Abstract
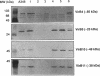
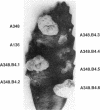
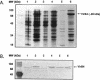
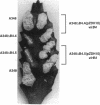
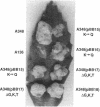
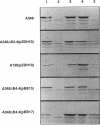
Products of the approximately 9.5-kb virB operon are proposed to direct the export of T-DNA/protein complexes across the Agrobacterium tumefaciens envelope en route to plant cells. The presence of conserved nucleoside triphosphate (NTP)-binding domains in VirB4 and VirB11 suggests that one or both proteins couple energy, via NTP hydrolysis, to T-complex transport. To assess the importance of VirB4 for virulence, a nonpolar virB4 null mutation was introduced into the pTiA6NC plasmid of strain A348. The 2.37-kb virB4 coding sequence was deleted precisely by oligonucleotide-directed mutagenesis in vitro. The resulting delta virB4 mutation was exchanged for the wild-type allele by two sequential recombination events with the counterselectable Bacillus subtilis sacB gene. Two derivatives, A348 delta B4.4 and A348 delta B4.5, sustained a nonpolar deletion of the wild-type virB4 allele, as judged by Southern blot hybridization and immunoblot analyses with antibodies specific for VirB4, VirB5, VirB10, and VirB11. Transcription of wild-type virB4 from the lac promoter restored virulence to the nonpolar null mutants on a variety of dicotyledonous species, establishing virB4 as an essential virulence gene. A substitution of glutamine for Lys-439 and a deletion of Gly-438, Lys-439, and Thr-440 within the glycine-rich NTP-binding domain (Gly-Pro-Iso-Gly-Arg-Gly-Lys-Thr) abolished complementation of A348 delta B4.4 or A348 delta B4.5, demonstrating that an intact NTP-binding domain is critical for VirB4 function. Merodiploids expressing both the mutant and wild-type virB4 alleles exhibited lower virulence than A348, suggesting that VirB4, a cytoplasmic membrane protein, may contribute as a homo- or heteromultimer to A. tumefaciens virulence.
Full text
PDF






Images in this article
Selected References
These references are in PubMed. This may not be the complete list of references from this article.
- Albano M., Breitling R., Dubnau D. A. Nucleotide sequence and genetic organization of the Bacillus subtilis comG operon. J Bacteriol. 1989 Oct;171(10):5386–5404. doi: 10.1128/jb.171.10.5386-5404.1989. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Albright L. M., Yanofsky M. F., Leroux B., Ma D. Q., Nester E. W. Processing of the T-DNA of Agrobacterium tumefaciens generates border nicks and linear, single-stranded T-DNA. J Bacteriol. 1987 Mar;169(3):1046–1055. doi: 10.1128/jb.169.3.1046-1055.1987. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Bagdasarian M. M., Amann E., Lurz R., Rückert B., Bagdasarian M. Activity of the hybrid trp-lac (tac) promoter of Escherichia coli in Pseudomonas putida. Construction of broad-host-range, controlled-expression vectors. Gene. 1983 Dec;26(2-3):273–282. doi: 10.1016/0378-1119(83)90197-x. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Becker K., Köster W., Braun V. Iron(III)hydroxamate transport of Escherichia coli K12: single amino acid replacements at potential ATP-binding sites inactivate the FhuC protein. Mol Gen Genet. 1990 Aug;223(1):159–162. doi: 10.1007/BF00315810. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Beijersbergen A., Dulk-Ras A. D., Schilperoort R. A., Hooykaas P. J. Conjugative Transfer by the Virulence System of Agrobacterium tumefaciens. Science. 1992 May 29;256(5061):1324–1327. doi: 10.1126/science.256.5061.1324. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Blomfield I. C., Vaughn V., Rest R. F., Eisenstein B. I. Allelic exchange in Escherichia coli using the Bacillus subtilis sacB gene and a temperature-sensitive pSC101 replicon. Mol Microbiol. 1991 Jun;5(6):1447–1457. doi: 10.1111/j.1365-2958.1991.tb00791.x. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Cangelosi G. A., Ankenbauer R. G., Nester E. W. Sugars induce the Agrobacterium virulence genes through a periplasmic binding protein and a transmembrane signal protein. Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A. 1990 Sep;87(17):6708–6712. doi: 10.1073/pnas.87.17.6708. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Cangelosi G. A., Best E. A., Martinetti G., Nester E. W. Genetic analysis of Agrobacterium. Methods Enzymol. 1991;204:384–397. doi: 10.1016/0076-6879(91)04020-o. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Chen C. Y., Winans S. C. Controlled expression of the transcriptional activator gene virG in Agrobacterium tumefaciens by using the Escherichia coli lac promoter. J Bacteriol. 1991 Feb;173(3):1139–1144. doi: 10.1128/jb.173.3.1139-1144.1991. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Christie P. J., Ward J. E., Jr, Gordon M. P., Nester E. W. A gene required for transfer of T-DNA to plants encodes an ATPase with autophosphorylating activity. Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A. 1989 Dec;86(24):9677–9681. doi: 10.1073/pnas.86.24.9677. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Christie P. J., Ward J. E., Winans S. C., Nester E. W. The Agrobacterium tumefaciens virE2 gene product is a single-stranded-DNA-binding protein that associates with T-DNA. J Bacteriol. 1988 Jun;170(6):2659–2667. doi: 10.1128/jb.170.6.2659-2667.1988. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Citovsky V., Wong M. L., Zambryski P. Cooperative interaction of Agrobacterium VirE2 protein with single-stranded DNA: implications for the T-DNA transfer process. Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A. 1989 Feb;86(4):1193–1197. doi: 10.1073/pnas.86.4.1193. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Citovsky V., Zupan J., Warnick D., Zambryski P. Nuclear localization of Agrobacterium VirE2 protein in plant cells. Science. 1992 Jun 26;256(5065):1802–1805. doi: 10.1126/science.1615325. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Das A. Agrobacterium tumefaciens virE operon encodes a single-stranded DNA-binding protein. Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A. 1988 May;85(9):2909–2913. doi: 10.1073/pnas.85.9.2909. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Dubnau D. Genetic competence in Bacillus subtilis. Microbiol Rev. 1991 Sep;55(3):395–424. doi: 10.1128/mr.55.3.395-424.1991. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Dürrenberger F., Crameri A., Hohn B., Koukolíková-Nicola Z. Covalently bound VirD2 protein of Agrobacterium tumefaciens protects the T-DNA from exonucleolytic degradation. Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A. 1989 Dec;86(23):9154–9158. doi: 10.1073/pnas.86.23.9154. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Ebina Y., Araki E., Taira M., Shimada F., Mori M., Craik C. S., Siddle K., Pierce S. B., Roth R. A., Rutter W. J. Replacement of lysine residue 1030 in the putative ATP-binding region of the insulin receptor abolishes insulin- and antibody-stimulated glucose uptake and receptor kinase activity. Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A. 1987 Feb;84(3):704–708. doi: 10.1073/pnas.84.3.704. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
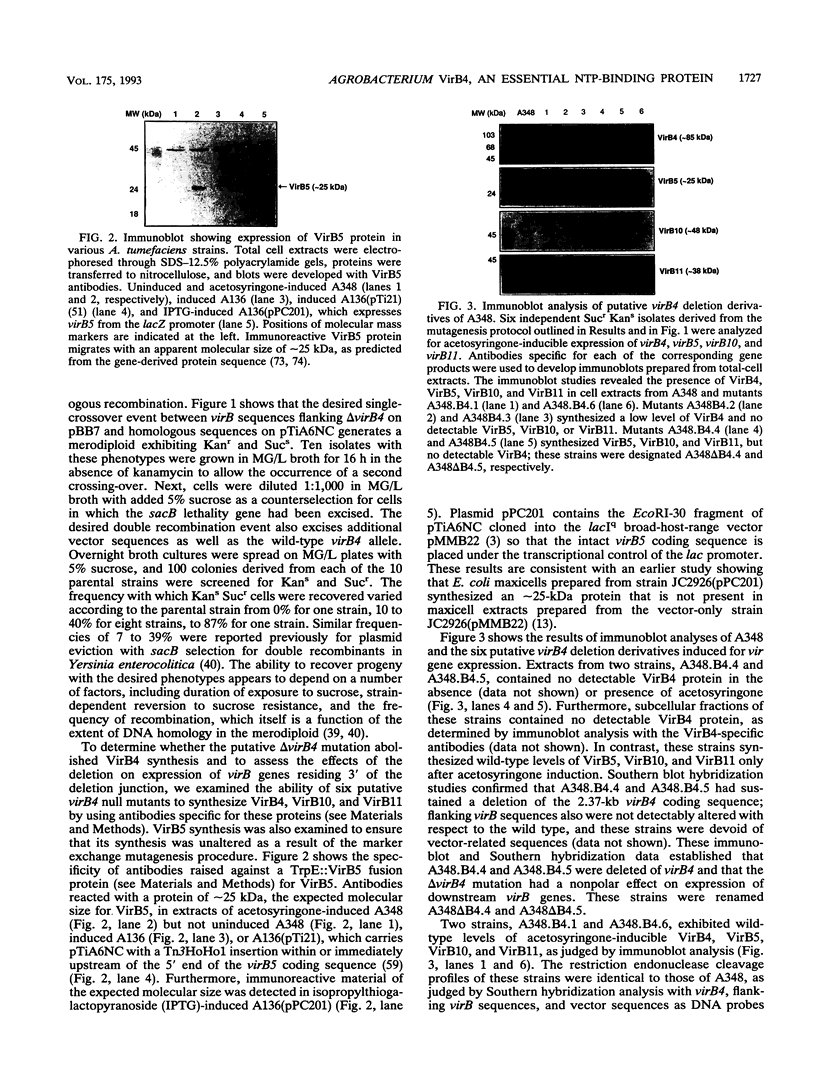
- Engström P., Zambryski P., Van Montagu M., Stachel S. Characterization of Agrobacterium tumefaciens virulence proteins induced by the plant factor acetosyringone. J Mol Biol. 1987 Oct 20;197(4):635–645. doi: 10.1016/0022-2836(87)90470-0. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
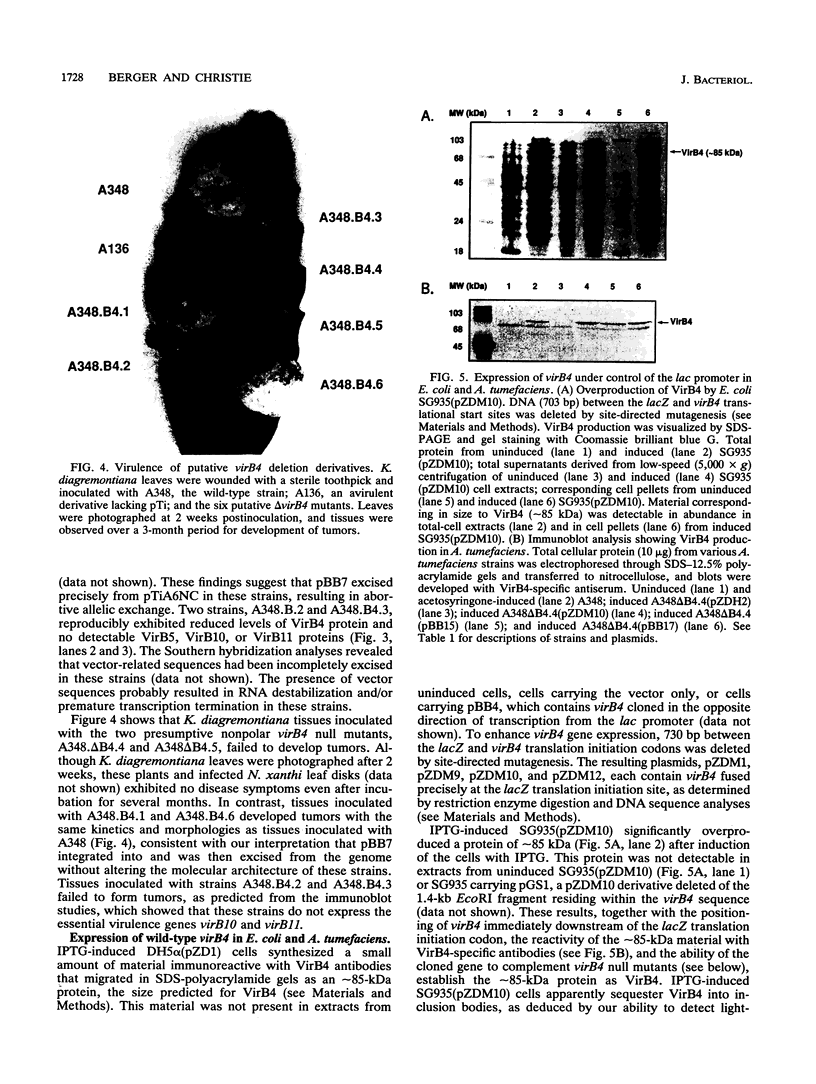
- Feldherr C. M., Kallenbach E., Schultz N. Movement of a karyophilic protein through the nuclear pores of oocytes. J Cell Biol. 1984 Dec;99(6):2216–2222. doi: 10.1083/jcb.99.6.2216. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Gay P., Le Coq D., Steinmetz M., Ferrari E., Hoch J. A. Cloning structural gene sacB, which codes for exoenzyme levansucrase of Bacillus subtilis: expression of the gene in Escherichia coli. J Bacteriol. 1983 Mar;153(3):1424–1431. doi: 10.1128/jb.153.3.1424-1431.1983. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
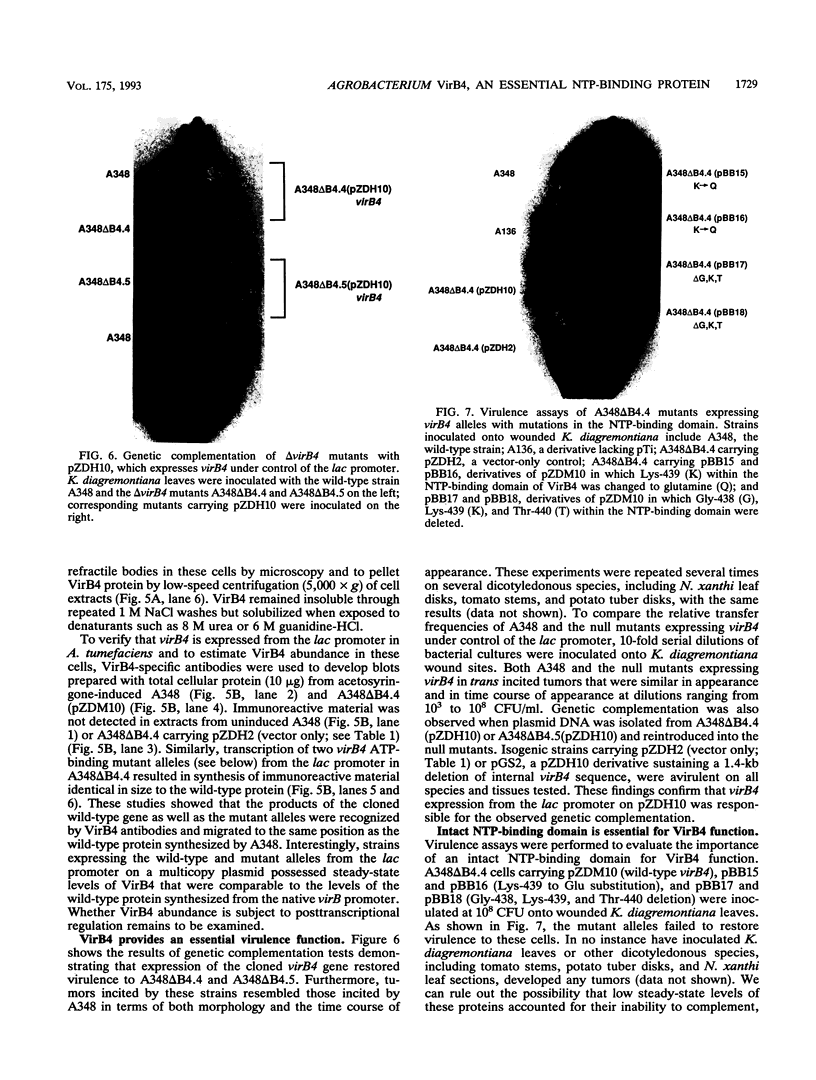
- Gelvin S. B., Habeck L. L. vir genes influence conjugal transfer of the Ti plasmid of Agrobacterium tumefaciens. J Bacteriol. 1990 Mar;172(3):1600–1608. doi: 10.1128/jb.172.3.1600-1608.1990. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Ghai J., Das A. The virD operon of Agrobacterium tumefaciens Ti plasmid encodes a DNA-relaxing enzyme. Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A. 1989 May;86(9):3109–3113. doi: 10.1073/pnas.86.9.3109. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Haber L. T., Walker G. C. Altering the conserved nucleotide binding motif in the Salmonella typhimurium MutS mismatch repair protein affects both its ATPase and mismatch binding activities. EMBO J. 1991 Sep;10(9):2707–2715. doi: 10.1002/j.1460-2075.1991.tb07815.x. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Herrera-Estrella A., Chen Z. M., Van Montagu M., Wang K. VirD proteins of Agrobacterium tumefaciens are required for the formation of a covalent DNA--protein complex at the 5' terminus of T-strand molecules. EMBO J. 1988 Dec 20;7(13):4055–4062. doi: 10.1002/j.1460-2075.1988.tb03299.x. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Higgins C. F., Hiles I. D., Salmond G. P., Gill D. R., Downie J. A., Evans I. J., Holland I. B., Gray L., Buckel S. D., Bell A. W. A family of related ATP-binding subunits coupled to many distinct biological processes in bacteria. Nature. 1986 Oct 2;323(6087):448–450. doi: 10.1038/323448a0. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Horsch R. B., Klee H. J., Stachel S., Winans S. C., Nester E. W., Rogers S. G., Fraley R. T. Analysis of Agrobacterium tumefaciens virulence mutants in leaf discs. Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A. 1986 Apr;83(8):2571–2575. doi: 10.1073/pnas.83.8.2571. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Howard E. A., Winsor B. A., De Vos G., Zambryski P. Activation of the T-DNA transfer process in Agrobacterium results in the generation of a T-strand-protein complex: Tight association of VirD2 with the 5' ends of T-strands. Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A. 1989 Jun;86(11):4017–4021. doi: 10.1073/pnas.86.11.4017. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Howard E. A., Zupan J. R., Citovsky V., Zambryski P. C. The VirD2 protein of A. tumefaciens contains a C-terminal bipartite nuclear localization signal: implications for nuclear uptake of DNA in plant cells. Cell. 1992 Jan 10;68(1):109–118. doi: 10.1016/0092-8674(92)90210-4. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Ippen-Ihler K. A., Minkley E. G., Jr The conjugation system of F, the fertility factor of Escherichia coli. Annu Rev Genet. 1986;20:593–624. doi: 10.1146/annurev.ge.20.120186.003113. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Jayaswal R. K., Veluthambi K., Gelvin S. B., Slightom J. L. Double-stranded cleavage of T-DNA and generation of single-stranded T-DNA molecules in Escherichia coli by a virD-encoded border-specific endonuclease from Agrobacterium tumefaciens. J Bacteriol. 1987 Nov;169(11):5035–5045. doi: 10.1128/jb.169.11.5035-5045.1987. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Jin S. G., Prusti R. K., Roitsch T., Ankenbauer R. G., Nester E. W. Phosphorylation of the VirG protein of Agrobacterium tumefaciens by the autophosphorylated VirA protein: essential role in biological activity of VirG. J Bacteriol. 1990 Sep;172(9):4945–4950. doi: 10.1128/jb.172.9.4945-4950.1990. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Jin S. G., Roitsch T., Christie P. J., Nester E. W. The regulatory VirG protein specifically binds to a cis-acting regulatory sequence involved in transcriptional activation of Agrobacterium tumefaciens virulence genes. J Bacteriol. 1990 Feb;172(2):531–537. doi: 10.1128/jb.172.2.531-537.1990. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Jin S., Roitsch T., Ankenbauer R. G., Gordon M. P., Nester E. W. The VirA protein of Agrobacterium tumefaciens is autophosphorylated and is essential for vir gene regulation. J Bacteriol. 1990 Feb;172(2):525–530. doi: 10.1128/jb.172.2.525-530.1990. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Kamoun S., Tola E., Kamdar H., Kado C. I. Rapid generation of directed and unmarked deletions in Xanthomonas. Mol Microbiol. 1992 Mar;6(6):809–816. doi: 10.1111/j.1365-2958.1992.tb01531.x. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Kaniga K., Delor I., Cornelis G. R. A wide-host-range suicide vector for improving reverse genetics in gram-negative bacteria: inactivation of the blaA gene of Yersinia enterocolitica. Gene. 1991 Dec 20;109(1):137–141. doi: 10.1016/0378-1119(91)90599-7. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Kuldau G. A., De Vos G., Owen J., McCaffrey G., Zambryski P. The virB operon of Agrobacterium tumefaciens pTiC58 encodes 11 open reading frames. Mol Gen Genet. 1990 Apr;221(2):256–266. doi: 10.1007/BF00261729. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Leroux B., Yanofsky M. F., Winans S. C., Ward J. E., Ziegler S. F., Nester E. W. Characterization of the virA locus of Agrobacterium tumefaciens: a transcriptional regulator and host range determinant. EMBO J. 1987 Apr;6(4):849–856. doi: 10.1002/j.1460-2075.1987.tb04830.x. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Lessl M., Balzer D., Pansegrau W., Lanka E. Sequence similarities between the RP4 Tra2 and the Ti VirB region strongly support the conjugation model for T-DNA transfer. J Biol Chem. 1992 Oct 5;267(28):20471–20480. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Miller V. L., Mekalanos J. J. A novel suicide vector and its use in construction of insertion mutations: osmoregulation of outer membrane proteins and virulence determinants in Vibrio cholerae requires toxR. J Bacteriol. 1988 Jun;170(6):2575–2583. doi: 10.1128/jb.170.6.2575-2583.1988. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Ooms G., Hooykaas P. J., Van Veen R. J., Van Beelen P., Regensburg-Tuïnk T. J., Schilperoort R. A. Octopine Ti-plasmid deletion mutants of agrobacterium tumefaciens with emphasis on the right side of the T-region. Plasmid. 1982 Jan;7(1):15–29. doi: 10.1016/0147-619x(82)90023-3. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Panicker M. M., Minkley E. G., Jr Purification and properties of the F sex factor TraD protein, an inner membrane conjugal transfer protein. J Biol Chem. 1992 Jun 25;267(18):12761–12766. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Peralta E. G., Hellmiss R., Ream W. Overdrive, a T-DNA transmission enhancer on the A. tumefaciens tumour-inducing plasmid. EMBO J. 1986 Jun;5(6):1137–1142. doi: 10.1002/j.1460-2075.1986.tb04338.x. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Ried J. L., Collmer A. An nptI-sacB-sacR cartridge for constructing directed, unmarked mutations in gram-negative bacteria by marker exchange-eviction mutagenesis. Gene. 1987;57(2-3):239–246. doi: 10.1016/0378-1119(87)90127-2. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Rogowsky P. M., Close T. J., Chimera J. A., Shaw J. J., Kado C. I. Regulation of the vir genes of Agrobacterium tumefaciens plasmid pTiC58. J Bacteriol. 1987 Nov;169(11):5101–5112. doi: 10.1128/jb.169.11.5101-5112.1987. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Scheer U., Dabauvalle M. C., Merkert H., Benevente R. The nuclear envelope and the organization of the pore complexes. Cell Biol Int Rep. 1988 Sep;12(9):669–689. doi: 10.1016/0309-1651(88)90083-5. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Schweizer H. P. Allelic exchange in Pseudomonas aeruginosa using novel ColE1-type vectors and a family of cassettes containing a portable oriT and the counter-selectable Bacillus subtilis sacB marker. Mol Microbiol. 1992 May;6(9):1195–1204. doi: 10.1111/j.1365-2958.1992.tb01558.x. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Shimoda N., Toyoda-Yamamoto A., Nagamine J., Usami S., Katayama M., Sakagami Y., Machida Y. Control of expression of Agrobacterium vir genes by synergistic actions of phenolic signal molecules and monosaccharides. Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A. 1990 Sep;87(17):6684–6688. doi: 10.1073/pnas.87.17.6684. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Shirasu K., Morel P., Kado C. I. Characterization of the virB operon of an Agrobacterium tumefaciens Ti plasmid: nucleotide sequence and protein analysis. Mol Microbiol. 1990 Jul;4(7):1153–1163. doi: 10.1111/j.1365-2958.1990.tb00690.x. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Stachel S. E., Nester E. W. The genetic and transcriptional organization of the vir region of the A6 Ti plasmid of Agrobacterium tumefaciens. EMBO J. 1986 Jul;5(7):1445–1454. doi: 10.1002/j.1460-2075.1986.tb04381.x. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Stachel S. E., Timmerman B., Zambryski P. Activation of Agrobacterium tumefaciens vir gene expression generates multiple single-stranded T-strand molecules from the pTiA6 T-region: requirement for 5' virD gene products. EMBO J. 1987 Apr;6(4):857–863. doi: 10.1002/j.1460-2075.1987.tb04831.x. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Stachel S. E., Zambryski P. C. Agrobacterium tumefaciens and the susceptible plant cell: a novel adaptation of extracellular recognition and DNA conjugation. Cell. 1986 Oct 24;47(2):155–157. doi: 10.1016/0092-8674(86)90437-x. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Stachel S. E., Zambryski P. C. virA and virG control the plant-induced activation of the T-DNA transfer process of A. tumefaciens. Cell. 1986 Aug 1;46(3):325–333. doi: 10.1016/0092-8674(86)90653-7. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Steck T. R., Close T. J., Kado C. I. High levels of double-stranded transferred DNA (T-DNA) processing from an intact nopaline Ti plasmid. Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A. 1989 Apr;86(7):2133–2137. doi: 10.1073/pnas.86.7.2133. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Sung P., Higgins D., Prakash L., Prakash S. Mutation of lysine-48 to arginine in the yeast RAD3 protein abolishes its ATPase and DNA helicase activities but not the ability to bind ATP. EMBO J. 1988 Oct;7(10):3263–3269. doi: 10.1002/j.1460-2075.1988.tb03193.x. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Thompson D. V., Melchers L. S., Idler K. B., Schilperoort R. A., Hooykaas P. J. Analysis of the complete nucleotide sequence of the Agrobacterium tumefaciens virB operon. Nucleic Acids Res. 1988 May 25;16(10):4621–4636. doi: 10.1093/nar/16.10.4621. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Toro N., Datta A., Carmi O. A., Young C., Prusti R. K., Nester E. W. The Agrobacterium tumefaciens virC1 gene product binds to overdrive, a T-DNA transfer enhancer. J Bacteriol. 1989 Dec;171(12):6845–6849. doi: 10.1128/jb.171.12.6845-6849.1989. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Toro N., Datta A., Yanofsky M., Nester E. Role of the overdrive sequence in T-DNA border cleavage in Agrobacterium. Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A. 1988 Nov;85(22):8558–8562. doi: 10.1073/pnas.85.22.8558. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Vogel A. M., Das A. The Agrobacterium tumefaciens virD3 gene is not essential for tumorigenicity on plants. J Bacteriol. 1992 Aug;174(15):5161–5164. doi: 10.1128/jb.174.15.5161-5164.1992. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Walker J. E., Saraste M., Runswick M. J., Gay N. J. Distantly related sequences in the alpha- and beta-subunits of ATP synthase, myosin, kinases and other ATP-requiring enzymes and a common nucleotide binding fold. EMBO J. 1982;1(8):945–951. doi: 10.1002/j.1460-2075.1982.tb01276.x. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Wang K., Stachel S. E., Timmerman B., VAN Montagu M., Zambryski P. C. Site-Specific Nick in the T-DNA Border Sequence as a Result of Agrobacterium vir Gene Expression. Science. 1987 Jan 30;235(4788):587–591. doi: 10.1126/science.235.4788.587. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Ward J. E., Akiyoshi D. E., Regier D., Datta A., Gordon M. P., Nester E. W. Characterization of the virB operon from an Agrobacterium tumefaciens Ti plasmid. J Biol Chem. 1988 Apr 25;263(12):5804–5814. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Ward J. E., Akiyoshi D. E., Regier D., Datta A., Gordon M. P., Nester E. W. Correction: characterization of the virB operon from Agrobacterium tumefaciens Ti plasmid. J Biol Chem. 1990 Mar 15;265(8):4768–4768. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Ward J. E., Jr, Dale E. M., Binns A. N. Activity of the Agrobacterium T-DNA transfer machinery is affected by virB gene products. Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A. 1991 Oct 15;88(20):9350–9354. doi: 10.1073/pnas.88.20.9350. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Ward J. E., Jr, Dale E. M., Christie P. J., Nester E. W., Binns A. N. Complementation analysis of Agrobacterium tumefaciens Ti plasmid virB genes by use of a vir promoter expression vector: virB9, virB10, and virB11 are essential virulence genes. J Bacteriol. 1990 Sep;172(9):5187–5199. doi: 10.1128/jb.172.9.5187-5199.1990. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Ward J. E., Jr, Dale E. M., Nester E. W., Binns A. N. Identification of a virB10 protein aggregate in the inner membrane of Agrobacterium tumefaciens. J Bacteriol. 1990 Sep;172(9):5200–5210. doi: 10.1128/jb.172.9.5200-5210.1990. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Winans S. C., Ebert P. R., Stachel S. E., Gordon M. P., Nester E. W. A gene essential for Agrobacterium virulence is homologous to a family of positive regulatory loci. Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A. 1986 Nov;83(21):8278–8282. doi: 10.1073/pnas.83.21.8278. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Winans S. C. Two-way chemical signaling in Agrobacterium-plant interactions. Microbiol Rev. 1992 Mar;56(1):12–31. doi: 10.1128/mr.56.1.12-31.1992. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Yanofsky M. F., Porter S. G., Young C., Albright L. M., Gordon M. P., Nester E. W. The virD operon of Agrobacterium tumefaciens encodes a site-specific endonuclease. Cell. 1986 Nov 7;47(3):471–477. doi: 10.1016/0092-8674(86)90604-5. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Young C., Nester E. W. Association of the virD2 protein with the 5' end of T strands in Agrobacterium tumefaciens. J Bacteriol. 1988 Aug;170(8):3367–3374. doi: 10.1128/jb.170.8.3367-3374.1988. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Zambryski P. Basic processes underlying Agrobacterium-mediated DNA transfer to plant cells. Annu Rev Genet. 1988;22:1–30. doi: 10.1146/annurev.ge.22.120188.000245. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]