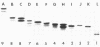Abstract
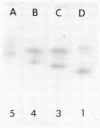
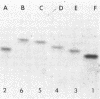
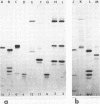
Forty Frankia strains belonging to the Alnus and Elaeagnus host specificity groups and isolated from various plant species from different geographical areas were characterized by the electrophoretic separation of isozymes of eight enzymes. All the enzyme systems that were investigated showed large variation. Diaphorases and esterases gave multiple band patterns and confirmed the identification of specific Frankia strains. Less variability was observed with enzymes such as phosphoglucose isomerase, leucine aminopeptidase, and malate dehydrogenase, which allowed for the delineation of larger groups of Frankia strains. Cluster analysis, based on the pair-wise similarity coefficients calculated between strains, delineated three large, dissimilar groups of Frankia strains, although each of these groups contained a large amount of heterogeneity. However, numerous Frankia strains, mainly from the Alnus host specificity group, demonstrated a perfect homology for all the enzymes tested.
Full text
PDF



Images in this article
Selected References
These references are in PubMed. This may not be the complete list of references from this article.
- Beauchamp C., Fridovich I. Superoxide dismutase: improved assays and an assay applicable to acrylamide gels. Anal Biochem. 1971 Nov;44(1):276–287. doi: 10.1016/0003-2697(71)90370-8. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Benson D. R., Buchholz S. E., Hanna D. G. Identification of frankia strains by two-dimensional polyacrylamide gel electrophoresis. Appl Environ Microbiol. 1984 Mar;47(3):489–494. doi: 10.1128/aem.47.3.489-494.1984. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Callaham D., Deltredici P., Torrey J. G. Isolation and Cultivation in vitro of the Actinomycete Causing Root Nodulation in Comptonia. Science. 1978 Feb 24;199(4331):899–902. doi: 10.1126/science.199.4331.899. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Caugant D. A., Bøvre K., Gaustad P., Bryn K., Holten E., Høiby E. A., Frøholm L. O. Multilocus genotypes determined by enzyme electrophoresis of Neisseria meningitidis isolated from patients with systemic disease and from healthy carriers. J Gen Microbiol. 1986 Mar;132(3):641–652. doi: 10.1099/00221287-132-3-641. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Caugant D. A., Levin B. R., Selander R. K. Genetic diversity and temporal variation in the E. coli population of a human host. Genetics. 1981 Jul;98(3):467–490. doi: 10.1093/genetics/98.3.467. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Chun P. K., Sensabaugh G. F., Vedros N. A. Genetic relationships among Neisseria species assessed by comparative enzyme electrophoresis. J Gen Microbiol. 1985 Nov;131(11):3105–3115. doi: 10.1099/00221287-131-11-3105. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Fottrell P. F., O'Hora A. Multiple forms of D (-)3-hydroxybutyrate dehydrogenase in Rhizobium. J Gen Microbiol. 1969 Aug;57(3):287–292. doi: 10.1099/00221287-57-3-287. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Goullet P. Distinctive electrophoretic patterns of esterases from Klebsiella pneumoniae, K. oxytoca, Enterobacter aerogenes and E. gergoviae. J Gen Microbiol. 1980 Apr;117(2):483–491. doi: 10.1099/00221287-117-2-483. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Goullet P. Esterase electrophoretic pattern relatedness between Shigella species and Escherichia coli. J Gen Microbiol. 1980 Apr;117(2):493–500. doi: 10.1099/00221287-117-2-493. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Goullet P., Picard B. Comparative esterase electrophoretic polymorphism of Escherichia coli isolates obtained from animal and human sources. J Gen Microbiol. 1986 Jul;132(7):1843–1851. doi: 10.1099/00221287-132-7-1843. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Goullet P., Picard B. Distinctive electrophoretic and isoelectric focusing patterns of esterases from Yersinia enterocolitica and Yersinia pseudotuberculosis. J Gen Microbiol. 1984 Jun;130(6):1471–1480. doi: 10.1099/00221287-130-6-1471. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Hartl D. L., Dykhuizen D. E. The population genetics of Escherichia coli. Annu Rev Genet. 1984;18:31–68. doi: 10.1146/annurev.ge.18.120184.000335. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Milkman R. Electrophoretic variation in Escherichia coli from natural sources. Science. 1973 Dec 7;182(4116):1024–1026. doi: 10.1126/science.182.4116.1024. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Murphy P. M., Masterson C. L. Determination of multiple forms of esterases in rhizobium by paper electrophoresis. J Gen Microbiol. 1970 Apr;61(1):121–129. doi: 10.1099/00221287-61-1-121. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Ochman H., Whittam T. S., Caugant D. A., Selander R. K. Enzyme polymorphism and genetic population structure in Escherichia coli and Shigella. J Gen Microbiol. 1983 Sep;129(9):2715–2726. doi: 10.1099/00221287-129-9-2715. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Picard B., Goullet P. Comparative electrophoretic profiles of esterases, and of glutamate, lactate and malate dehydrogenases, from Aeromonas hydrophila, A. caviae and A. sobria. J Gen Microbiol. 1985 Dec;131(12):3385–3391. doi: 10.1099/00221287-131-12-3385. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Selander R. K., Levin B. R. Genetic diversity and structure in Escherichia coli populations. Science. 1980 Oct 31;210(4469):545–547. doi: 10.1126/science.6999623. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Whittam T. S., Ochman H., Selander R. K. Multilocus genetic structure in natural populations of Escherichia coli. Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A. 1983 Mar;80(6):1751–1755. doi: 10.1073/pnas.80.6.1751. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Young J. P., Demetriou L., Apte R. G. Rhizobium Population Genetics: Enzyme Polymorphism in Rhizobium leguminosarum from Plants and Soil in a Pea Crop. Appl Environ Microbiol. 1987 Feb;53(2):397–402. doi: 10.1128/aem.53.2.397-402.1987. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]