Abstract
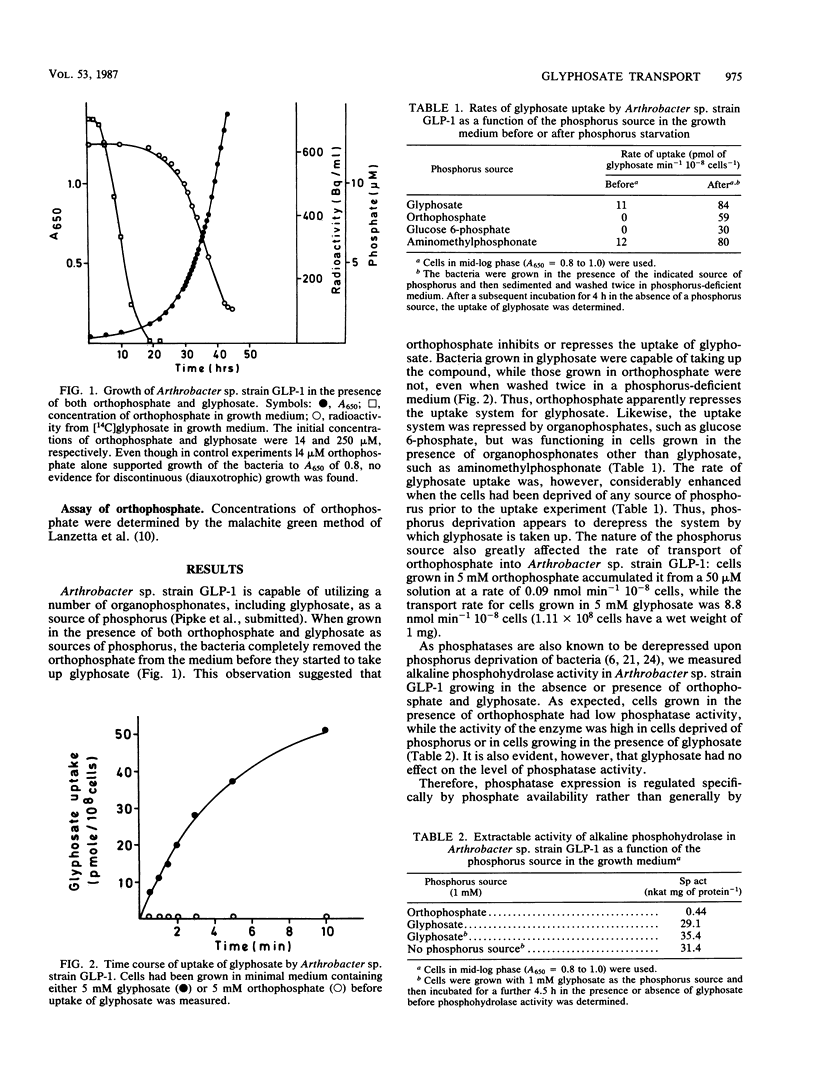
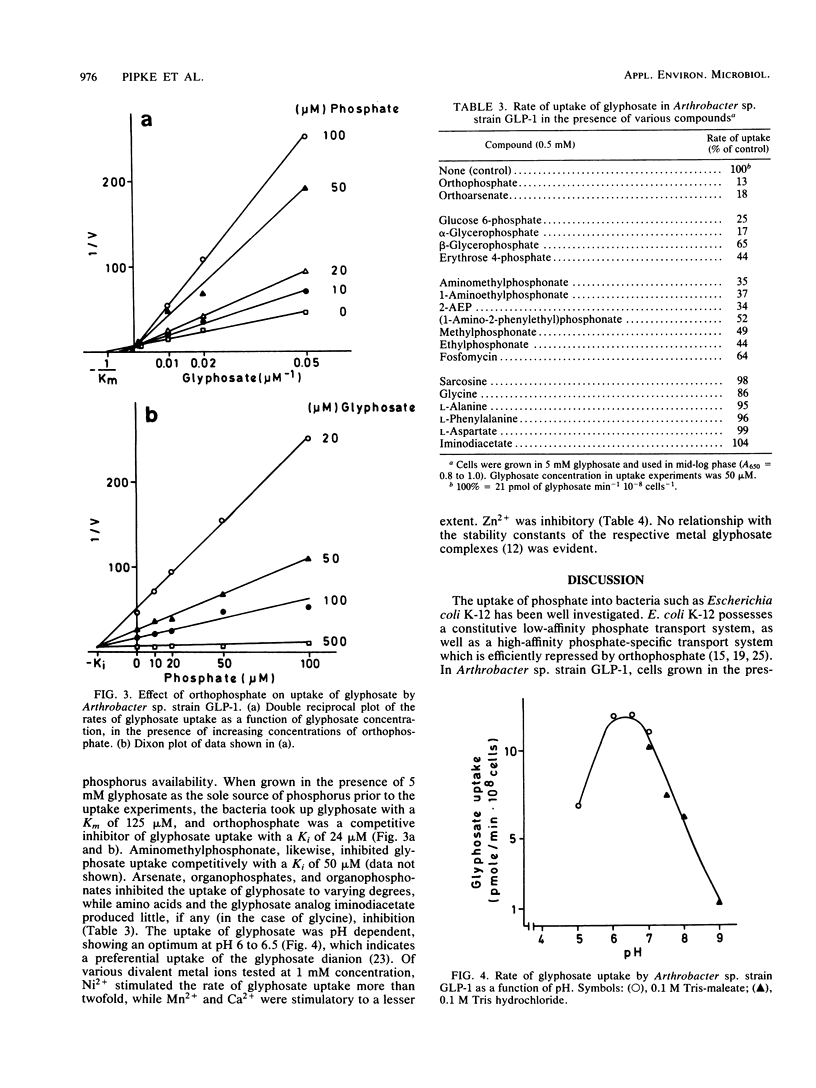
The uptake of glyphosate (N-[phosphonomethyl]glycine) by an Arthrobacter sp. which can utilize this herbicide as its sole source of phosphorus was investigated. Orthophosphate suppressed the expression of the uptake system for glyphosate and also competed with glyphosate for uptake. The Km for glyphosate uptake was 125 μM, and the Ki for orthophosphate was 24 μM. Organophosphonates as well as organophosphates inhibited glyphosate uptake, but only organophosphates and orthophosphate suppressed the uptake system. Glyphosate uptake was energy dependent, had a pH optimum of 6 to 7, and was differentially affected by divalent cations.
Full text
PDF


Selected References
These references are in PubMed. This may not be the complete list of references from this article.
- Balthazor T. M., Hallas L. E. Glyphosate-degrading microorganisms from industrial activated sludge. Appl Environ Microbiol. 1986 Feb;51(2):432–434. doi: 10.1128/aem.51.2.432-434.1986. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Brecke B. J., Duke W. B. Effect of Glyphosate on Intact Bean Plants (Phaseolus vulgaris L.) and Isolated Cells. Plant Physiol. 1980 Oct;66(4):656–659. doi: 10.1104/pp.66.4.656. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Gougler J. A., Geiger D. R. Uptake and distribution of N-phosphonomethylglycine in sugar beet plants. Plant Physiol. 1981 Sep;68(3):668–672. doi: 10.1104/pp.68.3.668. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- HORIUCHI T., HORIUCHI S., MIZUNO D. A possible negative feedback phenomenon controlling formation of alkaline phosphomonoesterase in Escherichia coli. Nature. 1959 May 30;183(4674):1529–1530. doi: 10.1038/1831529b0. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Holden J. T., Van Balgooy J. N., Kittredge J. S. Transport of aminophosphonic acids in Lactobacillus plantarum and Streptococcus faecalis. J Bacteriol. 1968 Oct;96(4):950–957. doi: 10.1128/jb.96.4.950-957.1968. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Jacob G. S., Schaefer J., Stejskal E. O., McKay R. A. Solid-state NMR determination of glyphosate metabolism in a Pseudomonas sp. J Biol Chem. 1985 May 25;260(10):5899–5905. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Lacoste A. M., Cassaigne A., Tamari M., Neuzil E. Transport de l'acide amino-2-éthylphosphonique chez Pseudomonas aeruginosa. Biochimie. 1976;58(6):703–712. doi: 10.1016/s0300-9084(76)80395-1. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Lanzetta P. A., Alvarez L. J., Reinach P. S., Candia O. A. An improved assay for nanomole amounts of inorganic phosphate. Anal Biochem. 1979 Nov 15;100(1):95–97. doi: 10.1016/0003-2697(79)90115-5. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Moore J. K., Braymer H. D., Larson A. D. Isolation of a Pseudomonas sp. Which Utilizes the Phosphonate Herbicide Glyphosate. Appl Environ Microbiol. 1983 Aug;46(2):316–320. doi: 10.1128/aem.46.2.316-320.1983. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Nafziger E. D., Widholm J. M., Steinrücken H. C., Killmer J. L. Selection and characterization of a carrot cell line tolerant to glyphosate. Plant Physiol. 1984 Nov;76(3):571–574. doi: 10.1104/pp.76.3.571. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Piperno J. R., Oxender D. L. Amino acid transport systems in Escherichia coli K-12. J Biol Chem. 1968 Nov 25;243(22):5914–5920. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Rosenberg H., Gerdes R. G., Chegwidden K. Two systems for the uptake of phosphate in Escherichia coli. J Bacteriol. 1977 Aug;131(2):505–511. doi: 10.1128/jb.131.2.505-511.1977. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Rosenberg H., La Nauze J. M. The metabolism of phosphonates by microorganisms. The transport of aminoethylphosphonic acid in Bacillus cereus. Biochim Biophys Acta. 1967 Jun 13;141(1):79–90. doi: 10.1016/0304-4165(67)90247-4. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Shinabarger D. L., Schmitt E. K., Braymer H. D., Larson A. D. Phosphonate Utilization by the Glyphosate-Degrading Pseudomonas sp. Strain PG2982. Appl Environ Microbiol. 1984 Nov;48(5):1049–1050. doi: 10.1128/aem.48.5.1049-1050.1984. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Steinrücken H. C., Amrhein N. 5-Enolpyruvylshikimate-3-phosphate synthase of Klebsiella pneumoniae. 1. Purification and properties. Eur J Biochem. 1984 Sep 3;143(2):341–349. doi: 10.1111/j.1432-1033.1984.tb08378.x. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Surin B. P., Rosenberg H., Cox G. B. Phosphate-specific transport system of Escherichia coli: nucleotide sequence and gene-polypeptide relationships. J Bacteriol. 1985 Jan;161(1):189–198. doi: 10.1128/jb.161.1.189-198.1985. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- TORRIANI A. Influence of inorganic phosphate in the formation of phosphatases by Escherichia coli. Biochim Biophys Acta. 1960 Mar 11;38:460–469. doi: 10.1016/0006-3002(60)91281-6. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Willsky G. R., Bennett R. L., Malamy M. H. Inorganic phosphate transport in Escherichia coli: involvement of two genes which play a role in alkaline phosphatase regulation. J Bacteriol. 1973 Feb;113(2):529–539. doi: 10.1128/jb.113.2.529-539.1973. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Willsky G. R., Malamy M. H. Characterization of two genetically separable inorganic phosphate transport systems in Escherichia coli. J Bacteriol. 1980 Oct;144(1):356–365. doi: 10.1128/jb.144.1.356-365.1980. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]



