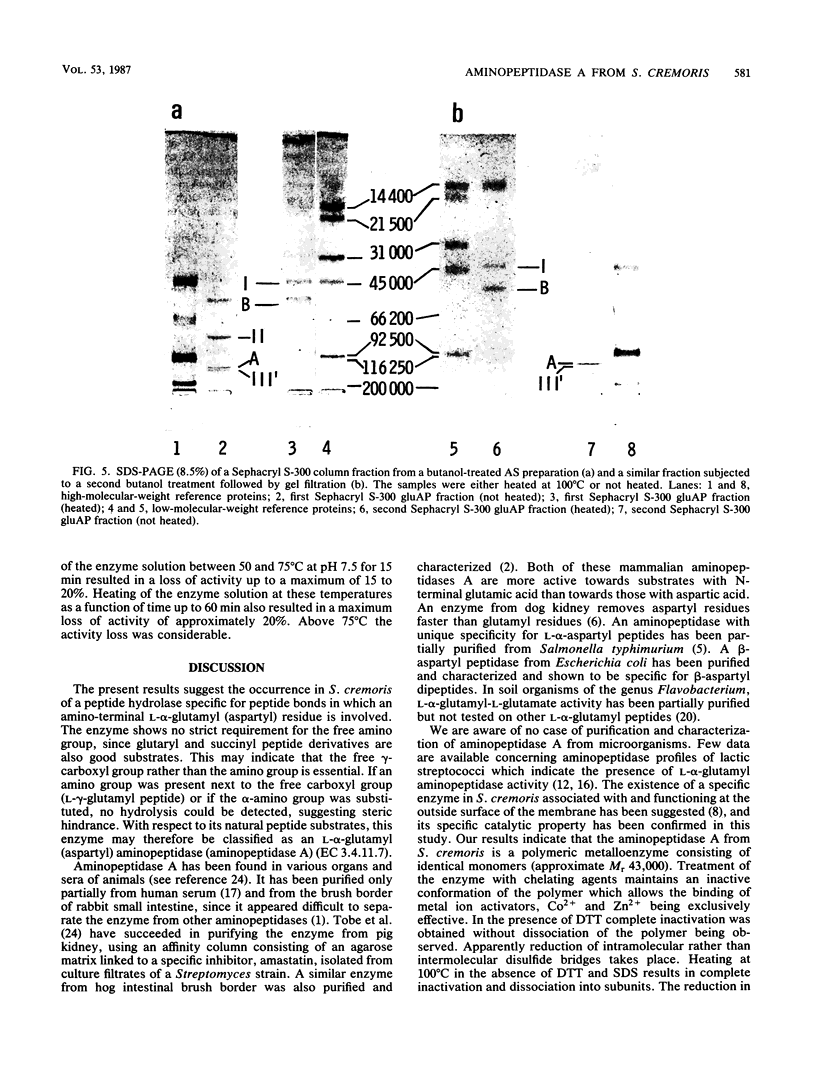
Abstract
A membrane-bound l-α-glutamyl (aspartyl)-peptide hydrolase (aminopeptidase A) (EC 3.4.11.7) from Streptococcus cremoris HP has been purified to homogeneity. The free γ-carboxyl group rather than the amino group of the N-terminal l-α-glutamyl (aspartyl) residue appeared to be essential for catalysis. No endopeptidase activity could be established with this enzyme. The native enzyme is a polymeric, most probably trimeric, metalloenzyme (relative molecular weight, approximately 130,000) which shows on sodium dodecyl sulfate-polyacrylamide gel electrophoresis gels apparent high relative molecular weight values due to (lipid?) material dissociable with butanol. The subunit (relative molecular weight, approximately 43,000) is catalytically inactive. The enzyme is inactivated completely by dithiothreitol, chelating agents, and the bivalent metal ions Cu2+ and Hg2+. Of the sulfhydryl-blocking reagents tested, only p-hydroxymercuribenzoate appeared to inhibit the enzyme. Activity lost by treatment with a chelating agent could be restored by Co2+ and Zn2+. The importance of the occurrence of an aminopeptidase A in S. cremoris with respect to growth in milk is discussed.
Full text
PDF



Images in this article
Selected References
These references are in PubMed. This may not be the complete list of references from this article.
- Andria G., Marzi A., Auricchio S. Alpha-Glutamyl-beta-naphthylamide hydrolase of rabbit small intestine. Localization in the brush border and separation from other brush border peptidases. Biochim Biophys Acta. 1976 Jan 8;419(1):42–50. doi: 10.1016/0005-2736(76)90370-9. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Benajiba A., Maroux S. Purification and characterization of an aminopeptidase A from hog intestinal brush-border membrane. Eur J Biochem. 1980 Jun;107(2):381–388. doi: 10.1111/j.1432-1033.1980.tb06040.x. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Bhown A. S., Mole J. E., Hunter F., Bennett J. C. High-sensitivity sequence determination of proteins quantitatively recovered from sodium dodecyl sulfate gels using an improved electrodialysis procedure. Anal Biochem. 1980 Mar 15;103(1):184–190. doi: 10.1016/0003-2697(80)90254-7. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Bradford M. M. A rapid and sensitive method for the quantitation of microgram quantities of protein utilizing the principle of protein-dye binding. Anal Biochem. 1976 May 7;72:248–254. doi: 10.1016/0003-2697(76)90527-3. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Carter T. H., Miller C. G. Aspartate-specific peptidases in Salmonella typhimurium: mutants deficient in peptidase E. J Bacteriol. 1984 Aug;159(2):453–459. doi: 10.1128/jb.159.2.453-459.1984. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Cheung H. S., Cushman D. W. A soluble aspartate aminopeptidase from dog kidney. Biochim Biophys Acta. 1971 Jul 21;242(1):190–193. doi: 10.1016/0005-2744(71)90098-2. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Exterkate F. A. Location of Peptidases Outside and Inside the Membrane of Streptococcus cremoris. Appl Environ Microbiol. 1984 Jan;47(1):177–183. doi: 10.1128/aem.47.1.177-183.1984. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Exterkate F. A., de Veer G. J. Partial Isolation and Degradation of Caseins by Cell Wall Proteinase(s) of Streptococcus cremoris HP. Appl Environ Microbiol. 1985 Feb;49(2):328–332. doi: 10.1128/aem.49.2.328-332.1985. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Haley E. E. Purification and properties of a beta-aspartyl peptidase from Escherichia coli. J Biol Chem. 1968 Nov 10;243(21):5748–5752. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Kolstad J., Law B. A. Comparative peptide specificity of cell wall, membrane and intracellular peptidases of group N streptococci. J Appl Bacteriol. 1985 May;58(5):449–455. doi: 10.1111/j.1365-2672.1985.tb01484.x. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Nagatsu I., Nagatsu T., Yamamoto T., Glenner G. G., Mehl J. W. Purification of aminopeptidase A in human serum and degradation of angiotensin II by the purified enzyme. Biochim Biophys Acta. 1970 Feb 11;198(2):255–270. doi: 10.1016/0005-2744(70)90058-6. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Pratt A. G., Crawford E. J., Friedkin M. The hydrolysis of mono-, di-, and triglutamate derivatives of folic acid with bacterial enzymes. J Biol Chem. 1968 Dec 25;243(24):6367–6372. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Sullivan J. J., Jago G. R., Mou L. Pptidase activities in group N streptococci. J Dairy Res. 1975 Feb;42(1):147–155. doi: 10.1017/s002202990001517x. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Thomas T. D., Jarvis B. D., Skipper N. A. Localization of proteinase(s) near the cell surface of Streptococcus lactis. J Bacteriol. 1974 May;118(2):329–333. doi: 10.1128/jb.118.2.329-333.1974. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Tobe H., Kojima F., Aoyagi T., Umezawa H. Purification by affinity chromatography using amastatin and properties of aminopeptidase A from pig kidney. Biochim Biophys Acta. 1980 Jun 13;613(2):459–468. doi: 10.1016/0005-2744(80)90100-x. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Weber K., Osborn M. The reliability of molecular weight determinations by dodecyl sulfate-polyacrylamide gel electrophoresis. J Biol Chem. 1969 Aug 25;244(16):4406–4412. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]