Abstract
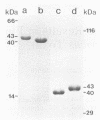
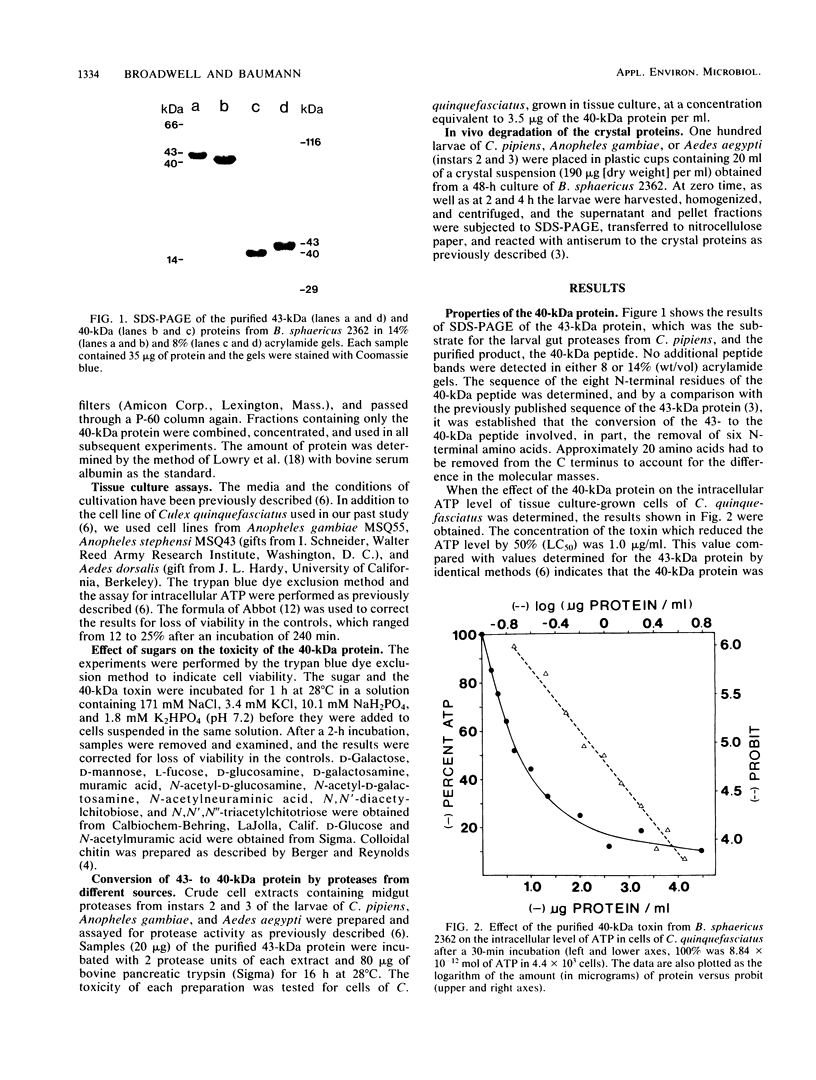
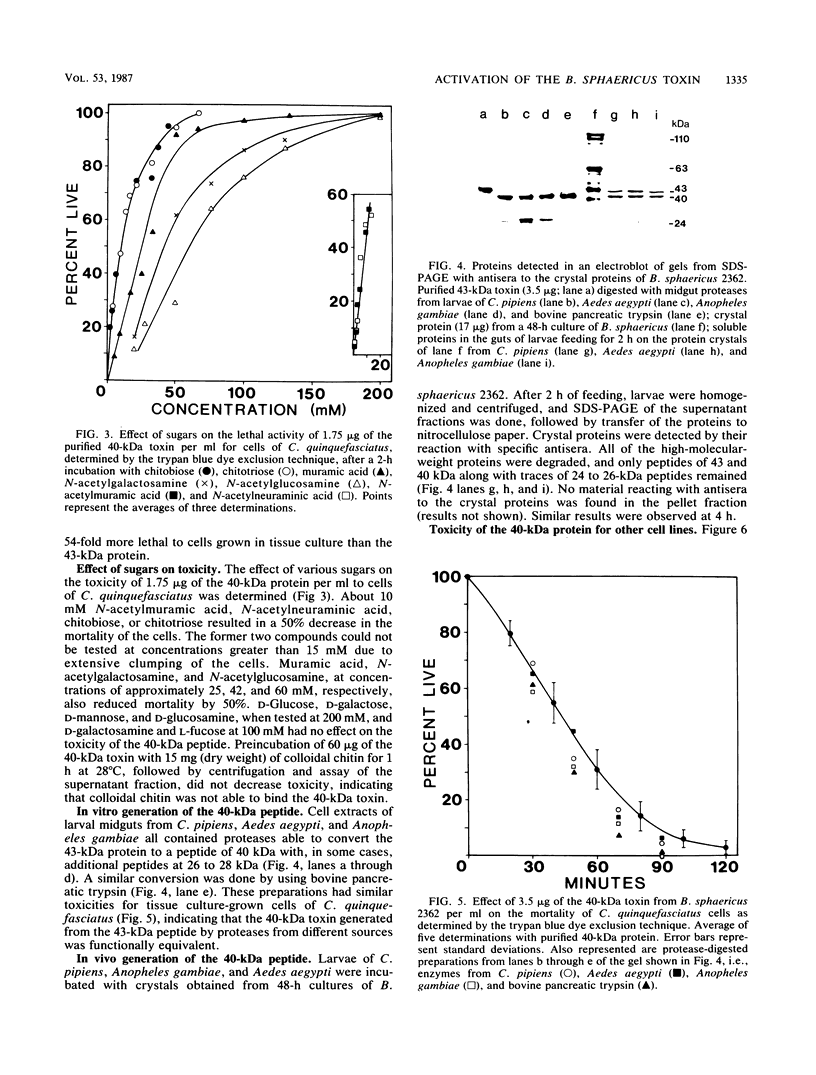
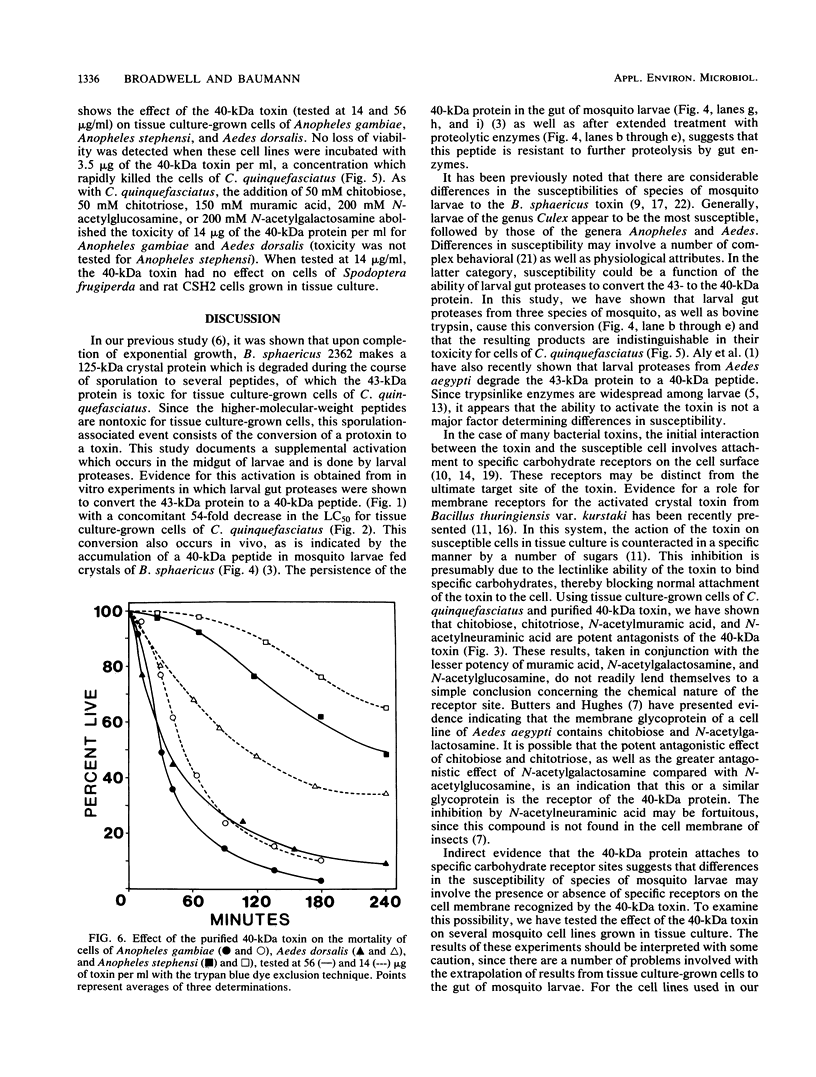
Gut proteases from the larvae of the mosquito Culex pipiens convert the 43-kilodalton (kDa) toxin from Bacillus sphaericus 2362 to a 40-kDa peptide. The 50% lethal concentration of this peptide for tissue culture-grown cells of Culex quinquefasciatus was 1.0 microgram/ml (as determined by the intracellular ATP assay), 54-fold less than that of the 43-kDa peptide. Gut proteases from Anopheles gambiae and Aedes aegypti, as well as bovine pancreatic trypsin, also converted the 43-kDa protein to a 40-kDa peptide which was indistinguishable from the peptide formed by the proteases from C. pipiens with respect to its toxicity to tissue culture-grown cells of C. quinquefasciatus. Evidence for the in vivo conversion of the 43-kDa protein to the 40-kDa peptide was also obtained from experiments in which larvae of C. pipiens, Anopheles gambiae, and Aedes aegypti were fed crystals from B. sphaericus 2362. By using the exclusion of trypan blue as an indication of cell viability, it was shown that chitobiose, chitotriose, N-acetylmuramic acid, and N-acetylneuraminic acid decreased the toxicity of the 40-kDa peptide (from 100 to 50% mortality at about 10 mM concentrations of these sugars). Muramic acid, N-acetylgalactosamine, and N-acetylglucosamine were less effective, while several sugars had no effect, suggesting that the 40-kDa toxin binds to specific receptors on the cell membrane. The 40-kDa protein was less toxic to tissue culture-grown cells of Anopheles gambiae and Aedes dorsalis, and the same sugars which reduced the toxicity for cells of C. quinquefasciatus were also effective in reduction of toxicity for these cell lines.(ABSTRACT TRUNCATED AT 250 WORDS)
Full text
PDF

Images in this article
Selected References
These references are in PubMed. This may not be the complete list of references from this article.
- BERGER L. R., REYNOLDS D. M. The chitinase system of a strain of Streptomyces griseus. Biochim Biophys Acta. 1958 Sep;29(3):522–534. doi: 10.1016/0006-3002(58)90008-8. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Baumann P., Unterman B. M., Baumann L., Broadwell A. H., Abbene S. J., Bowditch R. D. Purification of the larvicidal toxin of Bacillus sphaericus and evidence for high-molecular-weight precursors. J Bacteriol. 1985 Aug;163(2):738–747. doi: 10.1128/jb.163.2.738-747.1985. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Broadwell A. H., Baumann P. Sporulation-associated activation of Bacillus sphaericus larvicide. Appl Environ Microbiol. 1986 Oct;52(4):758–764. doi: 10.1128/aem.52.4.758-764.1986. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Butters T. D., Hughes R. C. Isolation and characterization of mosquito cell membrane glycoproteins. Biochim Biophys Acta. 1981 Feb 6;640(3):655–671. doi: 10.1016/0005-2736(81)90096-1. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Davidson E. W. Effects of Bacillus sphaericus 1593 and 2362 spore/crystal toxin on cultured mosquito cells. J Invertebr Pathol. 1986 Jan;47(1):21–31. doi: 10.1016/0022-2011(86)90159-x. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Eidels L., Proia R. L., Hart D. A. Membrane receptors for bacterial toxins. Microbiol Rev. 1983 Dec;47(4):596–620. doi: 10.1128/mr.47.4.596-620.1983. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Kalfon A., Charles J. F., Bourgouin C., de Barjac H. Sporulation of Bacillus sphaericus 2297: an electron microscope study of crystal-like inclusion biogenesis and toxicity to mosquito larvae. J Gen Microbiol. 1984 Apr;130(4):893–900. doi: 10.1099/00221287-130-4-893. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Knowles B. H., Ellar D. J. Characterization and partial purification of a plasma membrane receptor for Bacillus thuringiensis var. kurstaki lepidopteran-specific delta-endotoxin. J Cell Sci. 1986 Jul;83:89–101. doi: 10.1242/jcs.83.1.89. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- LOWRY O. H., ROSEBROUGH N. J., FARR A. L., RANDALL R. J. Protein measurement with the Folin phenol reagent. J Biol Chem. 1951 Nov;193(1):265–275. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Lacey L. A., Undeen A. H. Microbial control of black flies and mosquitoes. Annu Rev Entomol. 1986;31:265–296. doi: 10.1146/annurev.en.31.010186.001405. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Payne J. M., Davidson E. W. Insecticidal activity of the crystalline parasporal inclusions and other components of the Bacillus sphaericus 1593 spore complex. J Invertebr Pathol. 1984 May;43(3):383–388. doi: 10.1016/0022-2011(84)90084-3. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Yousten A. A. Bacillus sphaericus: microbiological factors related to its potential as a mosquito larvicide. Adv Biotechnol Processes. 1984;3:315–343. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]