Abstract
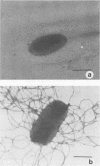
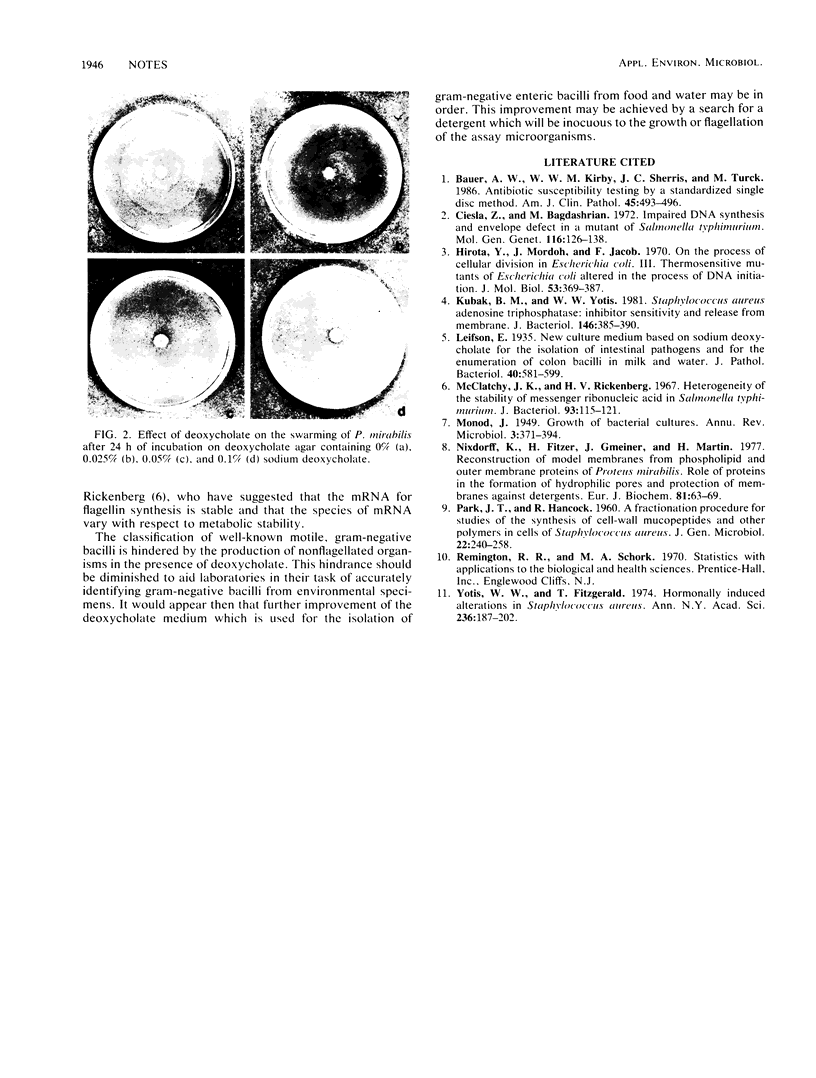
Sodium deoxycholate is used in a number of bacteriological media for the isolation and classification of gram-negative bacteria from food and the environment. Initial experiments to study the effect of deoxycholate on the growth parameters of Escherichia coli showed an increase in the lag time constant and generation time and a decrease in the growth rate constant and total cell yield of this microorganism. Cell fractionation studies indicated that sodium deoxycholate at levels used in bacteriological media interferes with the incorporation of [U-14C]glucose into the cold-trichloroacetic acid-soluble, ethanol-soluble, and trypsin-soluble cellular fractions of E. coli. Finally, sodium deoxycholate interfered with the flagellation and motility of Proteus mirabilis and E. coli. It would appear then that further improvement of the deoxycholate medium may be in order.
Full text
PDF

Images in this article
Selected References
These references are in PubMed. This may not be the complete list of references from this article.
- Bauer A. W., Kirby W. M., Sherris J. C., Turck M. Antibiotic susceptibility testing by a standardized single disk method. Am J Clin Pathol. 1966 Apr;45(4):493–496. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Cieśla Z., Bagdassarian M. Imparired DNA synthesis and envelope defect in a mutant of Salmonella typhimurium. Mol Gen Genet. 1972;116(2):126–138. doi: 10.1007/BF00582222. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Hirota Y., Mordoh J., Jacob F. On the process of cellular division in Escherichia coli. 3. Thermosensitive mutants of Escherichia coli altered in the process of DNA initiation. J Mol Biol. 1970 Nov 14;53(3):369–387. doi: 10.1016/0022-2836(70)90072-0. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Kubak B. M., Yotis W. W. Staphylococcus aureus adenosine triphosphatase: inhibitor sensitivity and release from membrane. J Bacteriol. 1981 Apr;146(1):385–390. doi: 10.1128/jb.146.1.385-390.1981. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- McClatchy J. K., Rickenberg H. V. Heterogeneity of the stability of messenger ribonucleic acid in Salmonella typhimurium. J Bacteriol. 1967 Jan;93(1):115–121. doi: 10.1128/jb.93.1.115-121.1967. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Nixdorff K., Fitzer H., Gmeiner J., Martin H. H. Reconstitution of model membranes from phospholipid and outer membrane proteins of Proteus mirabilis. Role of proteins in the formation of hydrophilic pores and protection of membranes against detergents. Eur J Biochem. 1977 Nov 15;81(1):63–69. doi: 10.1111/j.1432-1033.1977.tb11927.x. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- PARK J. T., HANCOCK R. A fractionation procedure for studies of the synthesis of cell-wall mucopeptide and of other polymers in cells of Staphylococcus aureus. J Gen Microbiol. 1960 Feb;22:249–258. doi: 10.1099/00221287-22-1-249. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Yotis W. W., Fitzgerald T. Hormonally induced alterations in S. aureus. Ann N Y Acad Sci. 1974 Jul 31;236(0):187–202. doi: 10.1111/j.1749-6632.1974.tb41491.x. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]