Abstract
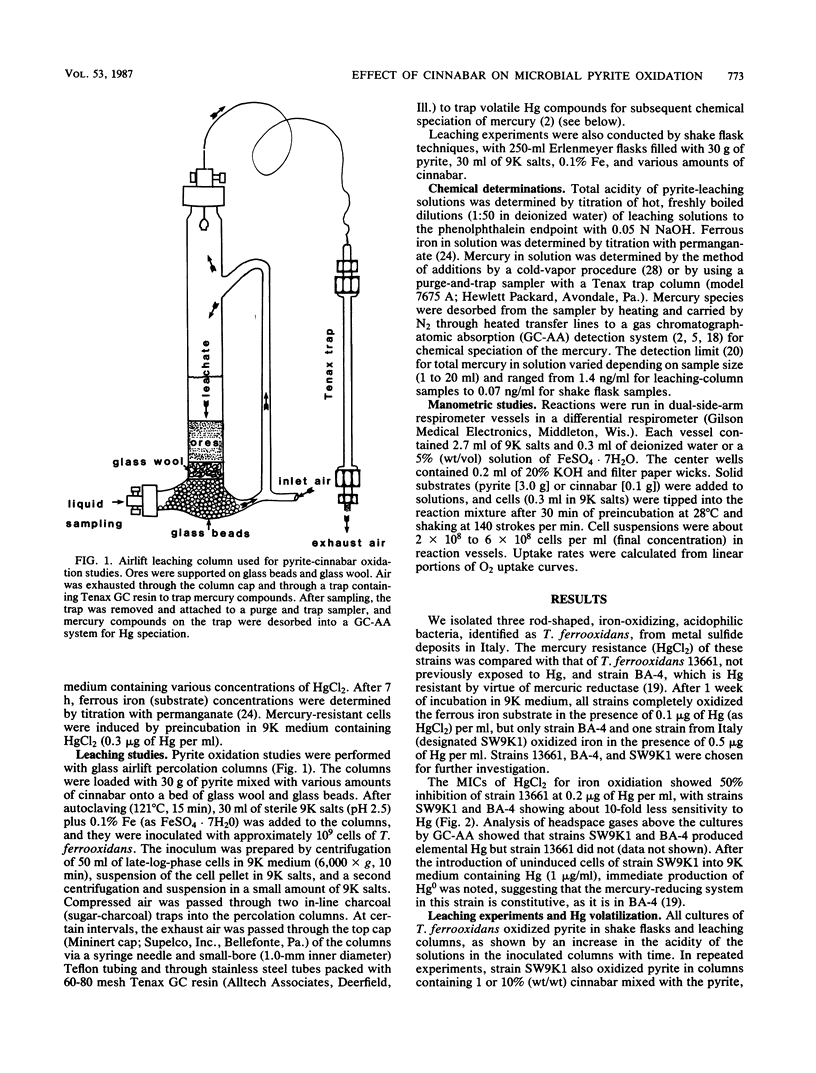
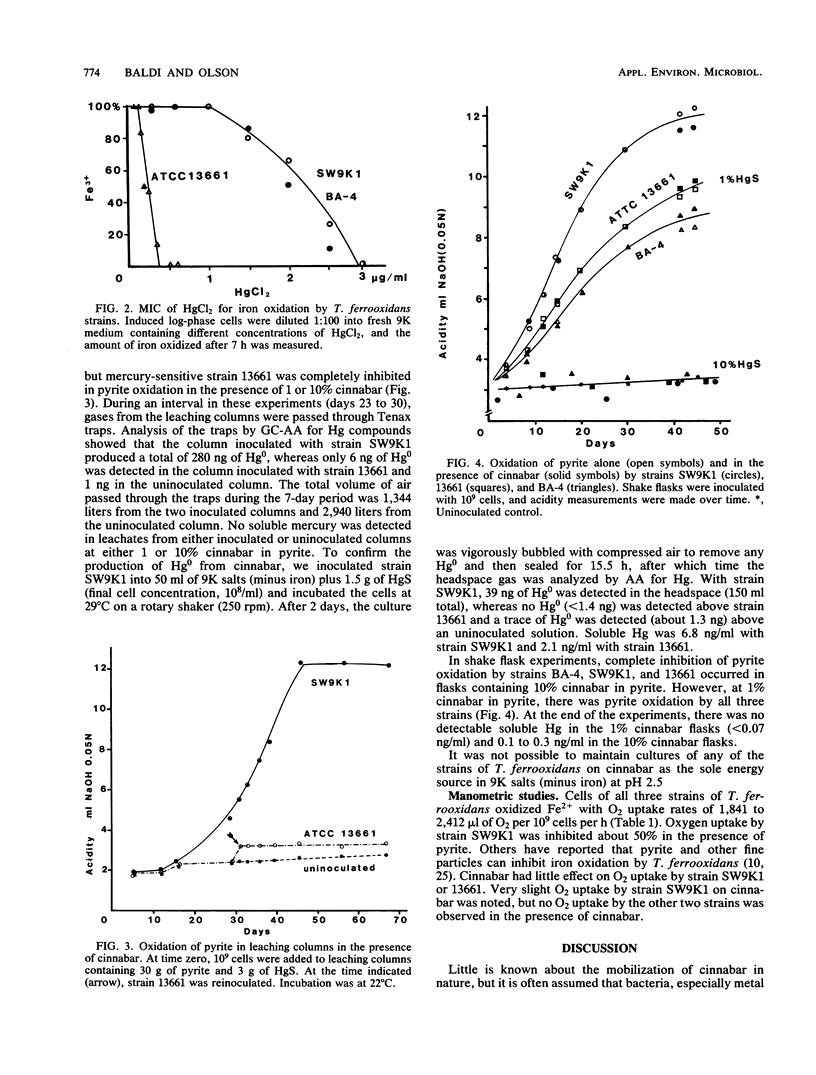
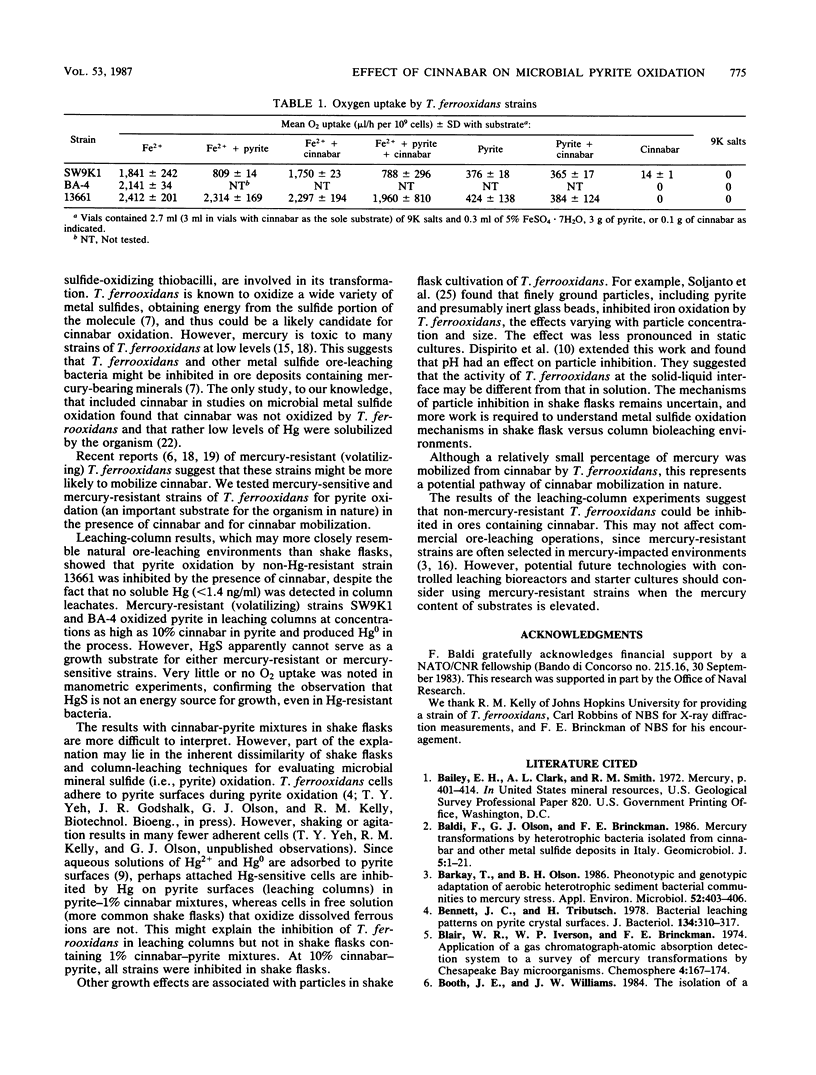
The effect of cinnabar on pyrite oxidation by mercury-sensitive and mercury-resistant strains of Thiobacillus ferrooxidans was investigated by using percolation columns. Mercury-resistant strains oxidized pyrite in pyrite-cinnabar mixtures (1 and 10%, wt/wt), whereas a mercury-sensitive strain did not. Elemental mercury was produced by the mercury-resistant strains growing in the pyrite-cinnabar mixtures in percolation columns and in flasks containing cinnabar only. Manometric experiments showed that cinnabar had little effect on oxygen uptake of mercury-sensitive or mercury-resistant cells growing on ferrous sulfate, pyrite, or pyrite-ferrous sulfate mixtures. In addition, shake flask leaching experiments showed that cinnabar had little effect on pyrite oxidation at 1% (wt/wt) but inhibited growth of mercury-sensitive and mercury-resistant strains at 10%. Mercury-resistant strains were unable to grow on cinnabar as an energy source.
Full text
PDF

Selected References
These references are in PubMed. This may not be the complete list of references from this article.
- Barkay T., Olson B. H. Phenotypic and genotypic adaptation of aerobic heterotrophic sediment bacterial communities to mercury stress. Appl Environ Microbiol. 1986 Aug;52(2):403–406. doi: 10.1128/aem.52.2.403-406.1986. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Bennett J. C., Tributsch H. Bacterial leaching patterns on pyrite crystal surfaces. J Bacteriol. 1978 Apr;134(1):310–317. doi: 10.1128/jb.134.1.310-317.1978. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Brierley C. L. Bacterial leaching. CRC Crit Rev Microbiol. 1978;6(3):207–26I. doi: 10.3109/10408417809090623. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Harrison A. P., Jr The acidophilic thiobacilli and other acidophilic bacteria that share their habitat. Annu Rev Microbiol. 1984;38:265–292. doi: 10.1146/annurev.mi.38.100184.001405. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Khesin R. B., Karasyova E. V. Mercury-resistant plasmids in bacteria from a mercury and antimony deposit area. Mol Gen Genet. 1984;197(2):280–285. doi: 10.1007/BF00330974. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Manning H. L. New medium for isolating iron-oxidizing and heterotrophic acidophilic bacteria from acid mine drainage. Appl Microbiol. 1975 Dec;30(6):1010–1016. doi: 10.1128/am.30.6.1010-1016.1975. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Olson G. J., Porter F. D., Rubinstein J., Silver S. Mercuric reductase enzyme from a mercury-volatilizing strain of Thiobacillus ferrooxidans. J Bacteriol. 1982 Sep;151(3):1230–1236. doi: 10.1128/jb.151.3.1230-1236.1982. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Parris G. E., Blair W. R., Brinckman F. E. Chemical and physical consideration in the use of atomic absorption detectors coupled with a gas chromatograph for determination of trace organometallic gases. Anal Chem. 1977 Mar;49(3):378–386. doi: 10.1021/ac50011a014. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Robinson J. B., Tuovinen O. H. Mechanisms of microbial resistance and detoxification of mercury and organomercury compounds: physiological, biochemical, and genetic analyses. Microbiol Rev. 1984 Jun;48(2):95–124. doi: 10.1128/mr.48.2.95-124.1984. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- SILVERMAN M. P., LUNDGREN D. G. Studies on the chemoautotrophic iron bacterium Ferrobacillus ferrooxidans. I. An improved medium and a harvesting procedure for securing high cell yields. J Bacteriol. 1959 May;77(5):642–647. doi: 10.1128/jb.77.5.642-647.1959. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Silver M., Torma A. E. Oxidation of metal sulfides by Thiobacillus ferrooxidans grown on different substrates. Can J Microbiol. 1974 Feb;20(2):141–147. doi: 10.1139/m74-023. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]



