Abstract
Determination of [3H] thymidine incorporation into bacterial DNA versus other macromolecules is usually achieved by NaOH and hot trichloroacetic acid hydrolysis. This procedure was found not to be specific enough. An alternative method founded on DNase treatment is proposed. Under the new method, the fraction of thymidine incorporated into DNA ranged from 10 to 83%.
Full text
PDF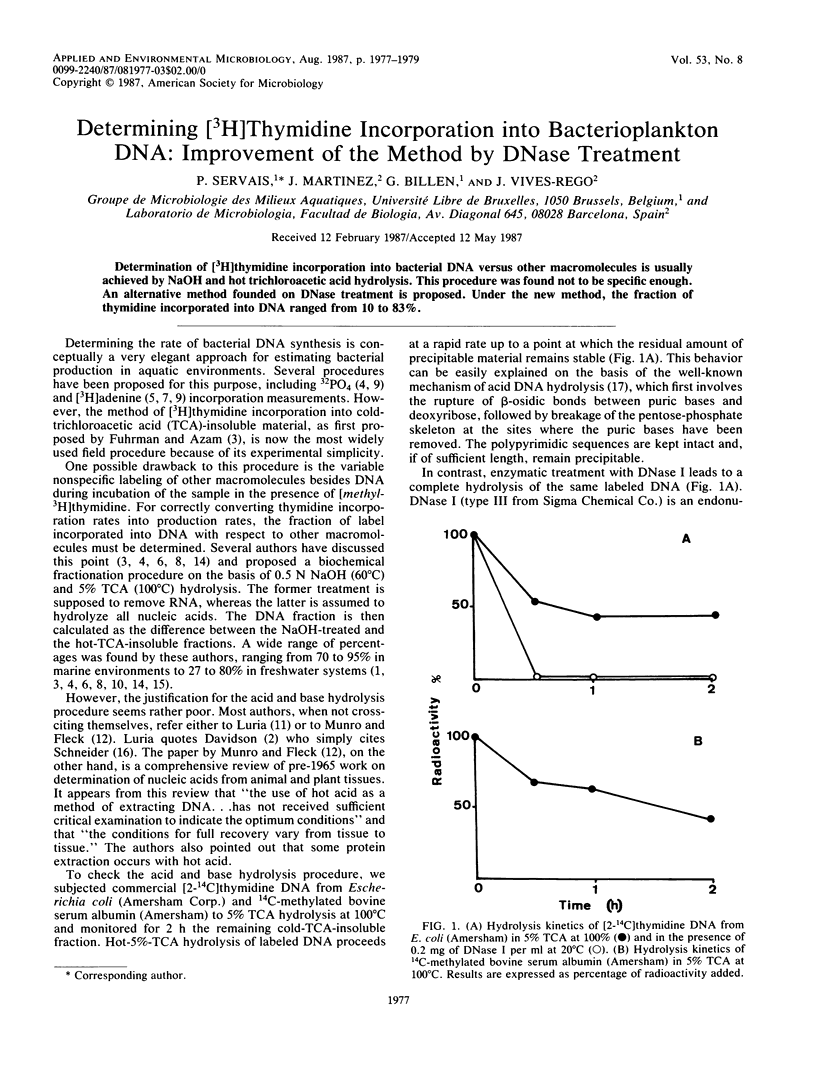

Selected References
These references are in PubMed. This may not be the complete list of references from this article.
- Bell R. T., Kuparinen J. Assessing phytoplankton and bacterioplankton production during early spring in lake erken, sweden. Appl Environ Microbiol. 1984 Dec;48(6):1221–1230. doi: 10.1128/aem.48.6.1221-1230.1984. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Fischer E., Graf F., Carli S. Rhythmusstörungen und Symptome Während Langzeit-EKG bei ambulanten Patienten. Schweiz Rundsch Med Prax. 1984 Jan 17;73(3):59–65. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Fuhrman J. A., Azam F. Bacterioplankton secondary production estimates for coastal waters of british columbia, antarctica, and california. Appl Environ Microbiol. 1980 Jun;39(6):1085–1095. doi: 10.1128/aem.39.6.1085-1095.1980. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Karl D. M. Selected nucleic Acid precursors in studies of aquatic microbial ecology. Appl Environ Microbiol. 1982 Oct;44(4):891–902. doi: 10.1128/aem.44.4.891-902.1982. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Karl D. M. Simultaneous rates of ribonucleic Acid and deoxyribonucleic Acid syntheses for estimating growth and cell division of aquatic microbial communities. Appl Environ Microbiol. 1981 Nov;42(5):802–810. doi: 10.1128/aem.42.5.802-810.1981. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Lovell C. R., Konopka A. Primary and bacterial production in two dimictic indiana lakes. Appl Environ Microbiol. 1985 Mar;49(3):485–491. doi: 10.1128/aem.49.3.485-491.1985. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Munro H. N. The determination of nucleic acids. Methods Biochem Anal. 1966;14:113–176. doi: 10.1002/9780470110324.ch5. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Paul J. H., Myers B. Fluorometric determination of DNA in aquatic microorganisms by use of hoechst 33258. Appl Environ Microbiol. 1982 Jun;43(6):1393–1399. doi: 10.1128/aem.43.6.1393-1399.1982. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Riemann B., Søndergaard M. Measurements of diel rates of bacterial secondary production in aquatic environments. Appl Environ Microbiol. 1984 Apr;47(4):632–638. doi: 10.1128/aem.47.4.632-638.1984. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- THOMAS R. Réactions chimiques au cours de l'hydrolyse préalable à la réaction de Feulgen. Bull Soc Chim Biol (Paris) 1950;32(7-8):469–472. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]



