Abstract
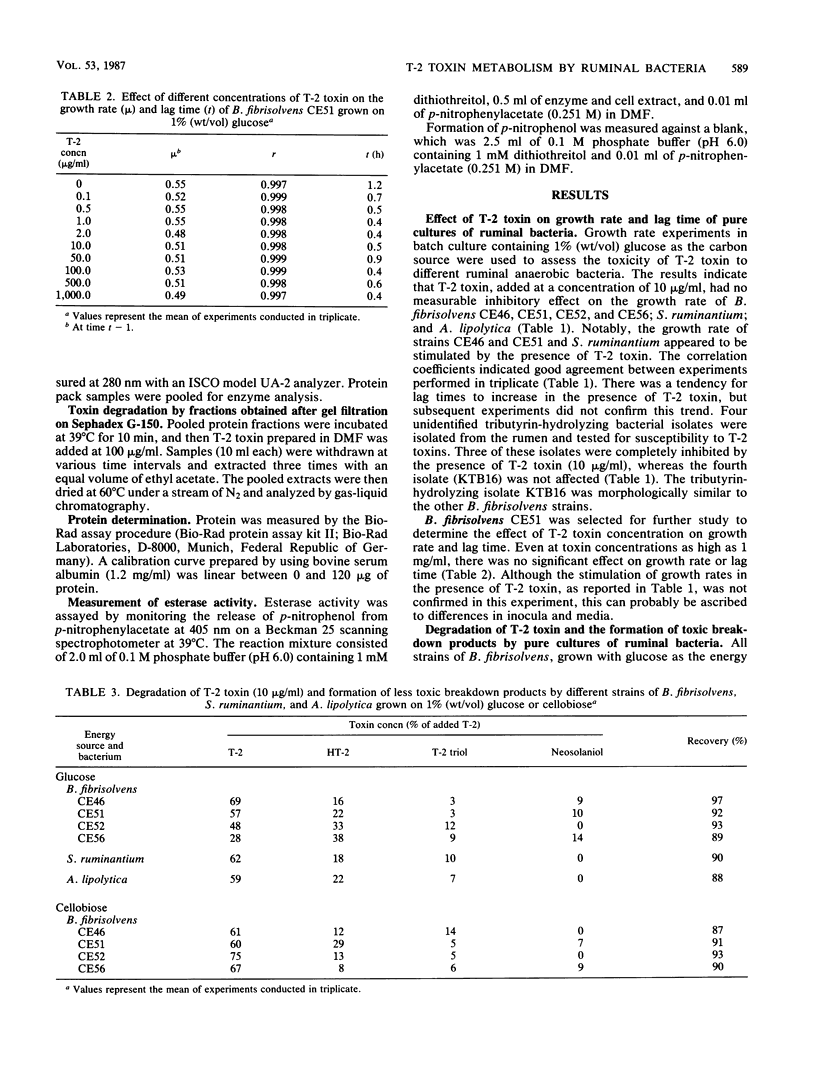
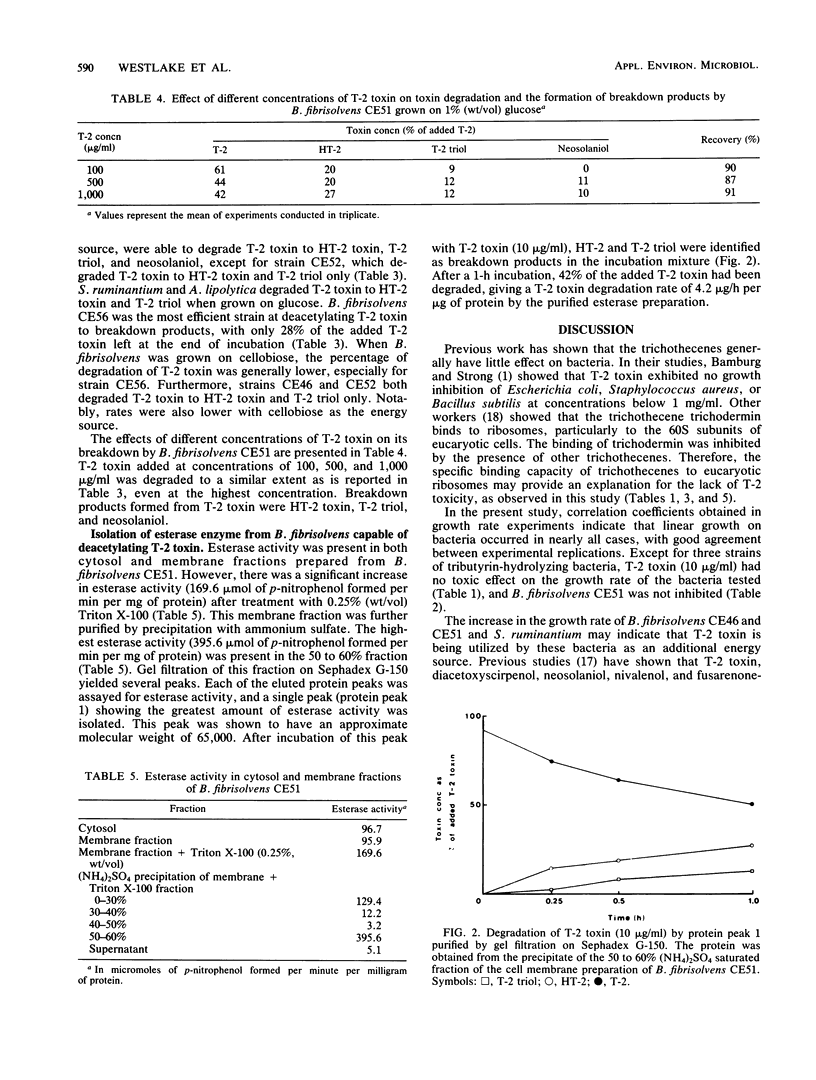
The effect of T-2 toxin on the growth rates of different bacteria was used as a measure of its toxicity. Toxin levels of 10 micrograms/ml did not decrease the growth rate of Selenomonas ruminantium and Anaerovibrio lipolytica, whereas the growth rate of Butyrivibrio fibrisolvens was uninhibited at toxin levels as high as 1 mg/ml. There was, however, a noticeable increase in the growth rate of B. fibrisolvens CE46 and CE51 and S. ruminantium in the presence of low concentrations (10 micrograms/ml) of T-2 toxin, which may indicate the assimilation of the toxin as an energy source by these bacteria. Three tributyrin-hydrolyzing bacterial isolates did not grow at all in the presence of T-2 toxin (10 micrograms/ml). The growth rate of a fourth tributyrin-hydrolyzing bacterial isolate was unaffected. B. fibrisolvens CE51 degraded T-2 toxin to HT-2 toxin (22%), T-2 triol (3%), and neosolaniol (10%), whereas A. lipolytica and S. ruminantium degraded the toxin to HT-2 toxin (22 and 18%, respectively) and T-2 triol (7 and 10%, respectively) only. These results have been explained in terms of the presence of two different toxin-hydrolyzing enzyme systems. Studies with B. fibrisolvens showed the presence of a T-2 toxin-degrading enzyme fraction in a bacterial membrane preparation. This fraction had an approximate molecular weight of 65,000 and showed esterase activity (395.6 mumol of p-nitrophenol formed per min per mg of protein with p-nitrophenylacetate as the substrate.
Full text
PDF



Selected References
These references are in PubMed. This may not be the complete list of references from this article.
- BRYANT M. P., ROBINSON I. M. Some nutritional characteristics of predominant culturable ruminal bacteria. J Bacteriol. 1962 Oct;84:605–614. doi: 10.1128/jb.84.4.605-614.1962. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Henderson C., Hodgkiss W. An electron microscopic study of Anaerovibrio lipolytica (strain 5S) and its lipolytic enzyme. J Gen Microbiol. 1973 Jun;76(2):389–393. doi: 10.1099/00221287-76-2-389. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Hobson P. N., Summers R. Effect of growth rate on the lipase activity of a rumen bacterium. Nature. 1966 Feb 12;209(5024):736–737. doi: 10.1038/209736a0. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Hsu I. C., Smalley E. B., Strong F. M., Ribelin W. E. Identification of T-2 toxin in moldy corn associated with a lethal toxicosis in dairy cattle. Appl Microbiol. 1972 Nov;24(5):684–690. doi: 10.1128/am.24.5.684-690.1972. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Hult K., Teiling A., Gatenbeck S. Degradation of ochratoxin A by a ruminant. Appl Environ Microbiol. 1976 Sep;32(3):443–444. doi: 10.1128/aem.32.3.443-444.1976. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Kiessling K. H., Pettersson H., Sandholm K., Olsen M. Metabolism of aflatoxin, ochratoxin, zearalenone, and three trichothecenes by intact rumen fluid, rumen protozoa, and rumen bacteria. Appl Environ Microbiol. 1984 May;47(5):1070–1073. doi: 10.1128/aem.47.5.1070-1073.1984. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Lanz W. W., Williams P. P. Characterization of esterases produced by a ruminal bacterium identified as Butyrivibrio fibrisolvens. J Bacteriol. 1973 Mar;113(3):1170–1176. doi: 10.1128/jb.113.3.1170-1176.1973. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Shane B. S., Gouws L., Kistner A. Cellulolytic bacteria occurring in the rumen of sheep conditioned to low-protein teff hay. J Gen Microbiol. 1969 Mar;55(3):445–457. doi: 10.1099/00221287-55-3-445. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Ueno Y., Nakayama K., Ishii K., Tashiro F., Minoda Y., Omori T., Komagata K. Metabolism of T-2 toxin in Curtobacterium sp. strain 114-2. Appl Environ Microbiol. 1983 Jul;46(1):120–127. doi: 10.1128/aem.46.1.120-127.1983. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Wei C. M., Campbell I. M., McLaughlin C. S., Vaughan M. H. Letter: Binding of trichodermin to mammalian ribosomes and its inhibition by other 12,13-epoxytrichothecenes. Mol Cell Biochem. 1974 May 30;3(3):215–219. doi: 10.1007/BF01686646. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]


