Abstract
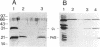
Ubiquinol-cytochrome c oxidoreductase (cytochrome bc1) complexes were demonstrated to be present in the membranes of the alkaliphilic and halophilic purple sulfur bacteria Ectothiorhodospira halophila, Ectothiorhodospira mobilis, and Ectothiorhodospira shaposhnikovii by protoheme extraction, immunoblotting, and electron paramagnetic resonance spectroscopy. The gy values of the Rieske [2Fe-2S] clusters observed in membranes of E. mobilis and E. halophila were 1.895 and 1.910, respectively. In E. mobilis membranes, the cytochrome bc1 complex was present in a stoichiometry of approximately 0.2 per reaction center. This complex was isolated and characterized. It contained four prosthetic groups: low-potential cytochrome b (cytochrome bL; Em = -142 mV), high-potential cytochrome b (cytochrome bH; Em = 116 mV), cytochrome c1 (Em = 341 mV), and a Rieske iron-sulfur cluster. The absorbance spectrum of cytochrome bL displayed an asymmetric alpha-band with a maximum at 564 nm and a shoulder at 559 nm. The alpha bands of cytochrome bH and cytochrome c1 peaked at 559.5 and 553 nm, respectively. These prosthetic groups were associated with three different polypeptides: cytochrome b, cytochrome c1, and the Rieske iron-sulfur protein, with apparent molecular masses of 43, 30, and 21 kDa, respectively. No evidence for the presence of a fourth subunit was obtained. Maximal ubiquinol-cytochrome c oxidoreductase activity of the purified complex was observed at pH 8; the turnover rate was 57 mol of cytochrome c reduced.(mol of cytochrome c1)-1.s-1. The complex showed a strikingly low sensitivity towards typical inhibitors of cytochrome bc1 complexes.
Full text
PDF







Images in this article
Selected References
These references are in PubMed. This may not be the complete list of references from this article.
- Andrews K. M., Crofts A. R., Gennis R. B. Large-scale purification and characterization of a highly active four-subunit cytochrome bc1 complex from Rhodobacter sphaeroides. Biochemistry. 1990 Mar 20;29(11):2645–2651. doi: 10.1021/bi00463a004. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Bell L. C., Richardson D. J., Ferguson S. J. Identification of nitric oxide reductase activity in Rhodobacter capsulatus: the electron transport pathway can either use or bypass both cytochrome c2 and the cytochrome bc1 complex. J Gen Microbiol. 1992 Mar;138(3):437–443. doi: 10.1099/00221287-138-3-437. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Berden J. A., Slater E. C. The reaction of antimycin with a cytochrome b preparation active in reconstitution of the respiratory chain. Biochim Biophys Acta. 1970 Sep 1;216(2):237–249. doi: 10.1016/0005-2728(70)90215-x. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Brune D. C. Sulfur oxidation by phototrophic bacteria. Biochim Biophys Acta. 1989 Jul 13;975(2):189–221. doi: 10.1016/s0005-2728(89)80251-8. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Daldal F., Tokito M. K., Davidson E., Faham M. Mutations conferring resistance to quinol oxidation (Qz) inhibitors of the cyt bc1 complex of Rhodobacter capsulatus. EMBO J. 1989 Dec 20;8(13):3951–3961. doi: 10.1002/j.1460-2075.1989.tb08578.x. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Davidson E., Ohnishi T., Atta-Asafo-Adjei E., Daldal F. Potential ligands to the [2Fe-2S] Rieske cluster of the cytochrome bc1 complex of Rhodobacter capsulatus probed by site-directed mutagenesis. Biochemistry. 1992 Apr 7;31(13):3342–3351. doi: 10.1021/bi00128a006. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- De Vries S., Albracht S. P., Berden J. A., Slater E. C. The pathway of electrons through OH2:cytochrome c oxidoreductase studied by pre-steady -state kinetics. Biochim Biophys Acta. 1982 Jul 22;681(1):41–53. doi: 10.1016/0005-2728(82)90276-6. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Dutton P. L., Petty K. M., Bonner H. S., Morse S. D. Cytochrome c2 and reaction center of Rhodospeudomonas spheroides Ga. membranes. Extinction coefficients, content, half-reduction potentials, kinetics and electric field alterations. Biochim Biophys Acta. 1975 Jun 17;387(3):536–556. doi: 10.1016/0005-2728(75)90092-4. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Gabellini N., Bowyer J. R., Hurt E., Melandri B. A., Hauska G. A cytochrome b/c1 complex with ubiquinol--cytochrome c2 oxidoreductase activity from Rhodopseudomonas sphaeroides GA. Eur J Biochem. 1982 Aug;126(1):105–111. doi: 10.1111/j.1432-1033.1982.tb06753.x. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Güner S., Robertson D. E., Yu L., Qiu Z. H., Yu C. A., Knaff D. B. The Rhodospirillum rubrum cytochrome bc1 complex: redox properties, inhibitor sensitivity and proton pumping. Biochim Biophys Acta. 1991 Jun 17;1058(2):269–279. doi: 10.1016/s0005-2728(05)80247-6. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Haley P. E., Yu L., Dong J. H., Keyser G. C., Sanborn M. R., Yu C. A. Immunological comparison of the b and c1 cytochromes from bovine heart mitochondria and the photosynthetic bacterium Rhodopseudomonas sphaeroides R-26. J Biol Chem. 1986 Nov 5;261(31):14593–14599. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Hauska G., Hurt E., Gabellini N., Lockau W. Comparative aspects of quinol-cytochrome c/plastocyanin oxidoreductases. Biochim Biophys Acta. 1983 Jul 15;726(2):97–133. doi: 10.1016/0304-4173(83)90002-2. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Hurt E., Hauska G. A cytochrome f/b6 complex of five polypeptides with plastoquinol-plastocyanin-oxidoreductase activity from spinach chloroplasts. Eur J Biochem. 1981 Jul;117(3):591–595. doi: 10.1111/j.1432-1033.1981.tb06379.x. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Knaff D. B. The cytochrome bc1 complex of photosynthetic bacteria. Trends Biochem Sci. 1990 Aug;15(8):289–291. doi: 10.1016/0968-0004(90)90013-2. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Kraayenhof R., Schuurmans J. J., Valkier L. J., Veen J. P., Van Marum D., Jasper C. G. A thermoelectrically regulated multipurpose cuvette for simultaneous time-dependent measurements. Anal Biochem. 1982 Nov 15;127(1):93–99. doi: 10.1016/0003-2697(82)90149-x. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Kriauciunas A., Yu L., Yu C. A., Wynn R. M., Knaff D. B. The Rhodospirillum rubrum cytochrome bc1 complex: peptide composition, prosthetic group content and quinone binding. Biochim Biophys Acta. 1989 Aug 17;976(1):70–76. doi: 10.1016/s0005-2728(89)80190-2. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Ljungdahl P. O., Pennoyer J. D., Robertson D. E., Trumpower B. L. Purification of highly active cytochrome bc1 complexes from phylogenetically diverse species by a single chromatographic procedure. Biochim Biophys Acta. 1987 May 6;891(3):227–241. doi: 10.1016/0005-2728(87)90218-0. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Matsuura K., Bowyer J. R., Ohnishi T., Dutton P. L. Inhibition of electron transfer by 3-alkyl-2-hydroxy-1,4-naphthoquinones in the ubiquinol-cytochrome c oxidoreductases of Rhodopseudomonas sphaeroides and mammalian mitochondria. Interaction with a ubiquinone-binding site and the Rieske iron-sulfur cluster. J Biol Chem. 1983 Feb 10;258(3):1571–1579. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- McCurley J. P., Miki T., Yu L., Yu C. A. EPR characterization of the cytochrome b-c1 complex from Rhodobacter sphaeroides. Biochim Biophys Acta. 1990 Nov 5;1020(2):176–186. doi: 10.1016/0005-2728(90)90049-a. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Meyer T. E. Isolation and characterization of soluble cytochromes, ferredoxins and other chromophoric proteins from the halophilic phototrophic bacterium Ectothiorhodospira halophila. Biochim Biophys Acta. 1985 Jan 23;806(1):175–183. doi: 10.1016/0005-2728(85)90094-5. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Meyer T. E., Przysiecki C. T., Watkins J. A., Bhattacharyya A., Simondsen R. P., Cusanovich M. A., Tollin G. Correlation between rate constant for reduction and redox potential as a basis for systematic investigation of reaction mechanisms of electron transfer proteins. Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A. 1983 Nov;80(22):6740–6744. doi: 10.1073/pnas.80.22.6740. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Prince R. C., Bashford C. L., Takamiya K. I., van den Berg W. H., Dutton P. L. Second order kinetics of the reduction of cytochrome c2 by the ubiquinone cytochrome b-c2 oxidoreductase of Rhodopseudomonas sphaeroides. J Biol Chem. 1978 Jun 25;253(12):4137–4142. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Purvis D. J., Theiler R., Niederman R. A. Chromatographic and protein chemical analysis of the ubiquinol-cytochrome c2 oxidoreductase isolated from Rhodobacter sphaeroides. J Biol Chem. 1990 Jan 15;265(2):1208–1215. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Sponholtz D. K., Brautigan D. L., Loach P. A., Margoliash E. Preparation of cytochrome c2 from Rhodospirillum rubrum. Anal Biochem. 1976 May 7;72:255–260. doi: 10.1016/0003-2697(76)90528-5. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Takaichi S., Morita S. Procedures and conditions for application of the pyridine hemochrome method to photosynthetically grown cells of Rhodopseudomonas sphaeroides. J Biochem. 1981 May;89(5):1513–1519. doi: 10.1093/oxfordjournals.jbchem.a133344. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Trumpower B. L. Cytochrome bc1 complexes of microorganisms. Microbiol Rev. 1990 Jun;54(2):101–129. doi: 10.1128/mr.54.2.101-129.1990. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Yu L., Yu C. A. Essentiality of the molecular weight 15,000 protein (subunit IV) in the cytochrome b-c1 complex of Rhodobacter sphaeroides. Biochemistry. 1991 May 21;30(20):4934–4939. doi: 10.1021/bi00234a014. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Yun C. H., Crofts A. R., Gennis R. B. Assignment of the histidine axial ligands to the cytochrome bH and cytochrome bL components of the bc1 complex from Rhodobacter sphaeroides by site-directed mutagenesis. Biochemistry. 1991 Jul 9;30(27):6747–6754. doi: 10.1021/bi00241a017. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- de Vries S., Albracht S. P., Leeuwerik F. J. The multiplicity and stoichiometry of the prosthetic groups in QH2: cytochrome c oxidoreductase as studied by EPR. Biochim Biophys Acta. 1979 May 9;546(2):316–333. doi: 10.1016/0005-2728(79)90049-5. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- van den Berg W. H., Prince R. C., Bashford C. L., Takamiya K. I., Bonner W. D., Jr, Dutton P. L. Electron and proton transport in the ubiquinone cytochrome b-c2 oxidoreductase of Rhodopseudomonas sphaeroides. Patterns of binding and inhibition by antimycin. J Biol Chem. 1979 Sep 10;254(17):8594–8604. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]