Abstract
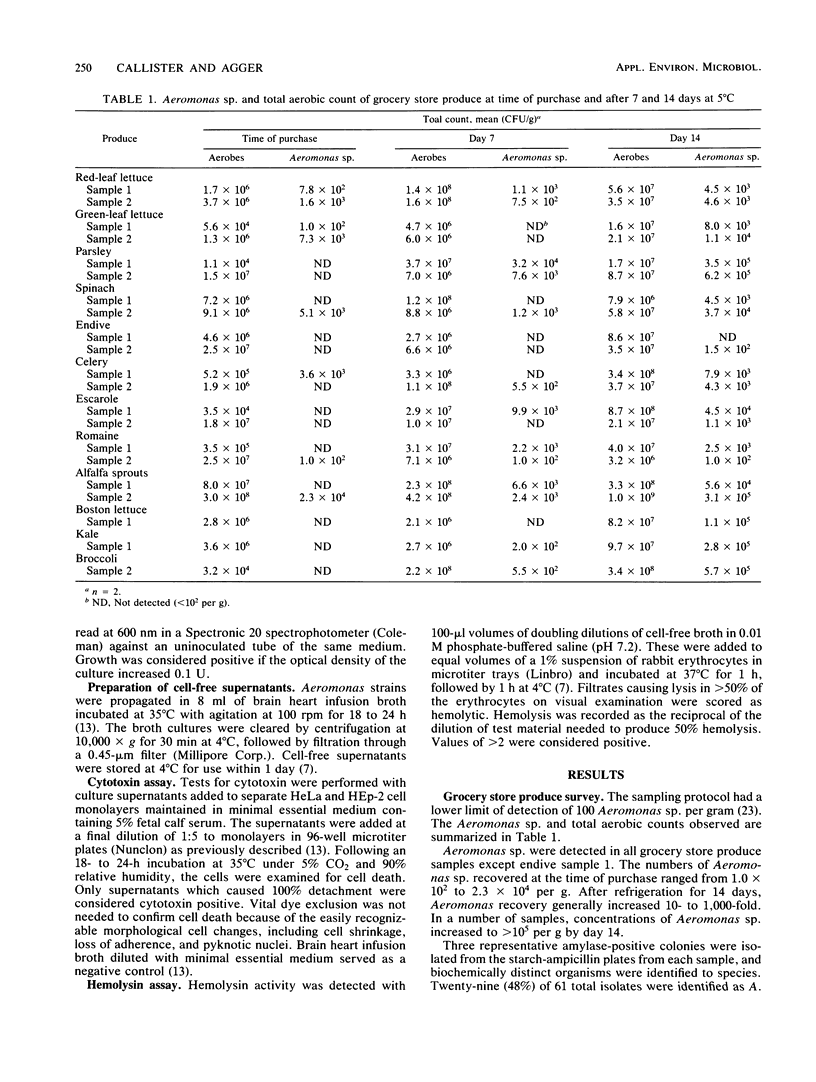
Starch-ampicillin agar was used to quantitatively isolate Aeromonas sp. from retail grocery store produce. All produce sampled, including parsley, spinach, celery, alfalfa sprouts, broccoli, and lettuce, contained Aeromonas sp. In most instances, the count of Aeromonas sp. increased 10- to 1,000-fold during 2 weeks of storage at 5 degrees C. Eleven (92%) of 12 kinds of produce yielded cytotoxic Aeromonas sp. Identification as Aeromonas hydrophila was the strongest indicator of cytotoxicity, and all 29 (100%) A. hydrophila isolates and 1 (6%) of 16 A. caviae isolates were cytotoxic. Twenty-seven (90%) of 30 cytotoxic Aeromonas sp. strains produced hemolysins. Strong correlations were also noted between ability to produce cytotoxin and positive Voges-Proskauer, lysine decarboxylase, and sorbitol fermentation reactions. It appears that grocery store produce is a potentially significant source of cytotoxic Aeromonas sp. and should be considered in the epidemiology of A. hydrophila gastroenteritis.
Full text
PDF



Selected References
These references are in PubMed. This may not be the complete list of references from this article.
- Agger W. A., McCormick J. D., Gurwith M. J. Clinical and microbiological features of Aeromonas hydrophila-associated diarrhea. J Clin Microbiol. 1985 Jun;21(6):909–913. doi: 10.1128/jcm.21.6.909-913.1985. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Bhat P., Shanthakumari S., Rajan D. The characterization and significance of Plesiomonas shigelloides and Aeromonas hydrophila isolated from an epidemic of diarrhoea. Indian J Med Res. 1974 Jul;62(7):1051–1060. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Boulanger Y., Lallier R., Cousineau G. Isolation of enterotoxigenic Aeromonas from fish. Can J Microbiol. 1977 Sep;23(9):1161–1164. doi: 10.1139/m77-174. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Burke V., Gracey M., Robinson J., Peck D., Beaman J., Bundell C. The microbiology of childhood gastroenteritis: Aeromonas species and other infective agents. J Infect Dis. 1983 Jul;148(1):68–74. doi: 10.1093/infdis/148.1.68. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Burke V., Robinson J., Atkinson H. M., Dibley M., Berry R. J., Gracey M. Exotoxins of Aeromonas hydrophila. Aust J Exp Biol Med Sci. 1981 Dec;59(Pt 6):753–761. doi: 10.1038/icb.1981.65. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Burke V., Robinson J., Atkinson H. M., Gracey M. Biochemical characteristics of enterotoxigenic Aeromonas spp. J Clin Microbiol. 1982 Jan;15(1):48–52. doi: 10.1128/jcm.15.1.48-52.1982. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Burke V., Robinson J., Beaman J., Gracey M., Lesmana M., Rockhill R., Echeverria P., Janda J. M. Correlation of enterotoxicity with biotype in Aeromonas spp. J Clin Microbiol. 1983 Nov;18(5):1196–1200. doi: 10.1128/jcm.18.5.1196-1200.1983. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Burke V., Robinson J., Cooper M., Beaman J., Partridge K., Peterson D., Gracey M. Biotyping and virulence factors in clinical and environmental isolates of Aeromonas species. Appl Environ Microbiol. 1984 May;47(5):1146–1149. doi: 10.1128/aem.47.5.1146-1149.1984. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Champsaur H., Adremont A., Mathieu D., Rottman E., Auzepy P. Cholera-like illness due to Aeromonas sobria. J Infect Dis. 1982 Feb;145(2):248–254. doi: 10.1093/infdis/145.2.248. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Chatterjee B. D., Neogy K. N. Studies on Aeromonas and Plesiomonas species isolated from cases of choleraic diarrhoea. Indian J Med Res. 1972 Apr;60(4):520–524. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Cumberbatch N., Gurwith M. J., Langston C., Sack R. B., Brunton J. L. Cytotoxic enterotoxin produced by Aeromonas hydrophila: relationship of toxigenic isolates to diarrheal disease. Infect Immun. 1979 Mar;23(3):829–837. doi: 10.1128/iai.23.3.829-837.1979. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Echeverria P., Blacklow N. R., Sanford L. B., Cukor G. G. Travelers' diarrhea among American Peace Corps volunteers in rural Thailand. J Infect Dis. 1981 Jun;143(6):767–771. doi: 10.1093/infdis/143.6.767. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Enfors S. O., Molin G., Ternström A. Effect of packaging under carbon dioxide, nitrogen or air on the microbial flora of pork stored at 4 degrees C. J Appl Bacteriol. 1979 Oct;47(2):197–208. doi: 10.1111/j.1365-2672.1979.tb01746.x. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Figura N., Marri L., Verdiani S., Ceccherini C., Barberi A. Prevalence, species differentiation, and toxigenicity of Aeromonas strains in cases of childhood gastroenteritis and in controls. J Clin Microbiol. 1986 Mar;23(3):595–599. doi: 10.1128/jcm.23.3.595-599.1986. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Goodwin C. S., Harper W. E., Stewart J. K., Gracey M., Burke V., Robinson J. Enterotoxigenic Aeromonas hydrophila and diarrhoea in adults. Med J Aust. 1983 Jan 8;1(1):25–26. doi: 10.5694/j.1326-5377.1983.tb136018.x. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Grau F. H. Role of pH, lactate, and anaerobiosis in controlling the growth of some fermentative Gram-negative bacteria on beef. Appl Environ Microbiol. 1981 Dec;42(6):1043–1050. doi: 10.1128/aem.42.6.1043-1050.1981. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Janda J. M., Bottone E. J., Skinner C. V., Calcaterra D. Phenotypic markers associated with gastrointestinal Aeromonas hydrophila isolates from symptomatic children. J Clin Microbiol. 1983 Apr;17(4):588–591. doi: 10.1128/jcm.17.4.588-591.1983. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Jiwa S. F. Enterotoxigenicity, hemagglutination and cell-surface hydrophobicity in Aeromonas hydrophila, A. sobria and A. salmonicida. Vet Microbiol. 1983 Feb;8(1):17–34. doi: 10.1016/0378-1135(83)90016-0. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Palumbo S. A., Maxino F., Williams A. C., Buchanan R. L., Thayer D. W. Starch-Ampicillin Agar for the Quantitative Detection of Aeromonas hydrophila. Appl Environ Microbiol. 1985 Oct;50(4):1027–1030. doi: 10.1128/aem.50.4.1027-1030.1985. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Popoff M., Véron M. A taxonomic study of the Aeromonas hydrophila-Aeromonas punctata group. J Gen Microbiol. 1976 May;94(1):11–22. doi: 10.1099/00221287-94-1-11. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Rippey S. R., Cabelli V. J. Membrane filter procedure for enumeration of Aeromonas hydrophila in fresh waters. Appl Environ Microbiol. 1979 Jul;38(1):108–113. doi: 10.1128/aem.38.1.108-113.1979. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Sanyal S. C., Singh S. J., Sen P. C. Enteropathogenicity of Aeromonas hydrophila and Plesiomonas shigelloides. J Med Microbiol. 1975 Feb;8(1):195–198. doi: 10.1099/00222615-8-1-195. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Seidler R. J., Allen D. A., Lockman H., Colwell R. R., Joseph S. W., Daily O. P. Isolation, enumeration, and characterization of Aeromonas from polluted waters encountered in diving operations. Appl Environ Microbiol. 1980 May;39(5):1010–1018. doi: 10.1128/aem.39.5.1010-1018.1980. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Thelen P., Burke V., Gracey M. Effects of intestinal micro-organisms on fluid and electrolyte transport in the jejunum of the rat. J Med Microbiol. 1978 Nov;11(4):463–470. doi: 10.1099/00222615-11-4-463. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Toule G., Murphy O. A study of bacteria contaminating refrigerated cooked chicken; their spoilage potential and possible origin. J Hyg (Lond) 1978 Oct;81(2):161–169. doi: 10.1017/s0022172400024980. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Turnbull P. C., Lee J. V., Miliotis M. D., Van de Walle S., Koornhof H. J., Jeffery L., Bryant T. N. Enterotoxin production in relation to taxonomic grouping and source of isolation of Aeromonas species. J Clin Microbiol. 1984 Feb;19(2):175–180. doi: 10.1128/jcm.19.2.175-180.1984. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]



