Abstract
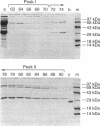
The red genes of bacteriophage lambda specify two proteins, exonuclease and beta protein, which are essential for general recombination of lambda in recA cells. Earlier studies suggested that these proteins form an equimolar complex (C. M. Radding, J. Rosenweig, F. Richards, and E. Cassuto, J. Biol. Chem. 246:2510-2512, 1971). A more recent study indicated that beta protein forms a strong complex with an unknown polypeptide of 70 kDa (K. Muniyappa and C. M. Radding, J. Biol. Chem. 261:7472-7478, 1986). In the present study, in addition to the complex of beta and the 70-kDa protein, a new association of beta protein with a 65-kDa protein was observed. N-terminal sequencing identified these proteins as host-encoded ribosomal protein S1 and transcription terminator protein NusA.
Full text
PDF

Images in this article
Selected References
These references are in PubMed. This may not be the complete list of references from this article.
- Ben-Ishai R., Scharf R., Sharon R., Kapten I. A human cellular sequence implicated in trk oncogene activation is DNA damage inducible. Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A. 1990 Aug;87(16):6039–6043. doi: 10.1073/pnas.87.16.6039. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Carter D. M., Radding C. M. The role of exonuclease and beta protein of phage lambda in genetic recombination. II. Substrate specificity and the mode of action of lambda exonuclease. J Biol Chem. 1971 Apr 25;246(8):2502–2512. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Cassuto E., Lash T., Sriprakash K. S., Radding C. M. Role of exonuclease and beta protein of phage lambda in genetic recombination. V. Recombination of lambda DNA in vitro. Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A. 1971 Jul;68(7):1639–1643. doi: 10.1073/pnas.68.7.1639. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Cassuto E., Radding C. M. Mechanism for the action of lambda exonuclease in genetic recombination. Nat New Biol. 1971 Jan 6;229(1):13–16. doi: 10.1038/newbio229013a0. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Das A. How the phage lambda N gene product suppresses transcription termination: communication of RNA polymerase with regulatory proteins mediated by signals in nascent RNA. J Bacteriol. 1992 Nov;174(21):6711–6716. doi: 10.1128/jb.174.21.6711-6716.1992. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Friedman D. I., Schauer A. T., Baumann M. R., Baron L. S., Adhya S. L. Evidence that ribosomal protein S10 participates in control of transcription termination. Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A. 1981 Feb;78(2):1115–1118. doi: 10.1073/pnas.78.2.1115. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Grabowski D. T., Pieper R. O., Futscher B. W., Deutsch W. A., Erickson L. C., Kelley M. R. Expression of ribosomal phosphoprotein PO is induced by antitumor agents and increased in Mer- human tumor cell lines. Carcinogenesis. 1992 Feb;13(2):259–263. doi: 10.1093/carcin/13.2.259. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Kmiec E., Holloman W. K. Beta protein of bacteriophage lambda promotes renaturation of DNA. J Biol Chem. 1981 Dec 25;256(24):12636–12639. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Kyte J., Doolittle R. F. A simple method for displaying the hydropathic character of a protein. J Mol Biol. 1982 May 5;157(1):105–132. doi: 10.1016/0022-2836(82)90515-0. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Laemmli U. K. Cleavage of structural proteins during the assembly of the head of bacteriophage T4. Nature. 1970 Aug 15;227(5259):680–685. doi: 10.1038/227680a0. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Little J. W. An exonuclease induced by bacteriophage lambda. II. Nature of the enzymatic reaction. J Biol Chem. 1967 Feb 25;242(4):679–686. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Matsudaira P. Limited N-terminal sequence analysis. Methods Enzymol. 1990;182:602–613. doi: 10.1016/0076-6879(90)82047-6. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Muniyappa K., Radding C. M. The homologous recombination system of phage lambda. Pairing activities of beta protein. J Biol Chem. 1986 Jun 5;261(16):7472–7478. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Muniyappa K., Shaner S. L., Tsang S. S., Radding C. M. Mechanism of the concerted action of recA protein and helix-destabilizing proteins in homologous recombination. Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A. 1984 May;81(9):2757–2761. doi: 10.1073/pnas.81.9.2757. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Radding C. M. Regulation of lambda exonuclease. I. Properties of lambda exonuclease purified from lysogens of lambda T11 and wild type. J Mol Biol. 1966 Jul;18(2):235–250. doi: 10.1016/s0022-2836(66)80243-7. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Rice P. A., Steitz T. A. Ribosomal protein L7/L12 has a helix-turn-helix motif similar to that found in DNA-binding regulatory proteins. Nucleic Acids Res. 1989 May 25;17(10):3757–3762. doi: 10.1093/nar/17.10.3757. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Rich B. E., Steitz J. A. Human acidic ribosomal phosphoproteins P0, P1, and P2: analysis of cDNA clones, in vitro synthesis, and assembly. Mol Cell Biol. 1987 Nov;7(11):4065–4074. doi: 10.1128/mcb.7.11.4065. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Signer E., Echols H., Weil J., Radding C., Shulman M., Moore L., Manly K. The general recombination system of bacteriophage lambda. Cold Spring Harb Symp Quant Biol. 1968;33:711–714. doi: 10.1101/sqb.1968.033.01.080. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Sriprakash K. S., Lundh N., Huh MM-O, Radding C. M. The specificity of lambda exonuclease. Interactions with single-stranded DNA. J Biol Chem. 1975 Jul 25;250(14):5438–5445. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Watson K. L., Konrad K. D., Woods D. F., Bryant P. J. Drosophila homolog of the human S6 ribosomal protein is required for tumor suppression in the hematopoietic system. Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A. 1992 Dec 1;89(23):11302–11306. doi: 10.1073/pnas.89.23.11302. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]