Abstract
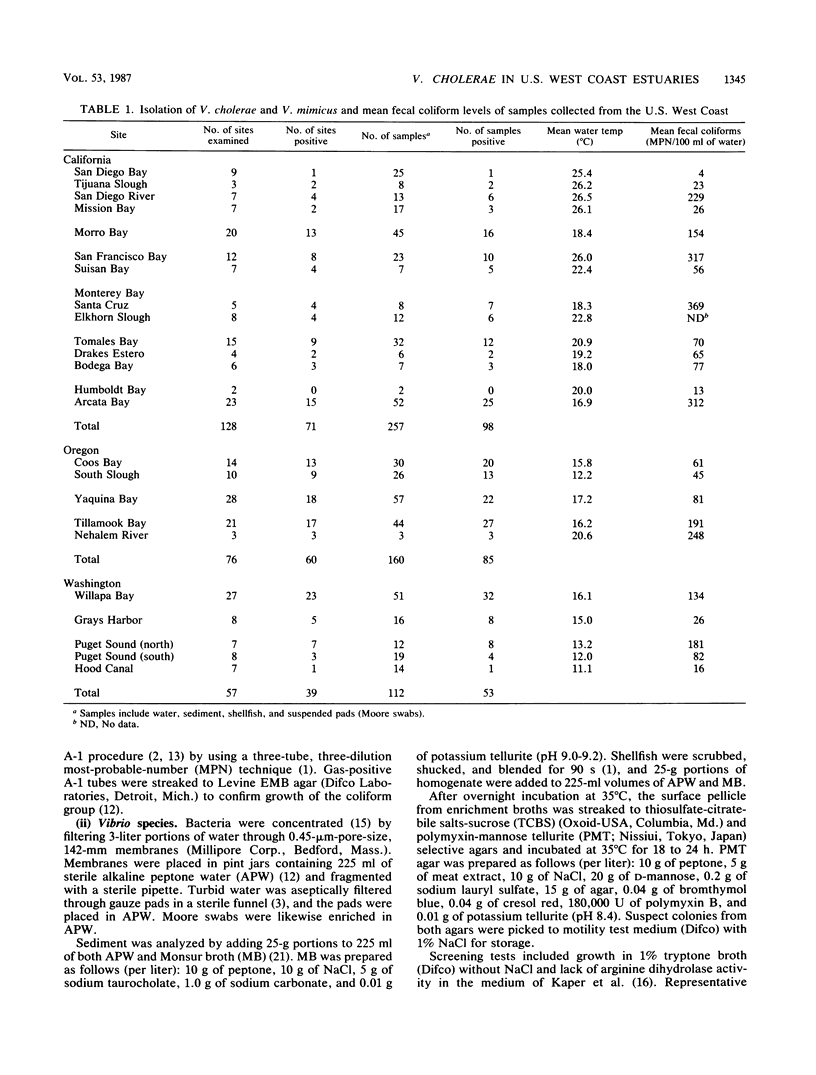
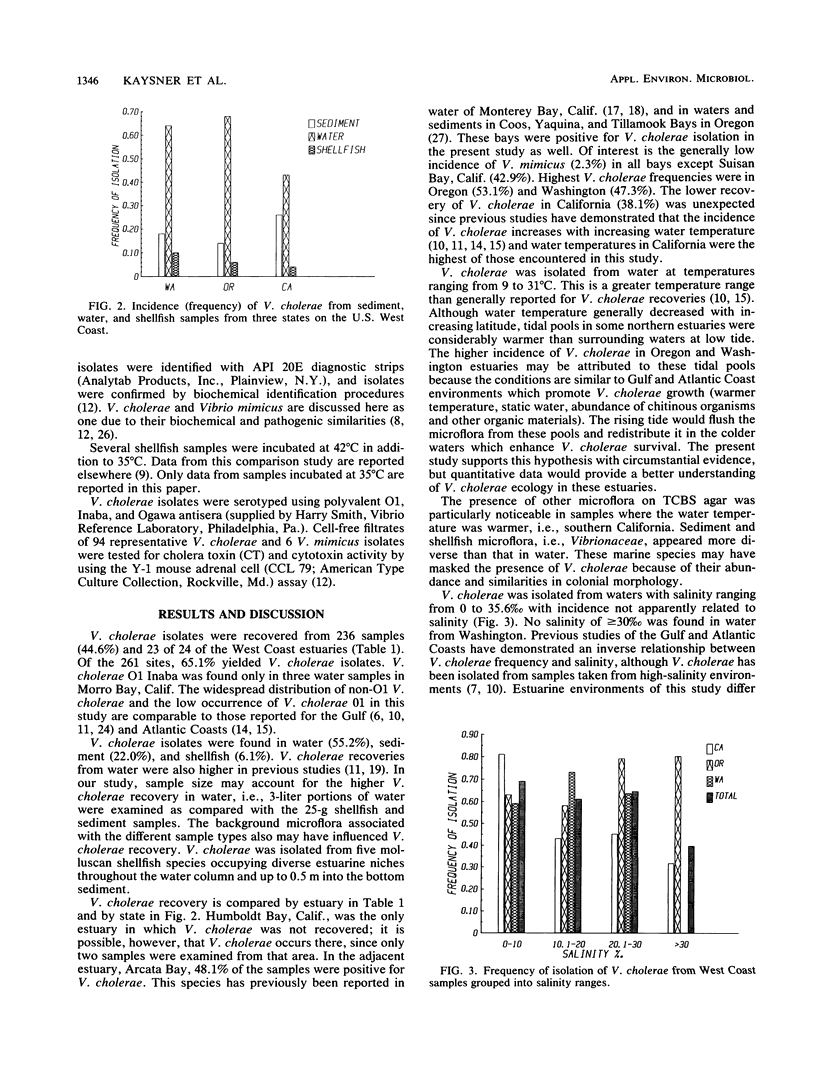
The incidence of Vibrio cholerae in shellfish, sediment, and waters of California, Oregon, and Washington was determined during the summer of 1984. Samples from 24 distinct estuaries were analyzed qualitatively. V. cholerae non-O1 was found in 23 estuaries and in 44.6% of the 529 samples examined. V. cholerae O1 Inaba was isolated from water samples in Morro Bay, Calif. Vibrio mimicus was found in 2.3% of the samples. Cholera enterotoxin was not found in cell-free filtrates of the 100 isolates tested in the Y-1 mouse adrenal cell assay, but heat-labile cytotoxic activity was observed with 3% of the isolates.
Full text
PDF


Selected References
These references are in PubMed. This may not be the complete list of references from this article.
- Andrews W. H., Presnell M. W. Rapid recovery of Escherichia coli from estuarine water. Appl Microbiol. 1972 Mar;23(3):521–523. doi: 10.1128/am.23.3.521-523.1972. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Barrett T. J., Blake P. A., Morris G. K., Puhr N. D., Bradford H. B., Wells J. G. Use of Moore swabs for isolating Vibrio cholerae from sewage. J Clin Microbiol. 1980 Apr;11(4):385–388. doi: 10.1128/jcm.11.4.385-388.1980. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Blake P. A., Allegra D. T., Snyder J. D., Barrett T. J., McFarland L., Caraway C. T., Feeley J. C., Craig J. P., Lee J. V., Puhr N. D. Cholera--a possible endemic focus in the United States. N Engl J Med. 1980 Feb 7;302(6):305–309. doi: 10.1056/NEJM198002073020601. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Davis B. R., Fanning G. R., Madden J. M., Steigerwalt A. G., Bradford H. B., Jr, Smith H. L., Jr, Brenner D. J. Characterization of biochemically atypical Vibrio cholerae strains and designation of a new pathogenic species, Vibrio mimicus. J Clin Microbiol. 1981 Dec;14(6):631–639. doi: 10.1128/jcm.14.6.631-639.1981. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- DePaola A., Kaysner C. A., McPhearson R. M. Elevated temperature method for recovery of Vibrio cholerae from oysters (Crassostrea gigas). Appl Environ Microbiol. 1987 May;53(5):1181–1182. doi: 10.1128/aem.53.5.1181-1182.1987. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Hunt D. A., Springer J. Comparison of two rapid test procedures with the standard EC test recovery of fecal coliform bacteria from shellfish-growing waters. J Assoc Off Anal Chem. 1978 Nov;61(6):1317–1323. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Huq A., Small E. B., West P. A., Huq M. I., Rahman R., Colwell R. R. Ecological relationships between Vibrio cholerae and planktonic crustacean copepods. Appl Environ Microbiol. 1983 Jan;45(1):275–283. doi: 10.1128/aem.45.1.275-283.1983. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Kaper J., Lockman H., Colwell R. R., Joseph S. W. Ecology, serology, and enterotoxin production of Vibrio cholerae in Chesapeake Bay. Appl Environ Microbiol. 1979 Jan;37(1):91–103. doi: 10.1128/aem.37.1.91-103.1979. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Kenyon J. E., Gillies D. C., Piexoto D. R., Austin B. Vibrio cholerae (non-O1) isolated from California coastal waters. Appl Environ Microbiol. 1983 Nov;46(5):1232–1233. doi: 10.1128/aem.46.5.1232-1233.1983. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Kenyon J. E., Piexoto D. R., Austin B., Gillies D. C. Seasonal variations of Vibrio cholerae (non-O1) isolated from California coastal waters. Appl Environ Microbiol. 1984 Jun;47(6):1243–1245. doi: 10.1128/aem.47.6.1243-1245.1984. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- McCardell B. A., Madden J. M., Shah D. B. Isolation and characterization of a cytolysin produced by Vibrio cholerae serogroup non-O1. Can J Microbiol. 1985 Aug;31(8):711–720. doi: 10.1139/m85-135. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Morris J. G., Jr, Wilson R., Davis B. R., Wachsmuth I. K., Riddle C. F., Wathen H. G., Pollard R. A., Blake P. A. Non-O group 1 Vibrio cholerae gastroenteritis in the United States: clinical, epidemiologic, and laboratory characteristics of sporadic cases. Ann Intern Med. 1981 May;94(5):656–658. doi: 10.7326/0003-4819-94-5-656. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Nolan C. M., Ballard J., Kaysner C. A., Lilja J. L., Williams L. P., Jr, Tenover F. C. Vibrio parahaemolyticus gastroenteritis. An outbreak associated with raw oysters in the Pacific northwest. Diagn Microbiol Infect Dis. 1984 Apr;2(2):119–128. doi: 10.1016/0732-8893(84)90007-5. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Spira W. M., Fedorka-Cray P. J. Purification of enterotoxins from Vibrio mimicus that appear to be identical to cholera toxin. Infect Immun. 1984 Sep;45(3):679–684. doi: 10.1128/iai.45.3.679-684.1984. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Tison D. L., Nishibuchi M., Seidler R. J., Siebeling R. J. Isolation of Non-O1 Vibrio cholerae Serovars from Oregon Coastal Environments. Appl Environ Microbiol. 1986 Feb;51(2):444–445. doi: 10.1128/aem.51.2.444-445.1986. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Wilson R., Lieb S., Roberts A., Stryker S., Janowski H., Gunn R., Davis B., Riddle C. F., Barrett T., Morris J. G., Jr Non-O group 1 Vibrio cholerae gastroenteritis associated with eating raw oysters. Am J Epidemiol. 1981 Aug;114(2):293–298. doi: 10.1093/oxfordjournals.aje.a113194. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]



