Abstract
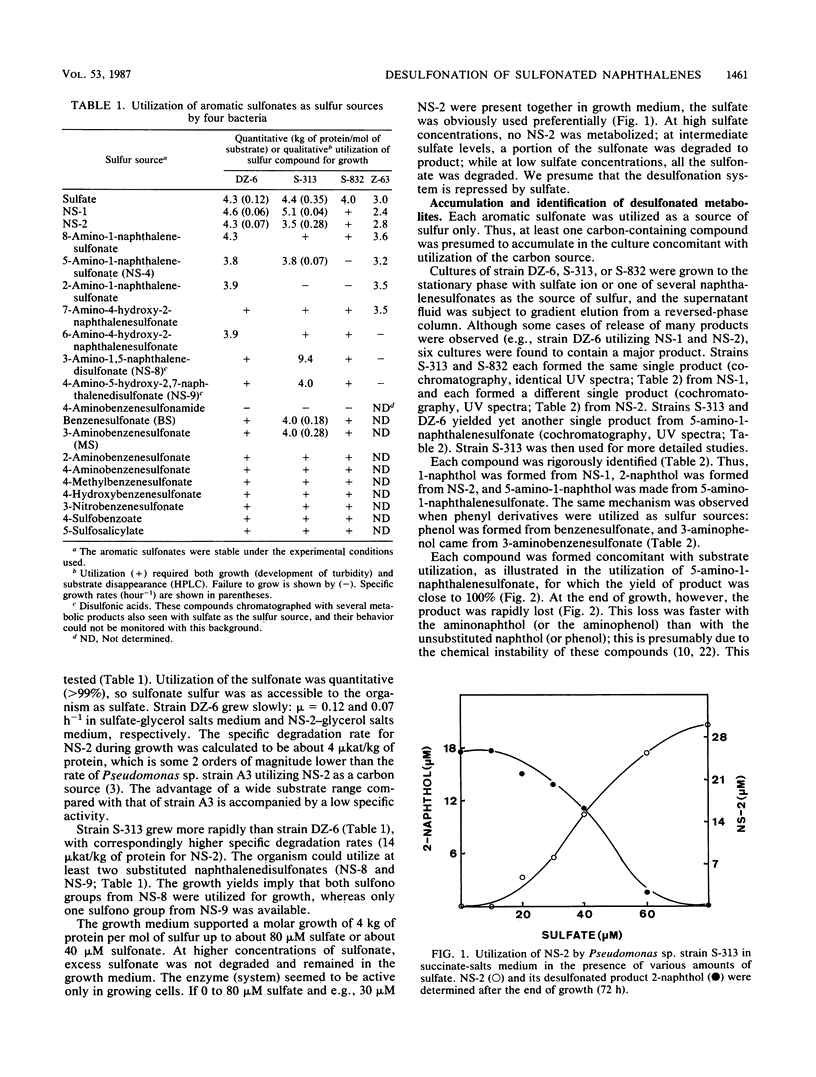
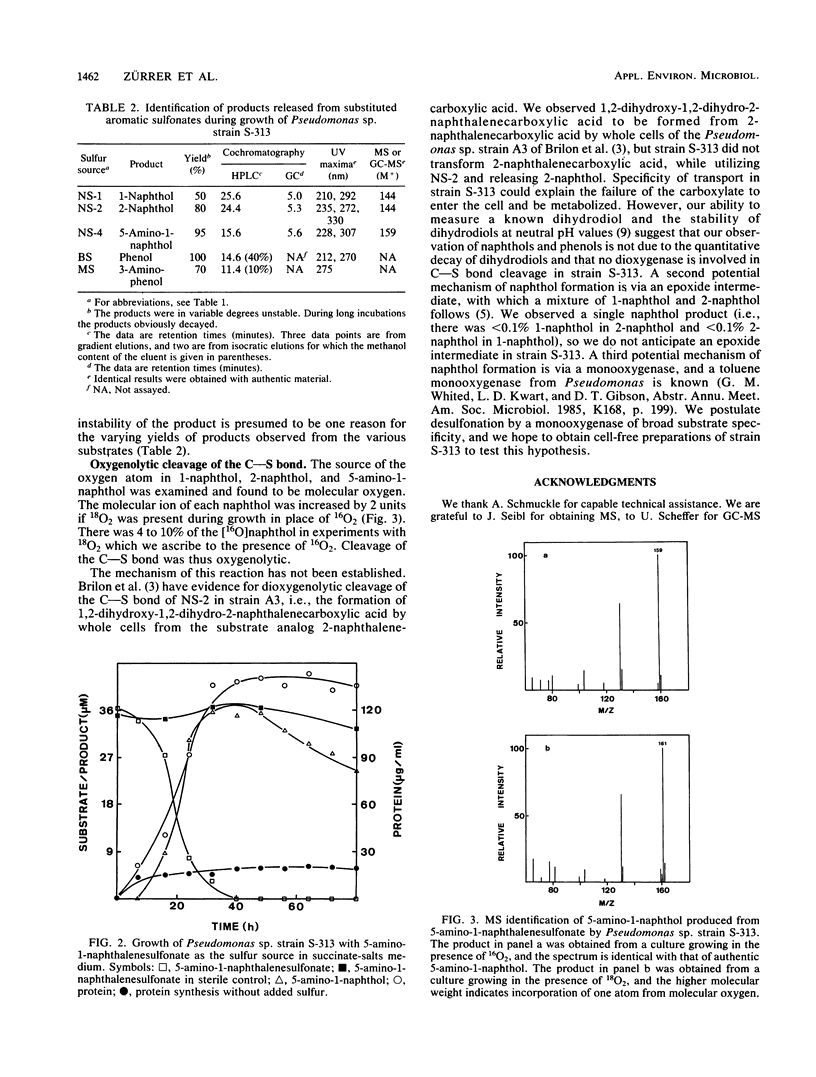
Sulfur-limited batch enrichment cultures containing one of nine multisubstituted naphthalenesulfonates and an inoculum from sewage yielded several taxa of bacteria which could quantitatively utilize 19 sulfonated aromatic compounds as the sole sulfur source for growth. Growth yields were about 4 kg of protein per mol of sulfur. Specific degradation rates were about 4 to 14 mu kat/kg of protein. A Pseudomonas sp., an Arthrobacter sp., and an unidentified bacterium were examined. Each desulfonated at least 16 aromatic compounds, none of which served as a carbon source. Pseudomonas sp. strain S-313 converted 1-naphthalenesulfonic acid, 2-naphthalenesulfonic acid, 5-amino-1-naphthalenesulfonic acid, benzenesulfonic acid, and 3-aminobenzenesulfonic acid to 1-naphthol, 2-naphthol, 5-amino-1-naphthol, phenol, and 3-aminophenol, respectively. Experiments with 18O2 showed that the hydroxyl group was derived from molecular oxygen.
Full text
PDF


Selected References
These references are in PubMed. This may not be the complete list of references from this article.
- Brilon C., Beckmann W., Knackmuss H. J. Catabolism of Naphthalenesulfonic Acids by Pseudomonas sp. A3 and Pseudomonas sp. C22. Appl Environ Microbiol. 1981 Jul;42(1):44–55. doi: 10.1128/aem.42.1.44-55.1981. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Cerniglia C. E., Gibson D. T. Metabolism of naphthalene by cell extracts of Cunninghamella elegans. Arch Biochem Biophys. 1978 Feb;186(1):121–127. doi: 10.1016/0003-9861(78)90471-x. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Cook A. M., Grossenbacher H., Hütter R. Isolation and cultivation of microbes with biodegradative potential. Experientia. 1983 Nov 15;39(11):1191–1198. doi: 10.1007/BF01990356. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Cook A. M., Hütter R. Ametryne and prometryne as sulfur sources for bacteria. Appl Environ Microbiol. 1982 Apr;43(4):781–786. doi: 10.1128/aem.43.4.781-786.1982. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- DeFrank J. J., Ribbons D. W. p-cymene pathway in Pseudomonas putida: initial reactions. J Bacteriol. 1977 Mar;129(3):1356–1364. doi: 10.1128/jb.129.3.1356-1364.1977. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Jutzi K., Cook A. M., Hütter R. The degradative pathway of the s-triazine melamine. The steps to ring cleavage. Biochem J. 1982 Dec 15;208(3):679–684. doi: 10.1042/bj2080679. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Kennedy S. I., Fewson C. A. Enzymes of the mandelate pathway in Bacterium N.C.I.B. 8250. Biochem J. 1968 Apr;107(4):497–506. doi: 10.1042/bj1070497. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Leidner H., Gloor R., Wüest D., Wuhrmann K. The influence of the sulphonic group on the biodegradability of n-alkylbenzene sulphonates. Xenobiotica. 1980 Jan;10(1):47–56. doi: 10.3109/00498258009033730. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Nörtemann B., Baumgarten J., Rast H. G., Knackmuss H. J. Bacterial communities degrading amino- and hydroxynaphthalene-2-sulfonates. Appl Environ Microbiol. 1986 Nov;52(5):1195–1202. doi: 10.1128/aem.52.5.1195-1202.1986. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Seiler H. Identification key for coryneform bacteria derived by numerical taxonomic studies. J Gen Microbiol. 1983 May;129(5):1433–1471. doi: 10.1099/00221287-129-5-1433. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]



