Abstract
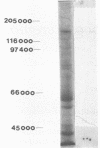
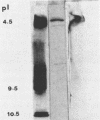
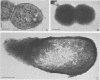
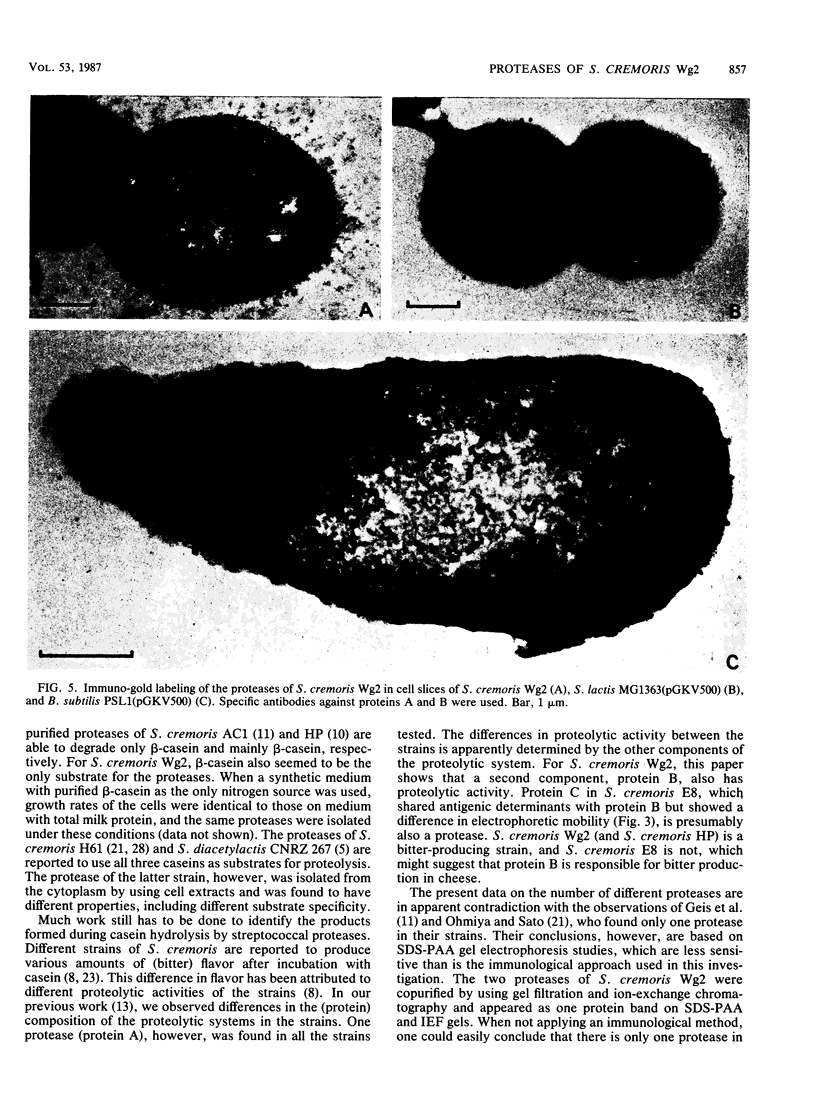
Two components of the proteolytic system, proteins A and B (J. Hugenholtz, F. Exterkate, and W. N. Konings, Appl. Environ. Microbiol. 48:1105-1110, 1984), have been studied in Streptococcus cremoris Wg2 by immunological methods. The components could not be separated by standard chromatography techniques because both proteins had almost identical molecular weights (about 140,000) and isoelectric points (pH 4.5). Specific antibodies were raised against proteins A and B by excision of the different immunoprecipitates from crossed immunoelectrophoresis gels. With these antibodies, protein A or B was removed from solutions containing both proteins. The purified proteins A and B possessed proteolytic activity and were inhibited by the serine protease inhibitor phenylmethylsulfonyl fluoride. Each of these proteins accounted for approximately 50% of the total proteolytic activity isolated from S. cremoris Wg2. The specific antibodies against the proteases were also used for immuno-gold labeling studies. The proteases were clearly seen to be located at the outside of the cell wall. The proteases had the same location when the genetic information coding for the proteases was cloned in Streptococcus lactis and Bacillus subtilis.
Full text
PDF




Images in this article
Selected References
These references are in PubMed. This may not be the complete list of references from this article.
- Elferink M. G., Hellingwerf K. J., Michels P. A., Seÿen H. G., Konings W. N. Immunochemical analysis of membrane vesicles and chromatophoresis of Rhodopseudomonas sphaeroides by crossed immunoelectrophoresis. FEBS Lett. 1979 Nov 15;107(2):300–307. doi: 10.1016/0014-5793(79)80395-6. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Exterkate F. A., de Veer G. J. Partial Isolation and Degradation of Caseins by Cell Wall Proteinase(s) of Streptococcus cremoris HP. Appl Environ Microbiol. 1985 Feb;49(2):328–332. doi: 10.1128/aem.49.2.328-332.1985. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Hugenholtz J., Exterkate F., Konings W. N. The Proteolytic Systems of Streptococcus cremoris: an Immunological Analysis. Appl Environ Microbiol. 1984 Dec;48(6):1105–1110. doi: 10.1128/aem.48.6.1105-1110.1984. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Hugenholtz J., Veldkamp H., Konings W. N. Detection of Specific Strains and Variants of Streptococcus cremoris in Mixed Cultures by Immunofluorescence. Appl Environ Microbiol. 1987 Jan;53(1):149–155. doi: 10.1128/aem.53.1.149-155.1987. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Kikuchi T., Bergère J. L., Desmazeaud M. J. Aptitude des streptocoques lactiques a la protéolyse. II. Etude de l'action du système protéolytique de Streptococcus lactis sur la caséine entière. Ann Biol Anim Biochim Biophys. 1974;14(2):313–326. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Kok J., van Dijl J. M., van der Vossen J. M., Venema G. Cloning and expression of a Streptococcus cremoris proteinase in Bacillus subtilis and Streptococcus lactis. Appl Environ Microbiol. 1985 Jul;50(1):94–101. doi: 10.1128/aem.50.1.94-101.1985. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- LOWRY O. H., ROSEBROUGH N. J., FARR A. L., RANDALL R. J. Protein measurement with the Folin phenol reagent. J Biol Chem. 1951 Nov;193(1):265–275. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Laemmli U. K., Favre M. Maturation of the head of bacteriophage T4. I. DNA packaging events. J Mol Biol. 1973 Nov 15;80(4):575–599. doi: 10.1016/0022-2836(73)90198-8. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Law B. A., Kolstad J. Proteolytic systems in lactic acid bacteria. Antonie Van Leeuwenhoek. 1983 Sep;49(3):225–245. doi: 10.1007/BF00399500. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Ohmiya K., Sato Y. Purification and Properties of Intracellular Proteinase from Streptococcus cremoris. Appl Microbiol. 1975 Nov;30(5):738–745. doi: 10.1128/am.30.5.738-745.1975. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Otto R., de Vos W. M., Gavrieli J. Plasmid DNA in Streptococcus cremoris Wg2: Influence of pH on Selection in Chemostats of a Variant Lacking a Protease Plasmid. Appl Environ Microbiol. 1982 Jun;43(6):1272–1277. doi: 10.1128/aem.43.6.1272-1277.1982. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Sogawa K., Takahashi K. Use of fluorescamine-labeled casein as a substrate for assay of proteinases. J Biochem. 1978 Jun;83(6):1783–1787. doi: 10.1093/oxfordjournals.jbchem.a132094. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Sorrells K. M., Cowman R. A., Swaisgood H. E. Hydrolysis of alpha(s, 1)-Casein B by Streptococcus lactis Membrane Proteinase. J Bacteriol. 1972 Oct;112(1):474–479. doi: 10.1128/jb.112.1.474-479.1972. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Thomas T. D., Jarvis B. D., Skipper N. A. Localization of proteinase(s) near the cell surface of Streptococcus lactis. J Bacteriol. 1974 May;118(2):329–333. doi: 10.1128/jb.118.2.329-333.1974. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Wray W., Boulikas T., Wray V. P., Hancock R. Silver staining of proteins in polyacrylamide gels. Anal Biochem. 1981 Nov 15;118(1):197–203. doi: 10.1016/0003-2697(81)90179-2. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- van der Plas J., Hellingwerf K. J., Seijen H. G., Guest J. R., Weiner J. H., Konings W. N. Identification and localization of enzymes of the fumarate reductase and nitrate respiration systems of escherichia coli by crossed immunoelectrophoresis. J Bacteriol. 1983 Feb;153(2):1027–1037. doi: 10.1128/jb.153.2.1027-1037.1983. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]