Abstract
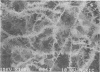
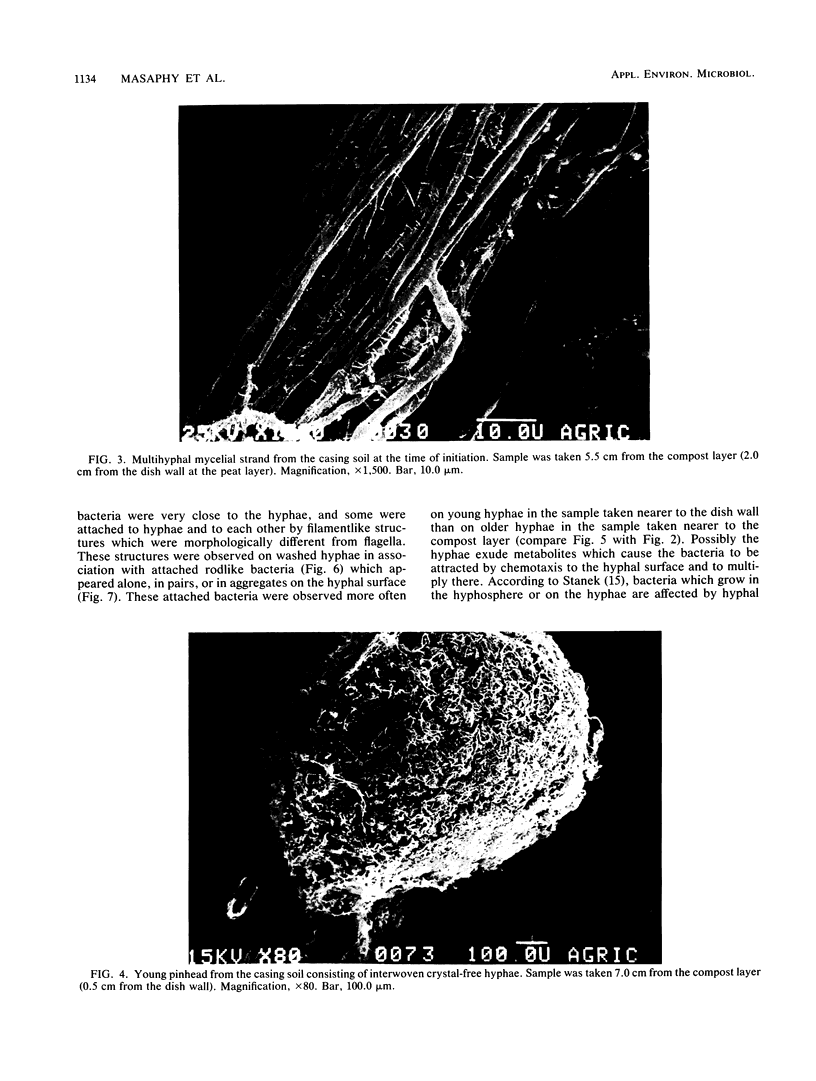
Relationships between the hyphae of Agaricus bisporus (Lang) Sing and bacteria from the mushroom bed casing layer were examined with a scanning electron microscope. Hyphae growing in the casing layer differed morphologically from compost-grown hyphae. Whereas the compost contained thin single hyphae surrounded by calcium oxalate crystals, the casing layer contained mainly wide hyphae or mycelial strands without crystals. The bacterial population in the hyphal environment consisted of several types, some attached to the hyphae with filamentlike structures. This attachment may be important in stimulation of pinhead initiation.
Full text
PDF




Images in this article
Selected References
These references are in PubMed. This may not be the complete list of references from this article.
- Ayers W. A. Induction of sporangia in Phytophthora cinnamomi by a substance from bacteria and soil. Can J Microbiol. 1971 Dec;17(12):1517–1523. doi: 10.1139/m71-242. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Henis Y., Inbar M. Effect of Bacillus subtilis on growth and sclerotium formation by Rhizoctonia solani. Phytopathology. 1968 Jul;58(7):933–938. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Pentland G. D. Ethanol produced by Aureobasidium pullulans and its effect on the growth of Armillaria mellea. Can J Microbiol. 1967 Dec;13(12):1631–1639. doi: 10.1139/m67-213. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]