Abstract
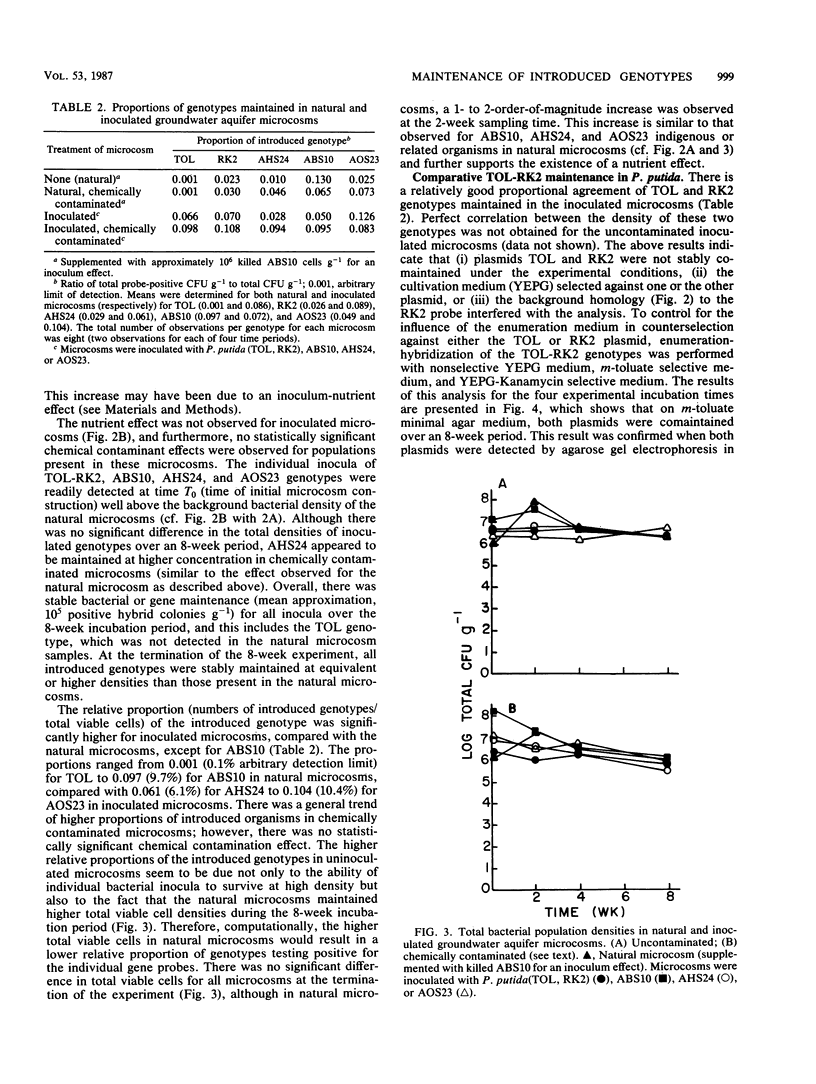
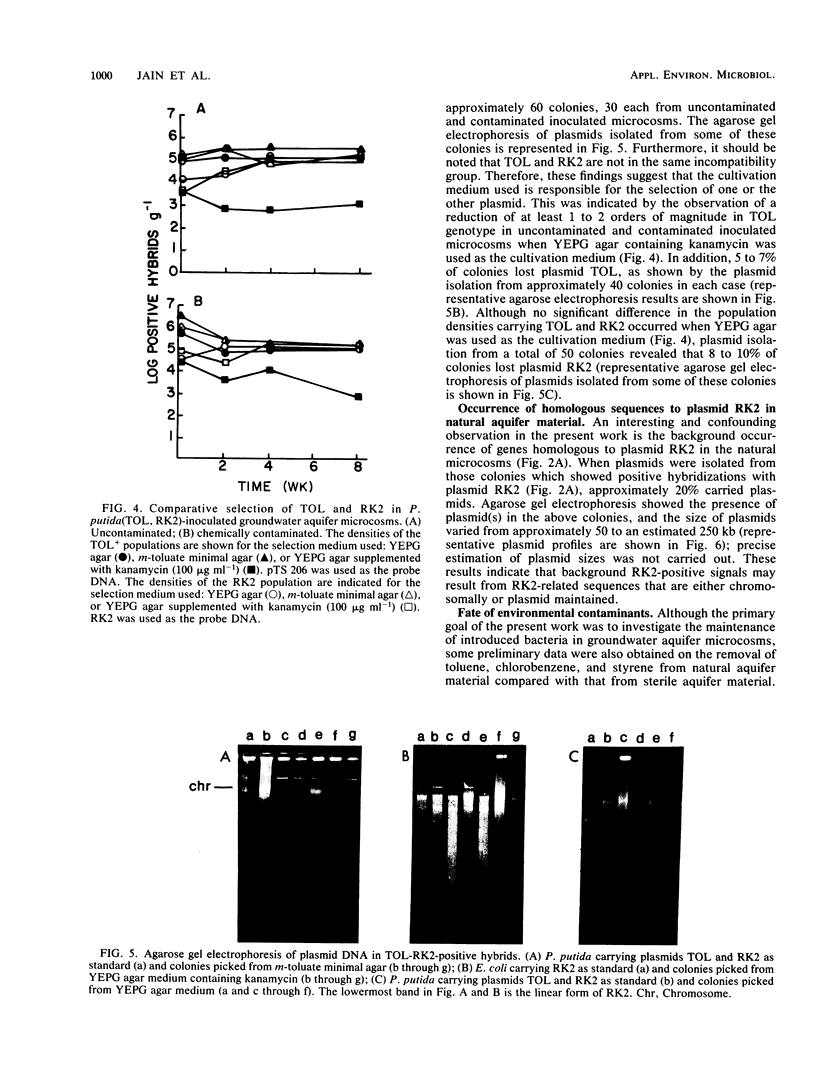
Three indigenous groundwater bacterial strains and Pseudomonas putida harboring plasmids TOL (pWWO) and RK2 were introduced into experimentally contaminated groundwater aquifer microcosms. Maintenance of the introduced genotypes was measured over time by colony hybridization with gene probes of various specificity. On the basis of the results of colony hybridization quantitation of the introduced organisms and genes, all introduced genotypes were stably maintained at approximately 10(5) positive hybrid colonies g-1 of aquifer microcosm material throughout an 8-week incubation period. Concomitant removal of the environmental contaminants, viz., toluene, chlorobenzene, and styrene, in both natural (uninoculated) and inoculated aquifer microcosms was also demonstrated. The results indicate that introduced catabolic plasmids, as well as indigenous organisms, can be stably maintained in groundwater aquifer material without specific selective pressure for the introduced genotypes. These results have positive implications for in situ treatment and biodegradation in contaminated aerobic groundwater aquifers.
Full text
PDF




Images in this article
Selected References
These references are in PubMed. This may not be the complete list of references from this article.
- Anderson D. G., McKay L. L. Simple and rapid method for isolating large plasmid DNA from lactic streptococci. Appl Environ Microbiol. 1983 Sep;46(3):549–552. doi: 10.1128/aem.46.3.549-552.1983. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Hanahan D., Meselson M. Plasmid screening at high colony density. Gene. 1980 Jun;10(1):63–67. doi: 10.1016/0378-1119(80)90144-4. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Hegeman G. D. Synthesis of the enzymes of the mandelate pathway by Pseudomonas putida. I. Synthesis of enzymes by the wild type. J Bacteriol. 1966 Mar;91(3):1140–1154. doi: 10.1128/jb.91.3.1140-1154.1966. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Inouye S., Nakazawa A., Nakazawa T. Determination of the transcription initiation site and identification of the protein product of the regulatory gene xylR for xyl operons on the TOL plasmid. J Bacteriol. 1985 Sep;163(3):863–869. doi: 10.1128/jb.163.3.863-869.1985. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Kado C. I., Liu S. T. Rapid procedure for detection and isolation of large and small plasmids. J Bacteriol. 1981 Mar;145(3):1365–1373. doi: 10.1128/jb.145.3.1365-1373.1981. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Kahn M., Kolter R., Thomas C., Figurski D., Meyer R., Remaut E., Helinski D. R. Plasmid cloning vehicles derived from plasmids ColE1, F, R6K, and RK2. Methods Enzymol. 1979;68:268–280. doi: 10.1016/0076-6879(79)68019-9. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Miki T., Kumahara H., Nakazawa A. Constriction of a fused operon consisting of the recA and kan (kanamycin resistance) genes and regulation of its expression by the lexA gene. Mol Gen Genet. 1981;183(1):25–31. doi: 10.1007/BF00270133. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Sayler G. S., Lund L. C., Shiaris M. P., Sherrill T. W., Perkins R. E. Comparative effects of Aroclor 1254 (polychlorinated biphenyls) and phenanthrene on glucose uptake by freshwater microbial populations. Appl Environ Microbiol. 1979 May;37(5):878–885. doi: 10.1128/aem.37.5.878-885.1979. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Sayler G. S., Shields M. S., Tedford E. T., Breen A., Hooper S. W., Sirotkin K. M., Davis J. W. Application of DNA-DNA colony hybridization to the detection of catabolic genotypes in environmental samples. Appl Environ Microbiol. 1985 May;49(5):1295–1303. doi: 10.1128/aem.49.5.1295-1303.1985. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Thomas C. M., Smith C. A., Shingler V., Cross M. A., Hussain A. A., Pinkney M. Regulation of replication and maintenance functions of broad host-range plasmid RK2. Basic Life Sci. 1985;30:261–276. doi: 10.1007/978-1-4613-2447-8_21. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Vieira J., Messing J. The pUC plasmids, an M13mp7-derived system for insertion mutagenesis and sequencing with synthetic universal primers. Gene. 1982 Oct;19(3):259–268. doi: 10.1016/0378-1119(82)90015-4. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]




