Abstract
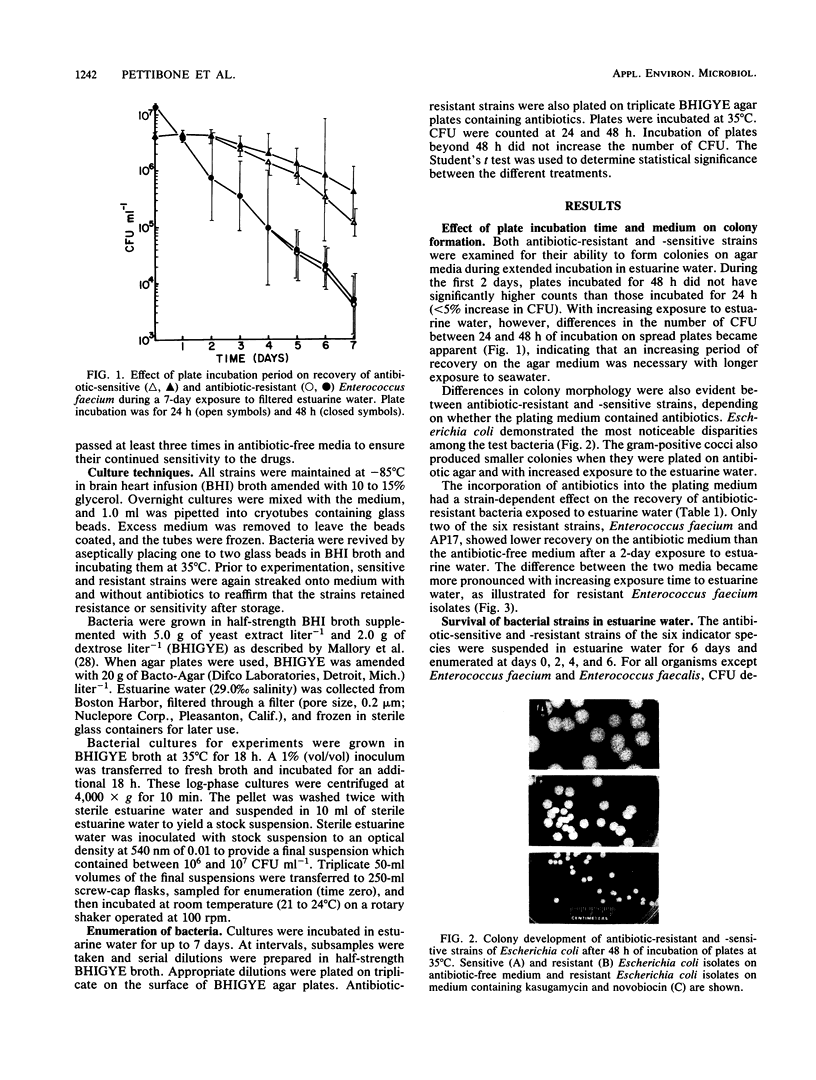
The survival of antibiotic-resistant and -sensitive strains of Escherichia coli, Enterococcus faecalis, Enterococcus faecium, Streptococcus equinus, and two environmental isolates, AP17 and AQ62, was examined in estuarine water. Each strain was rendered resistant to a combination of two antibiotics by serial passage in increasing concentrations of antibiotics. Cultures were incubated in filter-sterilized estuarine water for up to 7 days. Recovery was assessed by examining colony-forming ability on media with and without antibiotics. None of the antibiotic-resistant forms survived longer than its antibiotic-sensitive counterpart in estuarine water. Three of the resistant strains died off more rapidly than the antibiotic-sensitive wild type. Survival of the test bacteria in estuarine water was as follows: sensitive and resistant AQ62, resistant Escherichia coli less than sensitive Escherichia coli less than resistant AP17 less than resistant Enterococcus faecium less than sensitive AP17, sensitive and resistant S. equinus less than sensitive and resistant Enterococcus faecalis, sensitive Enterococcus faecium. The results supported the suggestion that fecal entercocci may serve as better indicators of fecal pollution than Escherichia coli in marine ecosystems. Moreover, the results indicated that the use of antibiotic-resistant mutants to follow the fate of bacteria in the environment is inappropriate without adequate studies to ensure that resistant and wild-type strains react similarly to environmental stressors.
Full text
PDF



Images in this article
Selected References
These references are in PubMed. This may not be the complete list of references from this article.
- Auban E. G., Ripolles A. A., Domarco M. J. Relative frequencies and significance of faecal coliforms as indicators related to water temperature. Zentralbl Mikrobiol. 1983;138(5):329–336. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Baross J. A., Hanus F. J., Morita R. Y. Survival of human enteric and other sewage microorganisms under simulated deep-sea conditions. Appl Microbiol. 1975 Aug;30(2):309–318. doi: 10.1128/am.30.2.309-318.1975. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- CARLUCCI A. F., PRAMER D. An evaluation of factors affecting the survival of Escherichia coli in sea water. II. Salinity, pH, and nutrients. Appl Microbiol. 1960 Jul;8:247–250. doi: 10.1128/am.8.4.247-250.1960. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Camper A. K., McFeters G. A. Chlorine injury and the enumeration of waterborne coliform bacteria. Appl Environ Microbiol. 1979 Mar;37(3):633–641. doi: 10.1128/aem.37.3.633-641.1979. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Carney J. F., Carty C. E., Colwell R. R. Seasonal occurrence and distribution of microbial indicators and pathogens in the Rhode River of Chesapeake Bay. Appl Microbiol. 1975 Nov;30(5):771–780. doi: 10.1128/am.30.5.771-780.1975. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Danso S. K., Habte M., Alexander M. Estimating the density of individual bacterial populations introduced into natural ecosytems. Can J Microbiol. 1973 Nov;19(11):1450–1451. doi: 10.1139/m73-234. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Domek M. J., LeChevallier M. W., Cameron S. C., McFeters G. A. Evidence for the role of copper in the injury process of coliform bacteria in drinking water. Appl Environ Microbiol. 1984 Aug;48(2):289–293. doi: 10.1128/aem.48.2.289-293.1984. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Fujioka R. S., Hashimoto H. H., Siwak E. B., Young R. H. Effect of sunlight on survival of indicator bacteria in seawater. Appl Environ Microbiol. 1981 Mar;41(3):690–696. doi: 10.1128/aem.41.3.690-696.1981. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Geldreich E. E., Best L. C., Kenner B. A., Van Donsel D. J. The bacteriological aspects of stormwater pollution. J Water Pollut Control Fed. 1968 Nov;40(11):1861–1872. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Goyal S. M., Gerba C. P., Melnick J. L. Occurrence and distribution of bacterial indicators and pathogens in canal communities along the Texas coast. Appl Environ Microbiol. 1977 Aug;34(2):139–149. doi: 10.1128/aem.34.2.139-149.1977. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Hanes N. B., Fragala R. Effect of seawater concentration on survival of indicator bacteria. J Water Pollut Control Fed. 1967 Jan;39(1):97–104. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Liang L. N., Sinclair J. L., Mallory L. M., Alexander M. Fate in model ecosystems of microbial species of potential use in genetic engineering. Appl Environ Microbiol. 1982 Sep;44(3):708–714. doi: 10.1128/aem.44.3.708-714.1982. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Ludwig W., Seewaldt E., Kilpper-Bälz R., Schleifer K. H., Magrum L., Woese C. R., Fox G. E., Stackebrandt E. The phylogenetic position of Streptococcus and Enterococcus. J Gen Microbiol. 1985 Mar;131(3):543–551. doi: 10.1099/00221287-131-3-543. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Mallory L. M., Sinclair J. L., Liang L. N., Alexander M. A simple and sensitive method for assessing survival in environmental samples of species used in recombinant DNA research. Recomb DNA Tech Bull. 1982 Mar;5(1):5–6. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- McCambridge J., McMeekin T. A. Effect of solar radiation and predacious microorganisms on survival of fecal and other bacteria. Appl Environ Microbiol. 1981 May;41(5):1083–1087. doi: 10.1128/aem.41.5.1083-1087.1981. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- McFeters G. A., Bissonnette G. K., Jezeski J. J., Thomson C. A., Stuart D. G. Comparative survival of indicator bacteria and enteric pathogens in well water. Appl Microbiol. 1974 May;27(5):823–829. doi: 10.1128/am.27.5.823-829.1974. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Moss C. W., Speck M. L. Release of biologically active peptides from Escherichia coli at subzero temperatures. J Bacteriol. 1966 Mar;91(3):1105–1111. doi: 10.1128/jb.91.3.1105-1111.1966. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Novick R. P. Plasmids. Sci Am. 1980 Dec;243(6):102-4, 106, 110 passim. doi: 10.1038/scientificamerican1280-102. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Pettibone G. W., Cooney J. J. Effect of organotins on fecal pollution indicator organisms. Appl Environ Microbiol. 1986 Sep;52(3):562–566. doi: 10.1128/aem.52.3.562-566.1986. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- SIJPESTEIJN A. K., RIJKENS F., LUIJTEN J. G., WILLEMSENS L. C. On the antifungal and antibacterial activity of some trisubstituted organogermanium, organotin and organolead compounds. Antonie Van Leeuwenhoek. 1962;28:346–356. doi: 10.1007/BF02538746. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- SLANETZ L. W., BARTLEY C. H. SURVIVAL OF FECAL STREPTOCCOCCI IN SEA WATER. Health Lab Sci. 1965 Jul;2:142–148. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Sinclair J. L., Alexander M. Role of resistance to starvation in bacterial survival in sewage and lake water. Appl Environ Microbiol. 1984 Aug;48(2):410–415. doi: 10.1128/aem.48.2.410-415.1984. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Smith P. R., Farrell E., Dunican K. Survival of R+ Escherichia coli in sea water. Appl Microbiol. 1974 May;27(5):983–984. doi: 10.1128/am.27.5.983-984.1974. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Stotzky G., Babich H. Fate of genetically-engineered microbes in natural environments. Recomb DNA Tech Bull. 1984 Dec;7(4):163–188. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Temple K. L., Camper A. K., McFeters G. A. Survival of two enterobacteria in feces buried in soil under field conditions. Appl Environ Microbiol. 1980 Oct;40(4):794–797. doi: 10.1128/aem.40.4.794-797.1980. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Vasconcelos G. J., Swartz R. G. Survival of bacteria in seawater using a diffusion chamber apparatus in situ. Appl Environ Microbiol. 1976 Jun;31(6):913–920. doi: 10.1128/aem.31.6.913-920.1976. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]