Abstract
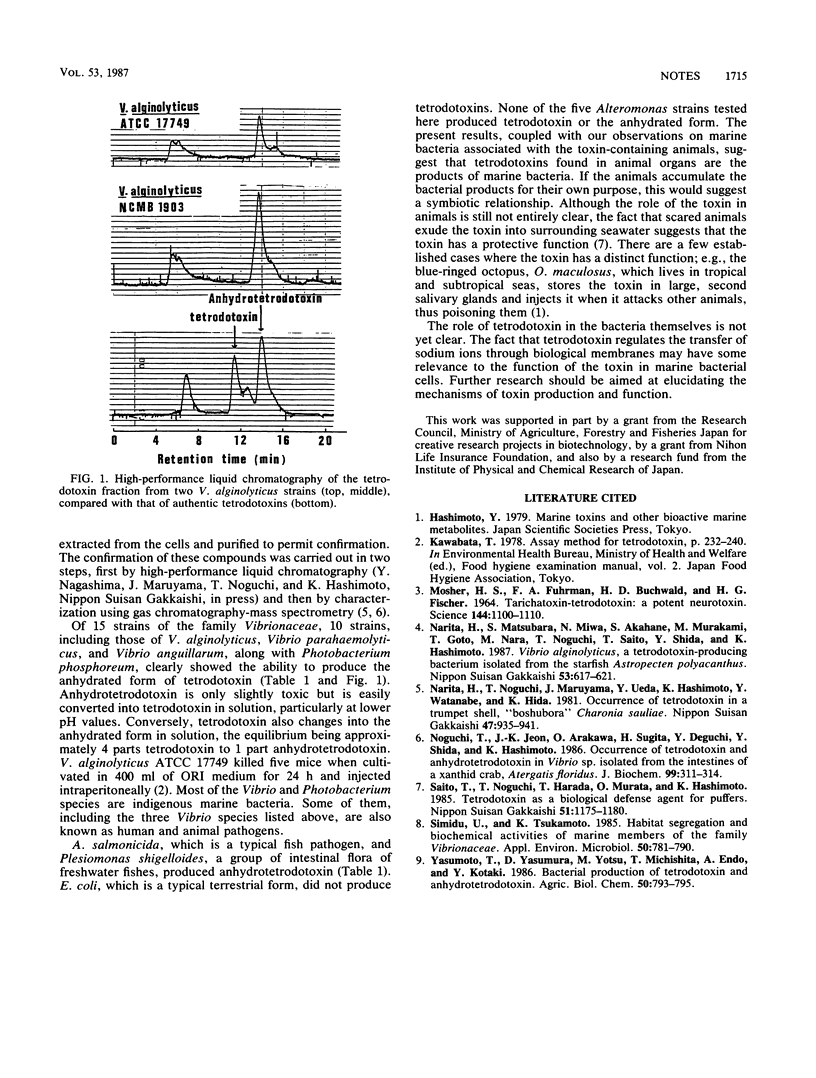
A number of type strains of marine bacteria, including members of the family Vibrionaceae, were cultured and examined for tetrodotoxin productivity by high-performance liquid chromatography and gas chromatography-mass spectrometry. Most of the Vibrionaceae strains produced tetrodotoxin, anhydrotetrodotoxin, or both.
Full text
PDF
Selected References
These references are in PubMed. This may not be the complete list of references from this article.
- MOSHER H. S., FUHRMAN F. A., BUCHWALD H. D., FISCHER H. G. TARICHATOXIN--TETRODOTOXIN: A POTENT NEUROTOXIN. Science. 1964 May 29;144(3622):1100–1110. doi: 10.1126/science.144.3622.1100. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Noguchi T., Jeon J. K., Arakawa O., Sugita H., Deguchi Y., Shida Y., Hashimoto K. Occurrence of tetrodotoxin and anhydrotetrodotoxin in Vibrio sp. isolated from the intestines of a xanthid crab, Atergatis floridus. J Biochem. 1986 Jan;99(1):311–314. doi: 10.1093/oxfordjournals.jbchem.a135476. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Simidu U., Tsukamoto K. Habitat segregation and biochemical activities of marine members of the family vibrionaceae. Appl Environ Microbiol. 1985 Oct;50(4):781–790. doi: 10.1128/aem.50.4.781-790.1985. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]


