Abstract
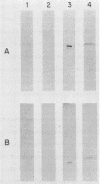
The expression of cosmid-borne Bradyrhizobium japonicum hydrogenase genes in alfalfa, clover, and soybean nodules harboring Rhizobium transconjugants was studied. Cosmid pHU52 conferred hydrogen uptake (Hup) activity in both free-living bacteria and in nodules on the different plant hosts, although in nodules the instability of the cosmid resulted in low levels of Hup activity. In contrast, cosmid pHU1, which does not confer Hup activity on free-living bacteria, gave a Hup+ phenotype in nodules on alfalfa and soybean. Nodules formed by B. japonicum USDA 123Spc(pHU1) recycled about 90% of nitrogenase-mediated hydrogen evolution. Both subunits of hydrogenase (30- and 60-kilodalton polypeptides) were detected in enzyme-linked immunosorbent assays of bacteroid preparations from nodules harboring B. japonicum strains with pHU1 or pHU52. Neither pHU53 nor pLAFR1 conferred detectable Hup activity in either nodules or free-living bacteria. Based on the physical maps of pHU1 and pHU52, it is suggested that a 5.5-kilobase EcoRI fragment unique to pHU52 contains a gene or part of a gene required for Hup activity in free-living bacteria but not in nodules. This conclusion is supported by the observation that two Tn5 insertions in the chromosome of B. japonicum USDA 122DES obtained by marker exchange with Tn5-mutagenized pHU1 abolished Hup activity in free-living bacteria but not in nodules.
Full text
PDF



Images in this article
Selected References
These references are in PubMed. This may not be the complete list of references from this article.
- Arunakumari A., Vidaver A. K. Transposon Mutagenesis and Excision of R' Plasmids by Conjugative, Chimeric Plasmid pUW942 in Extra-Slow-Growing Rhizobium japonicum Strains. Appl Environ Microbiol. 1986 Jan;51(1):6–11. doi: 10.1128/aem.51.1.6-11.1986. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Bedmar E. J., Edie S. A., Phillips D. A. Host Plant Cultivar Effects on Hydrogen Evolution by Rhizobium leguminosarum. Plant Physiol. 1983 Aug;72(4):1011–1015. doi: 10.1104/pp.72.4.1011. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Cantrell M. A., Haugland R. A., Evans H. J. Construction of a Rhizobium japonicum gene bank and use in isolation of a hydrogen uptake gene. Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A. 1983 Jan;80(1):181–185. doi: 10.1073/pnas.80.1.181. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Ditta G., Stanfield S., Corbin D., Helinski D. R. Broad host range DNA cloning system for gram-negative bacteria: construction of a gene bank of Rhizobium meliloti. Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A. 1980 Dec;77(12):7347–7351. doi: 10.1073/pnas.77.12.7347. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Dixon R. O. Hydrogenase in legume root nodule bacteroids: occurrence and properties. Arch Mikrobiol. 1972;85(3):193–201. doi: 10.1007/BF00408844. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Harker A. R., Lambert G. R., Hanus F. J., Evans H. J. Further evidence that two unique subunits are essential for expression of hydrogenase activity in Rhizobium japonicum. J Bacteriol. 1985 Oct;164(1):187–191. doi: 10.1128/jb.164.1.187-191.1985. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Harker A. R., Xu L. S., Hanus F. J., Evans H. J. Some properties of the nickel-containing hydrogenase of chemolithotrophically grown Rhizobium japonicum. J Bacteriol. 1984 Sep;159(3):850–856. doi: 10.1128/jb.159.3.850-856.1984. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Haugland R. A., Cantrell M. A., Beaty J. S., Hanus F. J., Russell S. A., Evans H. J. Characterization of Rhizobium japonicum hydrogen uptake genes. J Bacteriol. 1984 Sep;159(3):1006–1012. doi: 10.1128/jb.159.3.1006-1012.1984. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Haugland R. A., Hanus F. J., Cantrell M. A., Evans H. J. Rapid Colony Screening Method for Identifying Hydrogenase Activity in Rhizobium japonicum. Appl Environ Microbiol. 1983 Mar;45(3):892–897. doi: 10.1128/aem.45.3.892-897.1983. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Holmes D. S., Quigley M. A rapid boiling method for the preparation of bacterial plasmids. Anal Biochem. 1981 Jun;114(1):193–197. doi: 10.1016/0003-2697(81)90473-5. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Hom S. S., Graham L. A., Maier R. J. Isolation of genes (nif/hup cosmids) involved in hydrogenase and nitrogenase activities in Rhizobium japonicum. J Bacteriol. 1985 Mar;161(3):882–887. doi: 10.1128/jb.161.3.882-887.1985. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Kahn M. L., Timblin C. R. Gene fusion vehicles for the analysis of gene expression in Rhizobium meliloti. J Bacteriol. 1984 Jun;158(3):1070–1077. doi: 10.1128/jb.158.3.1070-1077.1984. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Keyser H. H., van Berkum P., Weber D. F. A Comparative Study of the Physiology of Symbioses Formed by Rhizobium japonicum with Glycine max, Vigna unguiculata, and Macroptilium atropurpurem. Plant Physiol. 1982 Dec;70(6):1626–1630. doi: 10.1104/pp.70.6.1626. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Lambert G. R., Cantrell M. A., Hanus F. J., Russell S. A., Haddad K. R., Evans H. J. Intra- and interspecies transfer and expression of Rhizobium japonicum hydrogen uptake genes and autotrophic growth capability. Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A. 1985 May;82(10):3232–3236. doi: 10.1073/pnas.82.10.3232. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Lepo J. E., Hanus F. J., Evans H. J. Chemoautotrophic growth of hydrogen-uptake-positive strains of Rhizobium japonicum. J Bacteriol. 1980 Feb;141(2):664–670. doi: 10.1128/jb.141.2.664-670.1980. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Lepo J. E., Hickok R. E., Cantrell M. A., Russell S. A., Evans H. J. Revertible hydrogen uptake-deficient mutants of Rhizobium japonicum. J Bacteriol. 1981 May;146(2):614–620. doi: 10.1128/jb.146.2.614-620.1981. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Maier R. J., Campbell N. E., Hanus F. J., Simpson F. B., Russell S. A., Evans H. J. Expression of hydrogenase activity in free-living Rhizobium japonicum. Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A. 1978 Jul;75(7):3258–3262. doi: 10.1073/pnas.75.7.3258. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Olivares J., Casadesús J., Bedmar E. J. Method for Testing Degree of Infectivity of Rhizobium meliloti Strains. Appl Environ Microbiol. 1980 May;39(5):967–970. doi: 10.1128/aem.39.5.967-970.1980. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Repaske R., Mayer R. Dense autotrophic cultures of Alcaligenes eutrophus. Appl Environ Microbiol. 1976 Oct;32(4):592–597. doi: 10.1128/aem.32.4.592-597.1976. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Repaske R., Repaske A. C. Quantitative requirements for exponential growth of Alcaligenes eutrophus. Appl Environ Microbiol. 1976 Oct;32(4):585–591. doi: 10.1128/aem.32.4.585-591.1976. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Schmidhauser T. J., Helinski D. R. Regions of broad-host-range plasmid RK2 involved in replication and stable maintenance in nine species of gram-negative bacteria. J Bacteriol. 1985 Oct;164(1):446–455. doi: 10.1128/jb.164.1.446-455.1985. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Schubert K. R., Evans H. J. Hydrogen evolution: A major factor affecting the efficiency of nitrogen fixation in nodulated symbionts. Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A. 1976 Apr;73(4):1207–1211. doi: 10.1073/pnas.73.4.1207. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Selvaraj G., Iyer V. N. Suicide plasmid vehicles for insertion mutagenesis in Rhizobium meliloti and related bacteria. J Bacteriol. 1983 Dec;156(3):1292–1300. doi: 10.1128/jb.156.3.1292-1300.1983. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Simon R. High frequency mobilization of gram-negative bacterial replicons by the in vitro constructed Tn5-Mob transposon. Mol Gen Genet. 1984;196(3):413–420. doi: 10.1007/BF00436188. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]