Abstract
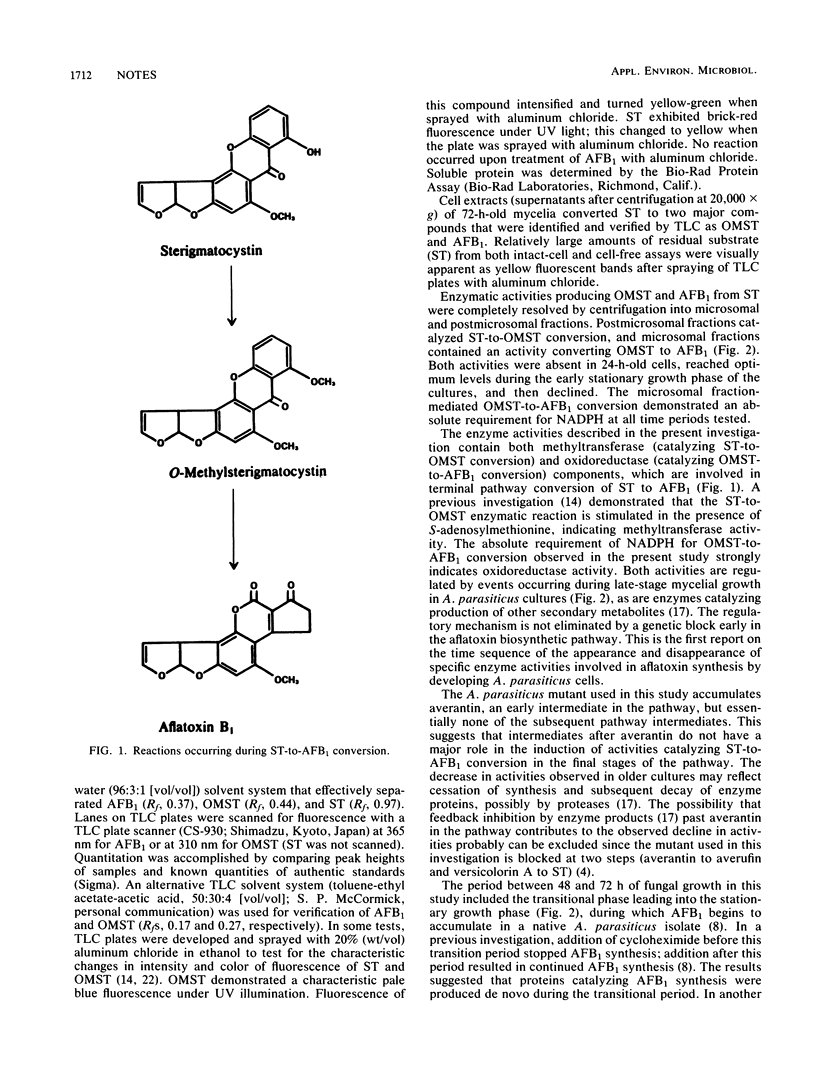
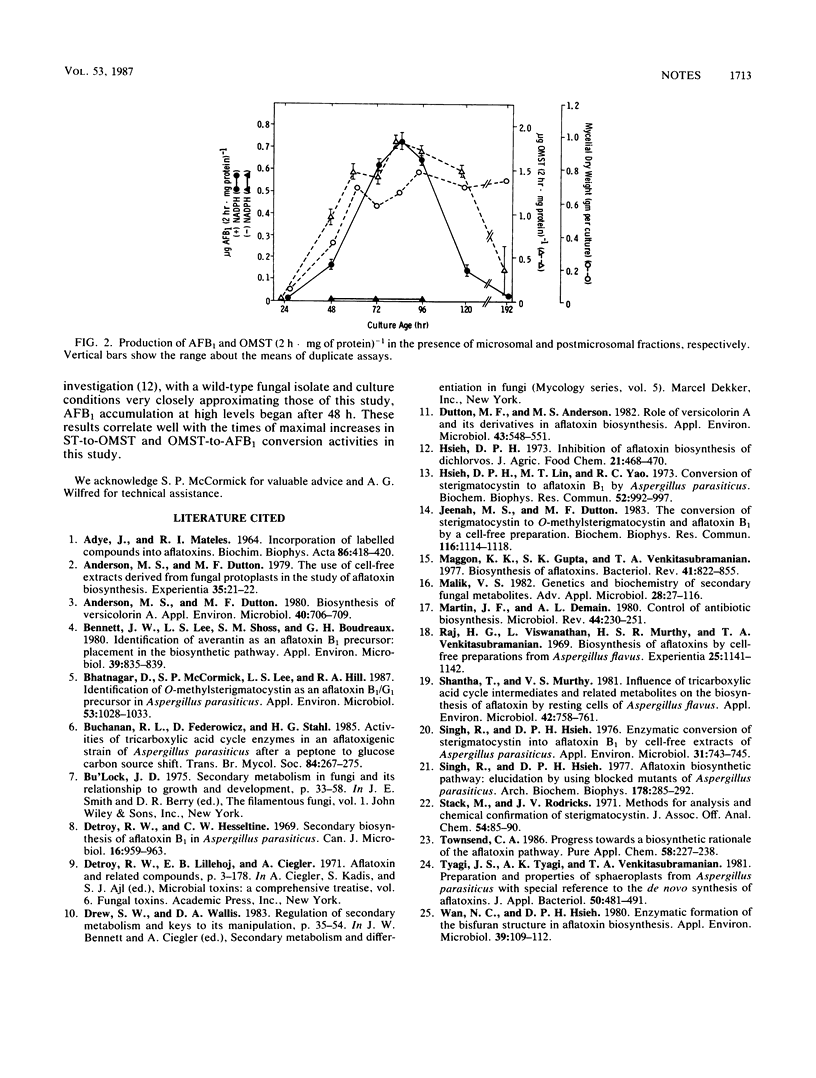
Two activities involved in terminal pathway conversion of sterigmatocystin to aflatoxin B1 were isolated from an aflatoxin-nonproducing mutant of Aspergillus parasiticus (avn-1), and the time course of appearance of the activities in culture was determined. Subcellular fractionation of fungal mycelia resolved the two activities into a postmicrosomal activity which catalyzed conversion of sterigmatocystin to O-methylsterigmatocystin and a microsomal activity which converted O-methylsterigmatocystin to aflatoxin B1. The two activities were absent in 24-h-old cells, increased to optimum levels during the stationary phase, and then declined.
Full text
PDF
Selected References
These references are in PubMed. This may not be the complete list of references from this article.
- ADYE J., MATELES R. I. INCORPORATION OF LABELLED COMPOUNDS INTO AFLATOXINS. Biochim Biophys Acta. 1964 May 11;86:418–420. doi: 10.1016/0304-4165(64)90077-7. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Anderson M. S., Dutton M. F. Biosynthesis of versicolorin A. Appl Environ Microbiol. 1980 Oct;40(4):706–709. doi: 10.1128/aem.40.4.706-709.1980. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Anderson M. S., Dutton M. F. The use of cell free extracts derived from fungal protoplasts in the study of aflatoxin biosynthesis. Experientia. 1979 Jan 15;35(1):21–22. doi: 10.1007/BF01917850. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Bennett J. W., Lee L. S., Shoss S. M., Boudreaux G. H. Identification of averantin as an aflatoxin B1 precursor: placement in the biosynthetic pathway. Appl Environ Microbiol. 1980 Apr;39(4):835–839. doi: 10.1128/aem.39.4.835-839.1980. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Bhatnagar D., McCormick S. P., Lee L. S., Hill R. A. Identification of O-methylsterigmatocystin as an aflatoxin B1 and G1 precursor in Aspergillus parasiticus. Appl Environ Microbiol. 1987 May;53(5):1028–1033. doi: 10.1128/aem.53.5.1028-1033.1987. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Detroy R. W., Hesseltine C. W. Secondary biosynthesis of aflatoxin B in Aspergillus parasiticus. Can J Microbiol. 1970 Oct;16(10):959–963. doi: 10.1139/m70-164. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Dutton M. F., Anderson M. S. Role of versicolorin A and its derivatives in aflatoxin biosynthesis. Appl Environ Microbiol. 1982 Mar;43(3):548–551. doi: 10.1128/aem.43.3.548-551.1982. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Hsieh D. P. Inhibition of aflatoxin biosynthesis of dichlorvos. J Agric Food Chem. 1973 May-Jun;21(3):468–470. doi: 10.1021/jf60187a035. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Hsieh D. P., Lin M. T., Yao R. C. Conversion of sterigmatocystin to aflatoxin B 1 by Aspergillus parasiticus. Biochem Biophys Res Commun. 1973 Jun 8;52(3):992–997. doi: 10.1016/0006-291x(73)91035-8. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Jeenah M. S., Dutton M. F. The conversion of sterigmatocystin to O-methylsterigmatocystin and aflatoxin B1 by a cell-free preparation. Biochem Biophys Res Commun. 1983 Nov 15;116(3):1114–1118. doi: 10.1016/s0006-291x(83)80257-5. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Maggon K. K., Gupta S. K., Venkitasubramanian T. A. Biosynthesis of aflatoxins. Bacteriol Rev. 1977 Dec;41(4):822–855. doi: 10.1128/br.41.4.822-855.1977. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Martin J. F., Demain A. L. Control of antibiotic biosynthesis. Microbiol Rev. 1980 Jun;44(2):230–251. doi: 10.1128/mr.44.2.230-251.1980. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Raj H. G., Viswanathan L., Murthy H. S., Venkitasubramanian T. A. Biosynthesis of aflatoxins by cell-free preparations from Aspergillus flavus. Experientia. 1969 Nov 15;25(11):1141–1142. doi: 10.1007/BF01900235. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Shantha T., Murthy V. S. Influence of tricarboxylic acid cycle intermediates and related metabolites on the biosynthesis of aflatoxin by resting cells of Aspergillus flavus. Appl Environ Microbiol. 1981 Nov;42(5):758–761. doi: 10.1128/aem.42.5.758-761.1981. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Singh R., Hsieh D. P. Aflatoxin biosynthetic pathway: elucidation by using blocked mutants of Aspergillus parasiticus. Arch Biochem Biophys. 1977 Jan 15;178(1):285–292. doi: 10.1016/0003-9861(77)90193-x. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Singh R., Hsieh D. P. Enzymatic conversion of sterigmatocystin into aflatoxin B1 by cell-free extracts of Aspergillus parasiticus. Appl Environ Microbiol. 1976 May;31(5):743–745. doi: 10.1128/aem.31.5.743-745.1976. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Stack M., Rodricks J. V. Method for analysis and chemical confirmation of sterigmatocystin. J Assoc Off Anal Chem. 1971 Jan;54(1):86–90. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Tyagi J. S., Tyagi A. K., Venkitasubramanian T. A. Preparation and properties of spheroplasts from Aspergillus parasiticus with special reference to the de novo synthesis of aflatoxins. J Appl Bacteriol. 1981 Jun;50(3):481–491. doi: 10.1111/j.1365-2672.1981.tb04251.x. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Wan N. C., Hsieh D. P. Enzymatic formation of the bisfuran structure in aflatoxin biosynthesis. Appl Environ Microbiol. 1980 Jan;39(1):109–112. doi: 10.1128/aem.39.1.109-112.1980. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]


