Abstract
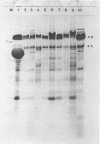
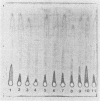
Ten different strains of Aeromonas salmonicida that were isolated from diseased fish were grown under identical conditions (24 h at 25 degree C) in 3% (wt/vol) tryptone soya broth medium supplemented with vitamins and inorganic ions. In each case the extracellular proteins that were formed were compared by sodium dodecyl sulfate-polyacrylamide gel electrophoresis, and it was found that there were two significant common components, one with a molecular weight of 70,000 and the other with a weight of 56,000. Application of enzyme purification techniques to the supernatant fraction proteins of a culture of one of the strains resulted in the isolation of a 70-kilodalton (kDa) component, which was found to be a serine protease, and a 56-kDa component, which was hemolytic to trout erythrocytes. Rocket immunoelectrophoresis with rabbit antibodies to the isolated protease and hemolysin showed the same antigenic components in the supernatant fractions of all the cultures. These activities were assayed, and protease activity was found to vary by a factor of three, from 59 to 195 U/ml, while the range of hemolytic activity was over a narrow band, from 28 to 43 U/ml. There was an inconsistency between the immunoelectrophoretic and direct assay data in only one case. This indicated the presence of additional hemolytic activity, in addition to the 56-kDa component. The detection of large amounts of the same protease and hemolysin, two potent degradative activities, in a random series of strains of A. salmonicida suggests that they may be obligatory virulence factors in the development of furunculosis.
Full text
PDF


Images in this article
Selected References
These references are in PubMed. This may not be the complete list of references from this article.
- Abbas-ali B., Coleman G. The characteristics of extracellular protein secretion by Staphylococcus aureus (Wood 46) and their relationship to the regulation of alpha-toxin formation. J Gen Microbiol. 1977 Apr;99(2):277–282. doi: 10.1099/00221287-99-2-277. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- BERNHEIMER A. W., SCHWARTZ L. L. Isolation and composition of staphylococcal alpha toxin. J Gen Microbiol. 1963 Mar;30:455–468. doi: 10.1099/00221287-30-3-455. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Buckley J. T., Halasa L. N., MacIntyre S. Purification and partial characterization of a bacterial phospholipid: cholesterol acyltransferase. J Biol Chem. 1982 Mar 25;257(6):3320–3325. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Dahle H. K. The purification and some properties of two Aeromonas proteinases. Acta Pathol Microbiol Scand B Microbiol Immunol. 1971;79(6):726–738. doi: 10.1111/j.1699-0463.1971.tb00104.x. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Laemmli U. K. Cleavage of structural proteins during the assembly of the head of bacteriophage T4. Nature. 1970 Aug 15;227(5259):680–685. doi: 10.1038/227680a0. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Mackman N., Holland I. B. Secretion of a 107 K dalton polypeptide into the medium from a haemolytic E. coli K12 strain. Mol Gen Genet. 1984;193(2):312–315. doi: 10.1007/BF00330686. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Mellergaard S. Purification and characterization of a new proteolytic enzyme produced by Aeromonas salmonicida. J Appl Bacteriol. 1983 Apr;54(2):289–294. doi: 10.1111/j.1365-2672.1983.tb02619.x. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- RAPPAPORT H. P., RIGGSBY W. S., HOLDEN D. A. A BACILLUS SUBTILIS PROTEINASE. I. PRODUCTION, PURIFICATION, AND CHARACTERIZATION OF A PROTEINASE FROM A TRANSFORMABLE STRAIN OF BACILLUS SUBTILIS. J Biol Chem. 1965 Jan;240:78–86. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Titball R. W., Munn C. B. The purification and some properties of H-lysin from Aeromonas salmonicida. J Gen Microbiol. 1985 Jul;131(7):1603–1609. doi: 10.1099/00221287-131-7-1603. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]