Abstract
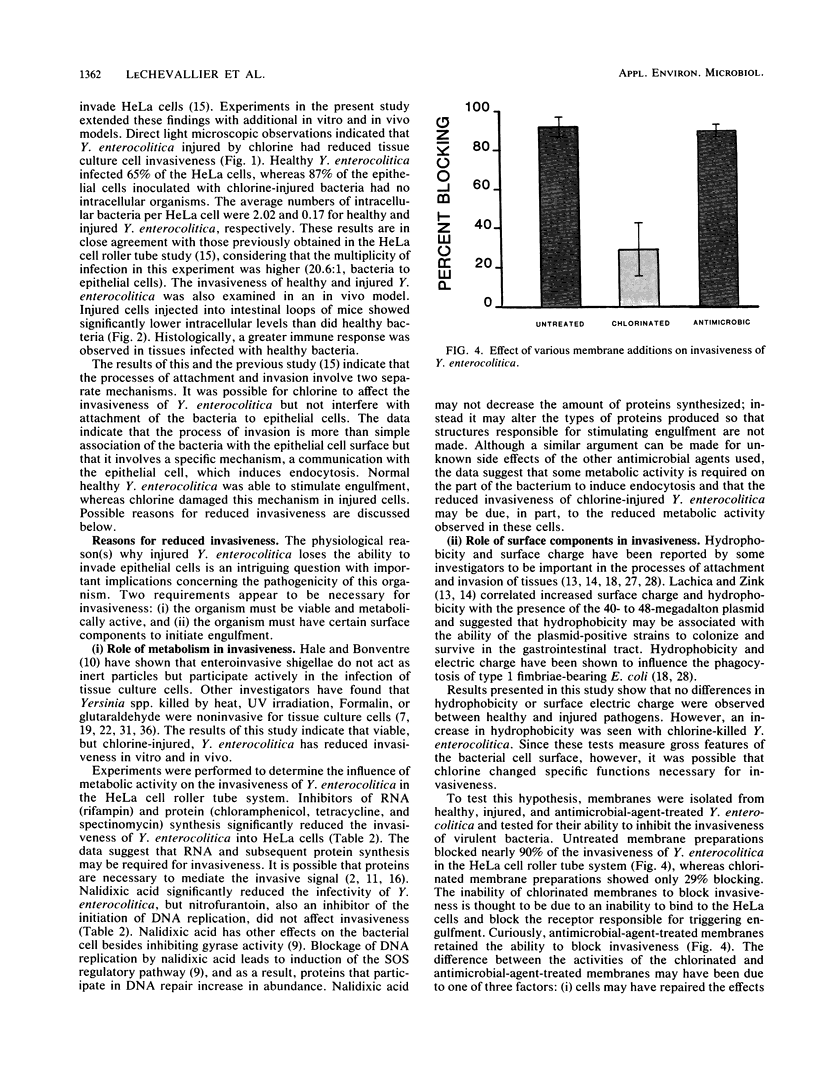
The invasion of epithelial cells in vitro and in vivo by chlorine-injured Yersinia enterocolitica was assessed by direct microscopic observations. These experiments showed that injury by chlorine inhibited invasiveness of virulent Y. enterocolitica. Two requirements appeared to be necessary for invasiveness: the organism must be viable and metabolically active, and the organism must have certain surface components to initiate engulfment. Inhibition of RNA synthesis by rifampin and protein synthesis by chloramphenicol, tetracycline, and spectinomycin inhibited the invasiveness but not the attachment of Y. enterocolitica to epithelial cells. Membrane preparations from untreated and antimicrobial-agent-treated Y. enterocolitica blocked the invasiveness of virulent Y. enterocolitica, whereas membranes from chlorinated cells were unable to block invasiveness. Chlorine did not change the hydrophobicity or surface charge of injured Y. enterocolitica. The results indicate that invasion was more than simple association of the bacterium with the epithelial cell and involved a specific trigger to stimulate engulfment.
Full text
PDF



Selected References
These references are in PubMed. This may not be the complete list of references from this article.
- Adamus G., Romanowska E. Outer membrane proteins of Shigella sonnei. II. Comparative studies on virulent and avirulent strains of phase I. Arch Immunol Ther Exp (Warsz) 1980;28(4):553–558. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Black R. E., Jackson R. J., Tsai T., Medvesky M., Shayegani M., Feeley J. C., MacLeod K. I., Wakelee A. M. Epidemic Yersinia enterocolitica infection due to contaminated chocolate milk. N Engl J Med. 1978 Jan 12;298(2):76–79. doi: 10.1056/NEJM197801122980204. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Bottone E. J. Yersinia enterocolitica: a panoramic view of a charismatic microorganism. CRC Crit Rev Microbiol. 1977;5(2):211–241. doi: 10.3109/10408417709102312. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Brunius G., Bölin I. Interaction between Yersinia pseudotuberculosis and the HeLa cell surface. J Med Microbiol. 1983 Aug;16(3):245–261. doi: 10.1099/00222615-16-3-245. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Devenish J. A., Schiemann D. A. HeLa cell infection by Yersinia enterocolitica: evidence for lack of intracellular multiplication and development of a new procedure for quantitative expression of infectivity. Infect Immun. 1981 Apr;32(1):48–55. doi: 10.1128/iai.32.1.48-55.1981. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Drlica K. Biology of bacterial deoxyribonucleic acid topoisomerases. Microbiol Rev. 1984 Dec;48(4):273–289. doi: 10.1128/mr.48.4.273-289.1984. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Hale T. L., Bonventre P. F. Shigella infection of Henle intestinal epithelial cells: role of the bacterium. Infect Immun. 1979 Jun;24(3):879–886. doi: 10.1128/iai.24.3.879-886.1979. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Hale T. L., Sansonetti P. J., Schad P. A., Austin S., Formal S. B. Characterization of virulence plasmids and plasmid-associated outer membrane proteins in Shigella flexneri, Shigella sonnei, and Escherichia coli. Infect Immun. 1983 Apr;40(1):340–350. doi: 10.1128/iai.40.1.340-350.1983. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Highsmith A. K., Feeley J. C., Morris G. K. Yersinia enterocolitica: a review of the bacterium and recommended laboratory methodology. Health Lab Sci. 1977 Oct;14(4):253–260. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Lachica R. V., Zink D. L. Determination of plasmid-associated hydrophobicity of Yersinia enterocolitica by a latex particle agglutination test. J Clin Microbiol. 1984 May;19(5):660–663. doi: 10.1128/jcm.19.5.660-663.1984. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Lachica R. V., Zink D. L. Plasmid-associated cell surface charge and hydrophobicity of Yersinia enterocolitica. Infect Immun. 1984 May;44(2):540–543. doi: 10.1128/iai.44.2.540-543.1984. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- LeChevallier M. W., Singh A., Schiemann D. A., McFeters G. A. Changes in virulence of waterborne enteropathogens with chlorine injury. Appl Environ Microbiol. 1985 Aug;50(2):412–419. doi: 10.1128/aem.50.2.412-419.1985. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Maurelli A. T., Blackmon B., Curtiss R., 3rd Temperature-dependent expression of virulence genes in Shigella species. Infect Immun. 1984 Jan;43(1):195–201. doi: 10.1128/iai.43.1.195-201.1984. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Moolenbeek C., Ruitenberg E. J. The "Swiss roll": a simple technique for histological studies of the rodent intestine. Lab Anim. 1981 Jan;15(1):57–59. doi: 10.1258/002367781780958577. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Ohman L., Hed J., Stendahl O. Interaction between human polymorphonuclear leukocytes and two different strains of type 1 fimbriae-bearing Escherichia coli. J Infect Dis. 1982 Dec;146(6):751–757. doi: 10.1093/infdis/146.6.751. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Okamoto K., Inoue T., Ichikawa H., Kawamoto Y., Hara S., Miyama A. Adherence of Yersinia enterocolitica to mammalian epithelial cell lines. Microbiol Immunol. 1980;24(11):1013–1022. doi: 10.1111/j.1348-0421.1980.tb02907.x. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Okamura N., Nagai T., Nakaya R., Kondo S., Murakami M., Hisatsune K. HeLa cell invasiveness and O antigen of Shigella flexneri as separate and prerequisite attributes of virulence to evoke keratoconjunctivitis in guinea pigs. Infect Immun. 1983 Feb;39(2):505–513. doi: 10.1128/iai.39.2.505-513.1983. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Osada Y., Ogawa H. A possible role of glycolipids in epithelial cell penetration by virulent Shigella flexneri 2a. Microbiol Immunol. 1977;21(7):405–410. doi: 10.1111/j.1348-0421.1977.tb00304.x. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Pedersen K. B., Winblad S., Bitsch V. Studies on the interaction between different O-serotypes of Yersinia enterocolitica and HeLa cells. Acta Pathol Microbiol Scand B. 1979 Apr;87B(2):141–145. doi: 10.1111/j.1699-0463.1979.tb02417.x. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Petrovskaya V. G., Bondarenko V. M., Mirolyubova L. V. The problem of interaction of shigella with epithelial cells. Zentralbl Bakteriol Orig A. 1979 Mar;243(1):57–73. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Sansonetti P. J., Hale T. L., Dammin G. J., Kapfer C., Collins H. H., Jr, Formal S. B. Alterations in the pathogenicity of Escherichia coli K-12 after transfer of plasmid and chromosomal genes from Shigella flexneri. Infect Immun. 1983 Mar;39(3):1392–1402. doi: 10.1128/iai.39.3.1392-1402.1983. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Schiemann D. A., Devenish J. A. Relationship of HeLa cell infectivity to biochemical, serological, and virulence characteristics of Yersinia enterocolitica. Infect Immun. 1982 Feb;35(2):497–506. doi: 10.1128/iai.35.2.497-506.1982. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Schiemann D. A., Swanz P. J. Epithelial cell association and hydrophobicity of Yersinia enterocolitica and related species. J Med Microbiol. 1985 Jun;19(3):309–315. doi: 10.1099/00222615-19-3-309. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Shayegani M., Morse D., DeForge I., Root T., Parsons L. M., Maupin P. S. Microbiology of a major foodborne outbreak of gastroenteritis caused by Yersinia enterocolitica serogroup O:8. J Clin Microbiol. 1983 Jan;17(1):35–40. doi: 10.1128/jcm.17.1.35-40.1983. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Singh A., LeChevallier M. W., McFeters G. A. Reduced virulence of Yersinia enterocolitica by copper-induced injury. Appl Environ Microbiol. 1985 Aug;50(2):406–411. doi: 10.1128/aem.50.2.406-411.1985. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Soemitro D. W., Wokatsch R., Bockemühl J. Interaction between HeLa cells and epidemiologically defined strains of Yersinia enterocolitica isolated in the Federal Republic of Germany. Zentralbl Bakteriol Mikrobiol Hyg A. 1981 Dec;251(2):203–212. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Tacket C. O., Ballard J., Harris N., Allard J., Nolan C., Quan T., Cohen M. L. An outbreak of Yersinia enterocolitica infections caused by contaminated tofu (soybean curd). Am J Epidemiol. 1985 May;121(5):705–711. doi: 10.1093/aje/121.5.705. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Veljanov D., Kantardziev V., Stankova-Shindarova I., Todorov S. On the interactions of Yersinia strains and cell cultures. Zentralbl Bakteriol Orig A. 1978 Nov;242(1):23–30. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Vesikari T., Sundqvist C., Mäki M. Adherence and toxicity of Yersinia enterocolitica 0:3 and 0:9 containing virulence-associated plasmids for various cultured cells. Acta Pathol Microbiol Immunol Scand B. 1983 Apr;91(2):121–127. doi: 10.1111/j.1699-0463.1983.tb00020.x. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Watanabe H., Nakamura A., Timmis K. N. Small virulence plasmid of Shigella dysenteriae 1 strain W30864 encodes a 41,000-dalton protein involved in formation of specific lipopolysaccharide side chains of serotype 1 isolates. Infect Immun. 1984 Oct;46(1):55–63. doi: 10.1128/iai.46.1.55-63.1984. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Watanabe H., Timmis K. N. A small plasmid in Shigella dysenteriae 1 specifies one or more functions essential for O antigen production and bacterial virulence. Infect Immun. 1984 Jan;43(1):391–396. doi: 10.1128/iai.43.1.391-396.1984. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]


