2-(3,4-dimethoxyphenyl)ethane-2-ol (I) and demonstrate that growth (as measured by mycelial nitrogen content) of the known lignin-degrading basidiomycete Phanerochaete chrysosporium Burds. with compound I as the nitrogen source depends on its production of ligninase. Ligninase is shown to catalyze the oxidative C—C cleavage of compound I, releasing glycine, formaldehyde, and veratraldehyde at a 1:1:1 stoichiometry. P. chrysosporium utilizes compound I as a nitrogen source, but only after the cultures enter secondary metabolism (day 3 of growth), at which time the ligninase and the other components of the ligninolytic system (lignin → CO2) are expressed. Compound I and related adducts have potential not only in the isolation of lignin-degrading microbes but, perhaps of equal importance, in strain improvement.
Full text
PDF

Selected References
These references are in PubMed. This may not be the complete list of references from this article.
- Alic M., Gold M. H. Genetic Recombination in the Lignin-Degrading Basidiomycete Phanerochaete chrysosporium. Appl Environ Microbiol. 1985 Jul;50(1):27–30. doi: 10.1128/aem.50.1.27-30.1985. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- FRAENKEL-CONRAT H., HARRIS J. I., LEVY A. L. Recent developments in techniques for terminal and sequence studies in peptides and proteins. Methods Biochem Anal. 1955;2:359–425. doi: 10.1002/9780470110188.ch12. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Faison B. D., Kirk T. K. Factors Involved in the Regulation of a Ligninase Activity in Phanerochaete chrysosporium. Appl Environ Microbiol. 1985 Feb;49(2):299–304. doi: 10.1128/aem.49.2.299-304.1985. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Glenn J. K., Morgan M. A., Mayfield M. B., Kuwahara M., Gold M. H. An extracellular H2O2-requiring enzyme preparation involved in lignin biodegradation by the white rot basidiomycete Phanerochaete chrysosporium. Biochem Biophys Res Commun. 1983 Aug 12;114(3):1077–1083. doi: 10.1016/0006-291x(83)90672-1. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Gold M. H., Kuwahara M., Chiu A. A., Glenn J. K. Purification and characterization of an extracellular H2O2-requiring diarylpropane oxygenase from the white rot basidiomycete, Phanerochaete chrysosporium. Arch Biochem Biophys. 1984 Nov 1;234(2):353–362. doi: 10.1016/0003-9861(84)90280-7. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Hammel K. E., Tien M., Kalyanaraman B., Kirk T. K. Mechanism of oxidative C alpha-C beta cleavage of a lignin model dimer by Phanerochaete chrysosporium ligninase. Stoichiometry and involvement of free radicals. J Biol Chem. 1985 Jul 15;260(14):8348–8353. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Jeffries T. W., Choi S., Kirk T. K. Nutritional Regulation of Lignin Degradation by Phanerochaete chrysosporium. Appl Environ Microbiol. 1981 Aug;42(2):290–296. doi: 10.1128/aem.42.2.290-296.1981. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Kersten P. J., Tien M., Kalyanaraman B., Kirk T. K. The ligninase of Phanerochaete chrysosporium generates cation radicals from methoxybenzenes. J Biol Chem. 1985 Mar 10;260(5):2609–2612. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Keyser P., Kirk T. K., Zeikus J. G. Ligninolytic enzyme system of Phanaerochaete chrysosporium: synthesized in the absence of lignin in response to nitrogen starvation. J Bacteriol. 1978 Sep;135(3):790–797. doi: 10.1128/jb.135.3.790-797.1978. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Kirk T. K., Connors W. J., Zeikus J. G. Requirement for a growth substrate during lignin decomposition by two wood-rotting fungi. Appl Environ Microbiol. 1976 Jul;32(1):192–194. doi: 10.1128/aem.32.1.192-194.1976. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Kirk T. K., Tien M., Kersten P. J., Mozuch M. D., Kalyanaraman B. Ligninase of Phanerochaete chrysosporium. Mechanism of its degradation of the non-phenolic arylglycerol beta-aryl ether substructure of lignin. Biochem J. 1986 May 15;236(1):279–287. doi: 10.1042/bj2360279. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- NASH T. The colorimetric estimation of formaldehyde by means of the Hantzsch reaction. Biochem J. 1953 Oct;55(3):416–421. doi: 10.1042/bj0550416. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Tien M., Kirk T. K., Bull C., Fee J. A. Steady-state and transient-state kinetic studies on the oxidation of 3,4-dimethoxybenzyl alcohol catalyzed by the ligninase of Phanerocheate chrysosporium Burds. J Biol Chem. 1986 Feb 5;261(4):1687–1693. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Tien M., Kirk T. K. Lignin-Degrading Enzyme from the Hymenomycete Phanerochaete chrysosporium Burds. Science. 1983 Aug 12;221(4611):661–663. doi: 10.1126/science.221.4611.661. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Tien M., Kirk T. K. Lignin-degrading enzyme from Phanerochaete chrysosporium: Purification, characterization, and catalytic properties of a unique H(2)O(2)-requiring oxygenase. Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A. 1984 Apr;81(8):2280–2284. doi: 10.1073/pnas.81.8.2280. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]


