Abstract
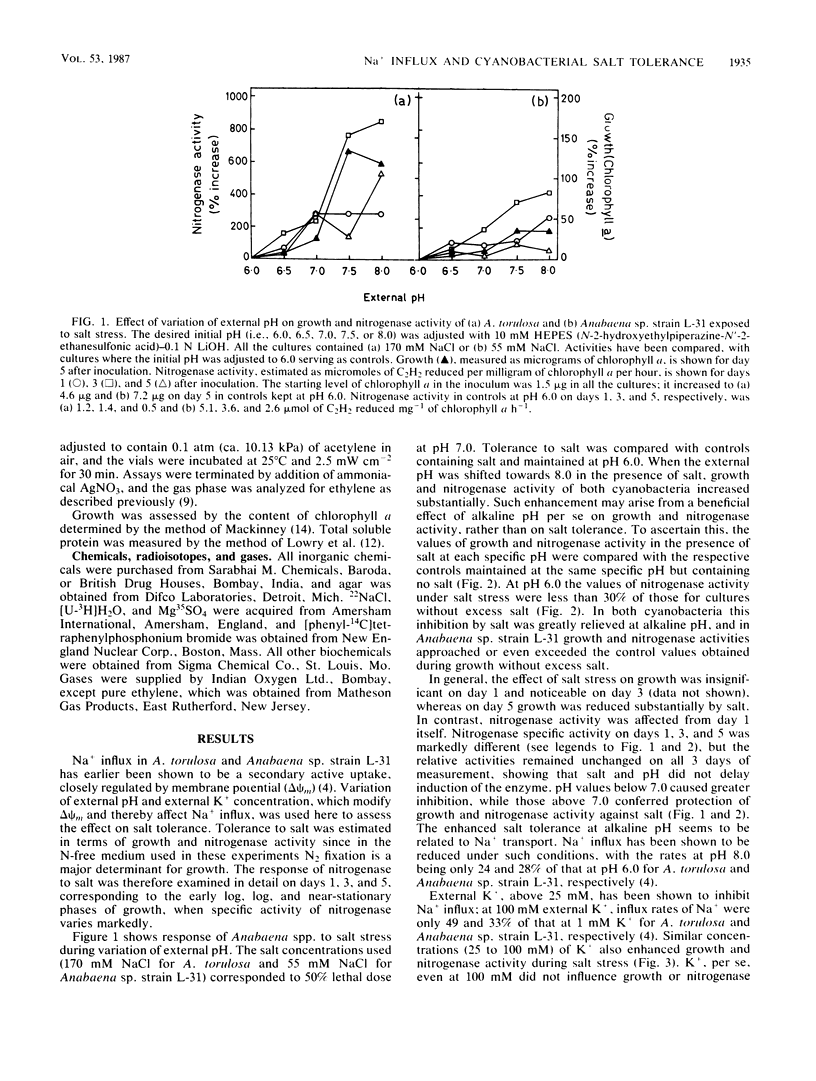
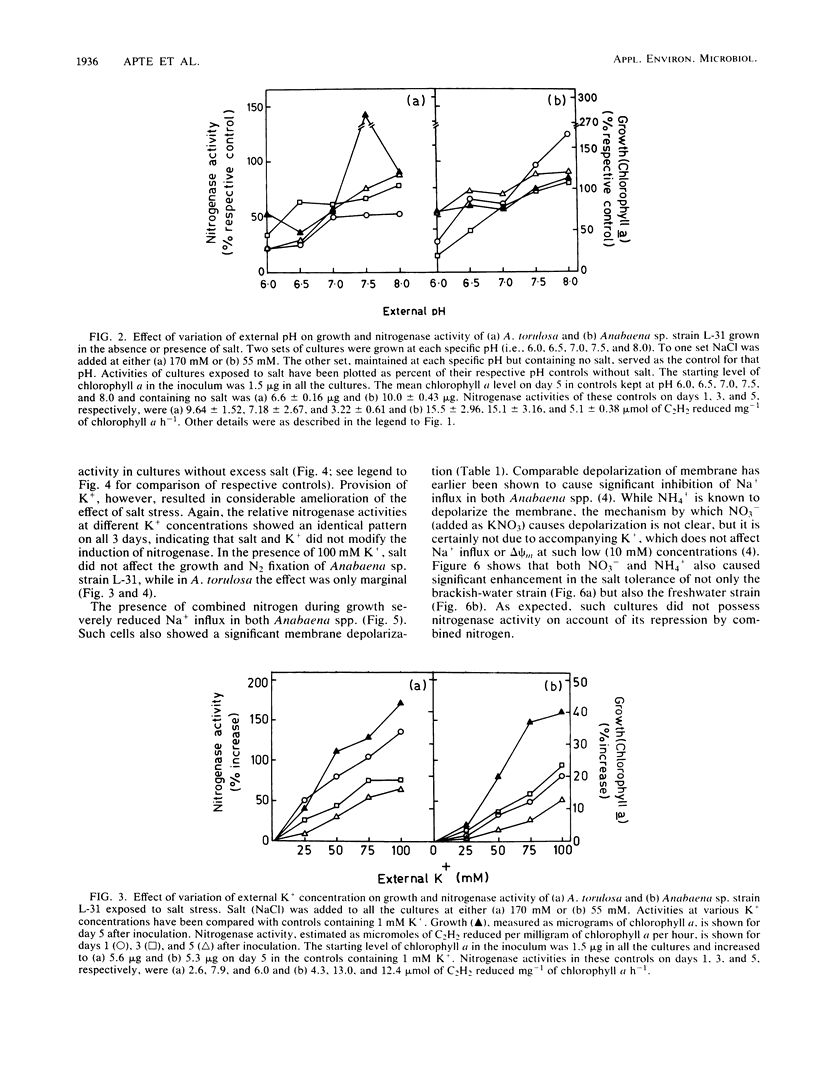
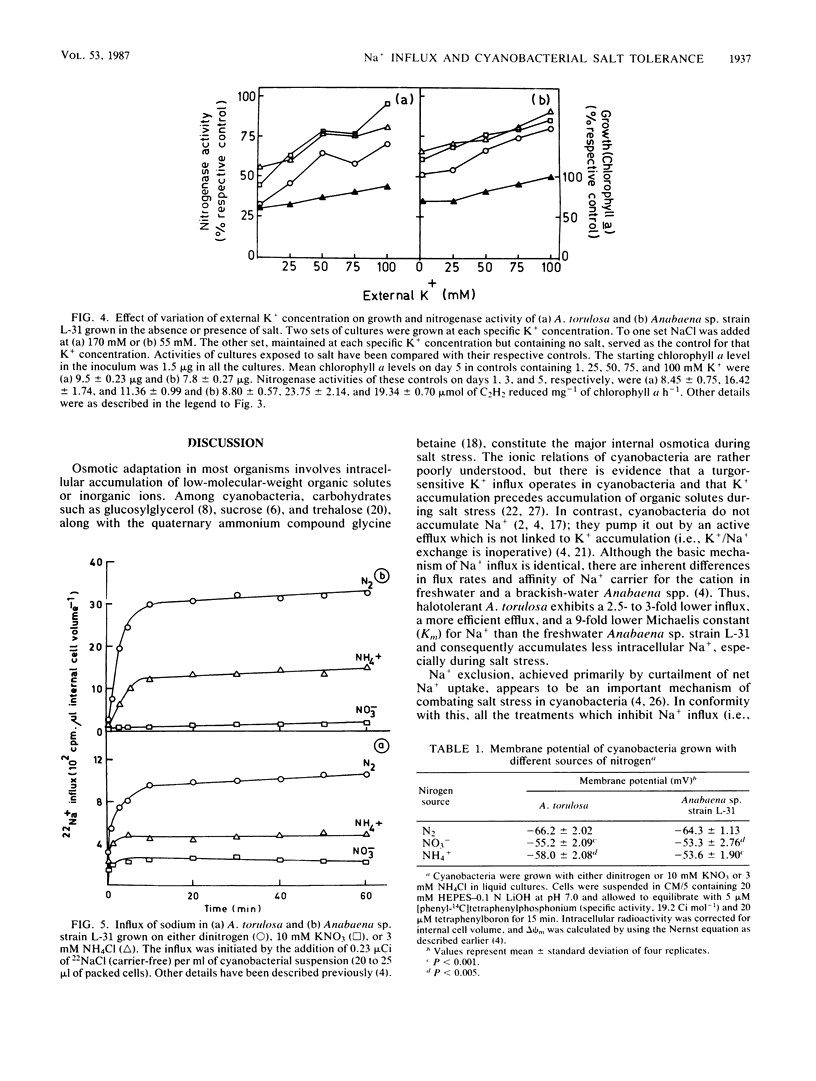
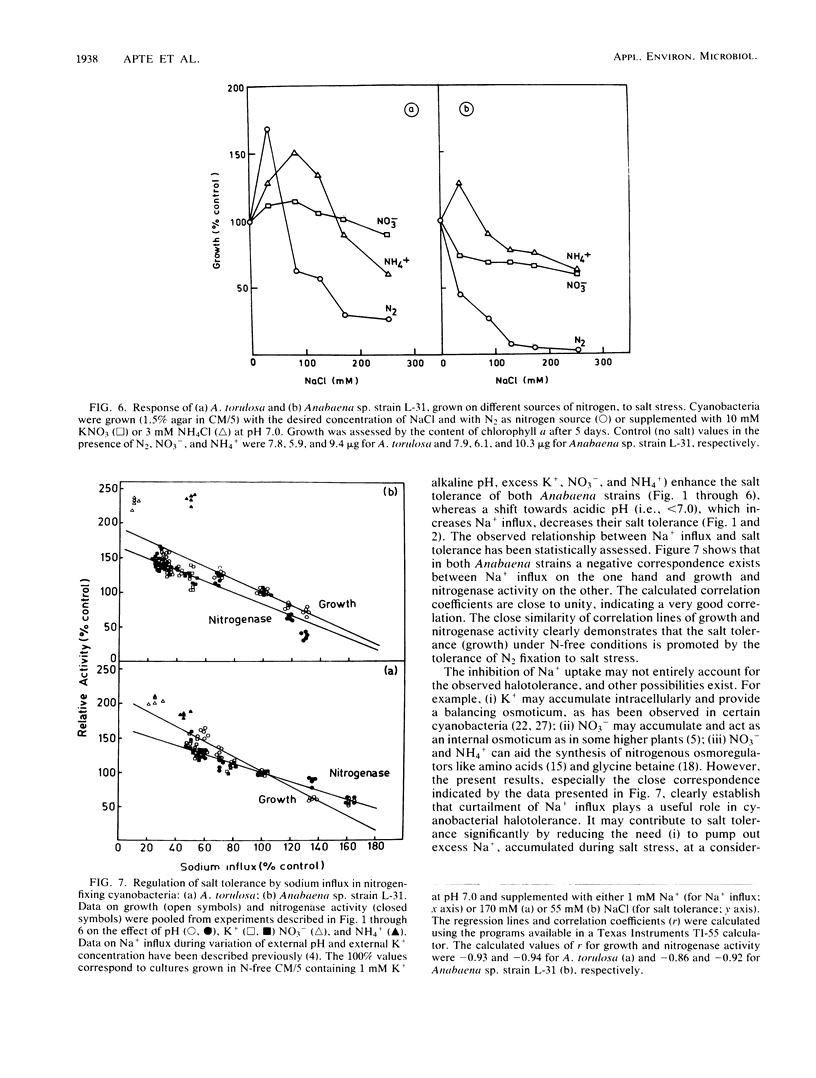
The relationship between sodium uptake and cyanobacterial salt (NaCl) tolerance has been examined in two filamentous, heterocystous, nitrogen-fixing species of Anabaena. During diazotrophic growth at neutral pH of the growth medium, Anabaena sp. strain L-31, a freshwater strain, showed threefold higher uptake of Na+ than Anabaena torulosa, a brackish-water strain, and was considerably less salt tolerant (50% lethal dose of NaCl, 55 mM) than the latter (50% lethal dose of NaCl, 170 mM). Alkaline pH or excess K+ (>25 mM) in the medium causes membrane depolarization and inhibits Na+ influx in both cyanobacteria (S. K. Apte and J. Thomas, Eur. J. Biochem. 154:395-401, 1986). The presence of nitrate or ammonium in the medium caused inhibition of Na+ influx accompanied by membrane depolarization. These experimental manipulations affecting Na+ uptake demonstrated a good negative correlation between Na+ influx and salt tolerance. All treatments which inhibited Na+ influx (such as alkaline pH, K+ above 25 mM, NO3−, and NH4+), enhanced salt tolerance of not only the brackish-water but also the freshwater cyanobacterium. The results indicate that curtailment of Na+ influx, whether inherent or effected by certain environmental factors (e.g., combined nitrogen, alkaline pH), is a major mechanism of salt tolerance in cyanobacteria.
Full text
PDF

Selected References
These references are in PubMed. This may not be the complete list of references from this article.
- Apte S. K., Thomas J. Membrane electrogenesis and sodium transport in filamentous nitrogen-fixing cyanobacteria. Eur J Biochem. 1986 Jan 15;154(2):395–401. doi: 10.1111/j.1432-1033.1986.tb09411.x. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Blumwald E., Mehlhorn R. J., Packer L. Studies of osmoregulation in salt adaptation of cyanobacteria with ESR spin-probe techniques. Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A. 1983 May;80(9):2599–2602. doi: 10.1073/pnas.80.9.2599. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Blumwald E., Tel-Or E. Salt adaptation of the cyanobacterium synechococcus 6311 growing in a continuous culture (turbidostat). Plant Physiol. 1984 Jan;74(1):183–185. doi: 10.1104/pp.74.1.183. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Borowitzka L. J., Demmerle S., Mackay M. A., Norton R. S. Carbon-13 nuclear magnetic resonance study of osmoregulation in a blue-green alga. Science. 1980 Nov 7;210(4470):650–651. doi: 10.1126/science.210.4470.650. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- David K. A., Apte S. K., Banerji A., Thomas J. Acetylene reduction assay for nitrogenase activity: gas chromatographic determination of ethylene per sample in less than one minute. Appl Environ Microbiol. 1980 May;39(5):1078–1080. doi: 10.1128/aem.39.5.1078-1080.1980. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- LOWRY O. H., ROSEBROUGH N. J., FARR A. L., RANDALL R. J. Protein measurement with the Folin phenol reagent. J Biol Chem. 1951 Nov;193(1):265–275. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Measures J. C. Role of amino acids in osmoregulation of non-halophilic bacteria. Nature. 1975 Oct 2;257(5525):398–400. doi: 10.1038/257398a0. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Miller D. M., Jones J. H., Yopp J. H., Tindall D. R., Schmid W. E. Ion metabolism in a halophilic blue-green alga, Aphanothece halophytica. Arch Microbiol. 1976 Dec 1;111(1-2):145–149. doi: 10.1007/BF00446561. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Paschinger H. DCCD induced sodium uptake by Anacystis nidulans. Arch Microbiol. 1977 Jun 20;113(3):285–291. doi: 10.1007/BF00492037. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Reed R. H., Rowell P., Stewart W. D. Characterization of the transport of potassium ions in the cyanobacterium Anabaena variabilis Kütz. Eur J Biochem. 1981 May 15;116(2):323–330. doi: 10.1111/j.1432-1033.1981.tb05337.x. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Rottenberg H. The measurement of membrane potential and deltapH in cells, organelles, and vesicles. Methods Enzymol. 1979;55:547–569. doi: 10.1016/0076-6879(79)55066-6. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Thomas J. Absence of the pigments of photosystem II of photosynthesis in heterocysts of a blue-green alga. Nature. 1970 Oct 10;228(5267):181–183. doi: 10.1038/228181b0. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]



