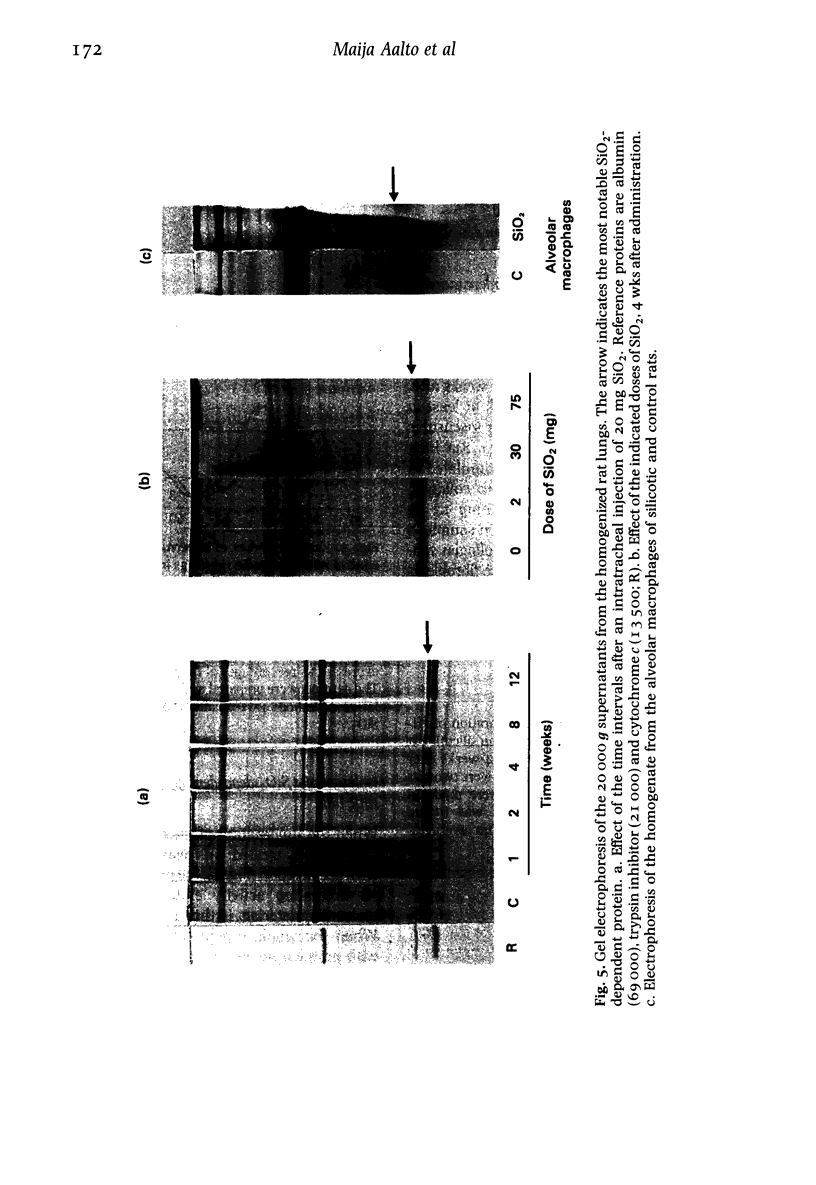
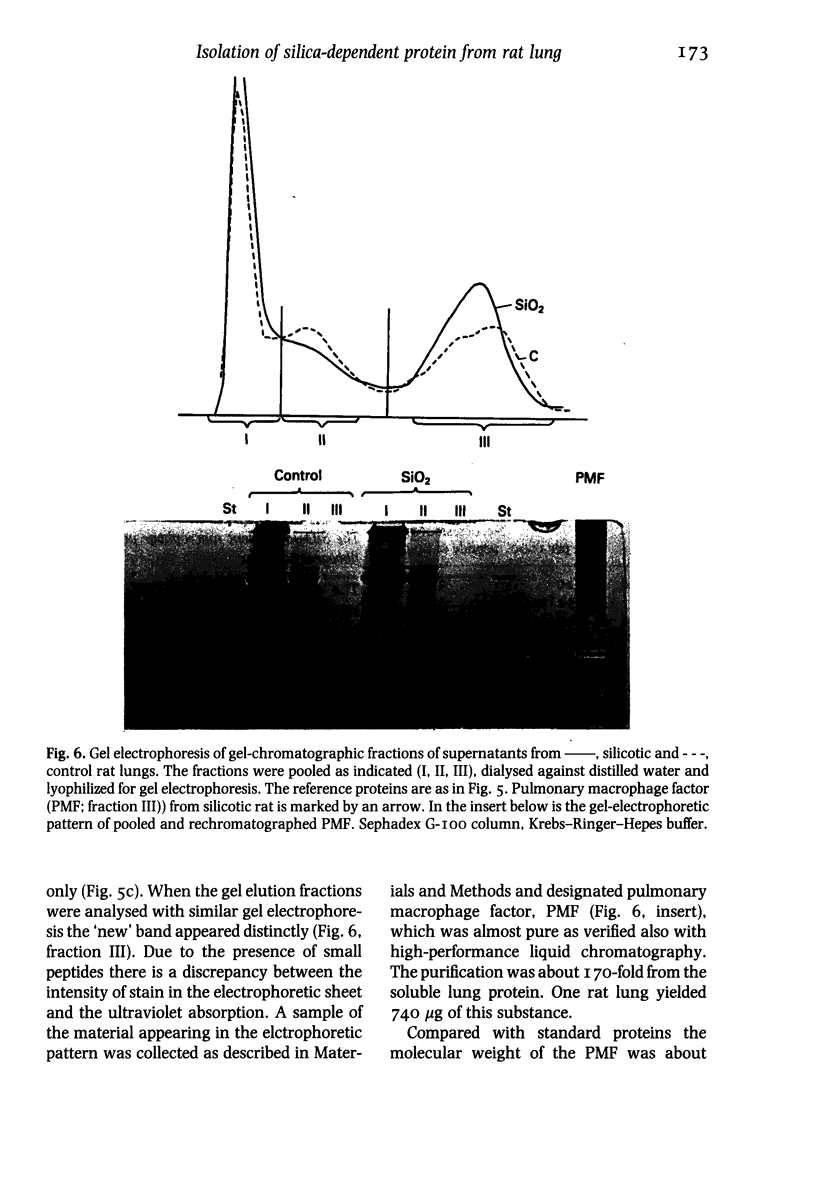
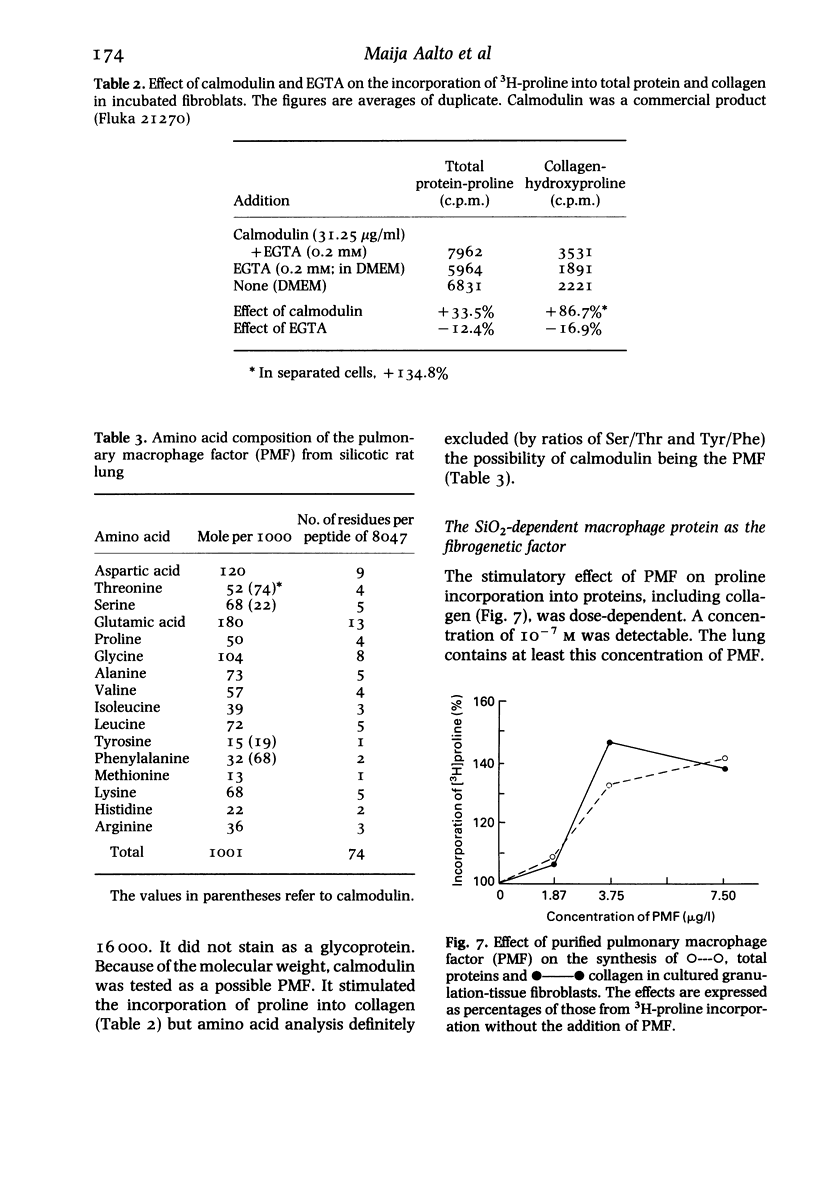
Abstract
Silicosis was produced experimentally in rats by single intratracheal injections of various doses of SiO2 dust. The weight of the lungs as well as the contents of total nitrogen, collagen, nucleic acids (especially RNA), and lipids increased in accordance with the dose and the time interval. Fibrogenic stimulation in vitro was shown by the supernatant of the homogenized lung in the incorporation of proline into incubated granulation tissue or lung fibroblasts. The fibrogenic factor-activity depended more on the time interval after the injection than on the SiO2 dose. Electrophoresis of the soluble proteins in the silicotic rat lungs showed a protein of 16,000 Da, which was dependent on the time interval following SiO2 administration as well as on the dose itself, and which originated from macrophages. This protein was purified by repeated gel-filtration chromatography. It stimulated collagen synthesis in granulation-tissue cells at a concentration of about 10(-10) M in a dose-dependent way. It was acidic by amino acid composition but differed from calmodulin which also increased collagen synthesis in granulation-tissue cells in vitro. The ability of non-fractionated macrophage preparations to stimulate the incorporation of proline into collagen correlated inversely with the gross alkaline RNase activity.
Full text
PDF










Images in this article
Selected References
These references are in PubMed. This may not be the complete list of references from this article.
- Aalto M., Kulonen E. Fractionation of connective-tissue-activating factors from the culture medium of silica-treated macrophages. Acta Pathol Microbiol Scand C. 1979 Jun;87C(3):241–250. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Aalto M., Kulonen E., Penttinen R., Renvall S. Collagen synthesis in cultured mesothelial cells. Response to silica. Acta Chir Scand. 1981;147(1):1–6. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Aalto M., Potila M., Kulonen E. The effect of silica-treated macrophages on the synthesis of collagen and other proteins in vitro. Exp Cell Res. 1976 Jan;97:193–202. doi: 10.1016/0014-4827(76)90668-6. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Aalto M., Potila M., Kulonen E. The effect of silica-treated macrophages on the synthesis of collagen and other proteins in vitro. Exp Cell Res. 1976 Jan;97:193–202. doi: 10.1016/0014-4827(76)90668-6. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Aalto M., Turakainen H., Kulonen E. Effect of SiO2-liberated macrophage factor on protein synthesis in connective tissue in vitro. Scand J Clin Lab Invest. 1979 May;39(3):205–213. doi: 10.1080/00365517909106095. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Aho S., Kulonen E. Involvement of ribonuclease in the interactions of macrophages and fibroblasts in experimental silicosis. Experientia. 1980 Jan 15;36(1):29–31. doi: 10.1007/BF02003951. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Aho S., Kulonen E. Involvement of ribonuclease in the interactions of macrophages and fibroblasts in experimental silicosis. Experientia. 1980 Jan 15;36(1):29–31. doi: 10.1007/BF02003951. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Aho S., Peltonen J., Jalkanen M., Kulonen E. Effect of silica on a culture of rat peritoneal macrophages. Ann Occup Hyg. 1979;22(3):285–296. doi: 10.1093/annhyg/22.3.285. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- BARTLETT G. R. Phosphorus assay in column chromatography. J Biol Chem. 1959 Mar;234(3):466–468. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- BURTON K. A study of the conditions and mechanism of the diphenylamine reaction for the colorimetric estimation of deoxyribonucleic acid. Biochem J. 1956 Feb;62(2):315–323. doi: 10.1042/bj0620315. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Badzio T., Boczon H. The determination of free and esterified cholesterol in blood after separation by thin-layer chromatography. Clin Chim Acta. 1966 Jun;13(6):794–797. doi: 10.1016/0009-8981(66)90152-5. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Bitterman P. B., Rennard S. I., Hunninghake G. W., Crystal R. G. Human alveolar macrophage growth factor for fibroblasts. Regulation and partial characterization. J Clin Invest. 1982 Oct;70(4):806–822. doi: 10.1172/JCI110677. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Chvapil M., Eskelson C. D., Stiffel V., Owen J. A. Early changes in the chemical composition of the rat lung after silica administration. Arch Environ Health. 1979 Nov-Dec;34(6):402–406. doi: 10.1080/00039896.1979.10667440. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- FOLCH J., LEES M., SLOANE STANLEY G. H. A simple method for the isolation and purification of total lipides from animal tissues. J Biol Chem. 1957 May;226(1):497–509. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Glenn K. C., Ross R. Human monocyte-derived growth factor(s) for mesenchymal cells: activation of secretion by endotoxin and concanavalin A. Cell. 1981 Sep;25(3):603–615. doi: 10.1016/0092-8674(81)90168-9. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Hauser P., Vaes G. Degradation of cartilage proteoglycans by a neutral proteinase secreted by rabbit bone-marrow macrophages in culture. Biochem J. 1978 May 15;172(2):275–284. doi: 10.1042/bj1720275. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Heppleston A. G., Fletcher K., Wyatt I. Changes in the composition of lung lipids and the "turnover" of dipalmitoyl lecithin in experimental alveolar lipo-proteinosis induced by inhaled quartz. Br J Exp Pathol. 1974 Aug;55(4):384–395. [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Hsueh W., Desai U., Gonzalez-Crussi F., Lamb R., Chu A. Two phospholipase pools for prostaglandin synthesis in macrophages. Nature. 1981 Apr 23;290(5808):710–713. doi: 10.1038/290710a0. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Jimenez S. A., McArthur W., Rosenbloom J. Inhibition of collagen synthesis by mononuclear cell supernates. J Exp Med. 1979 Dec 1;150(6):1421–1431. doi: 10.1084/jem.150.6.1421. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Kay J., Siemankowski R. F., Siemankowski L. M., Goll D. E. Degradation of smooth-muscle myosin by trypsin-like serine proteinases. Biochem J. 1982 Feb 1;201(2):267–278. doi: 10.1042/bj2010267. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
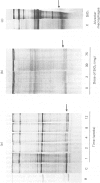
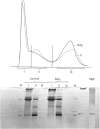
- Kulonen E., Aalto M., Aho S., Lehtinen P., Potila M. Increase of RNA and appearance of new protein in silicotic lung tissue. Ann Occup Hyg. 1982;26(1-4):463–471. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Kulonen E., Aalto M., Aho S., Lehtinen P., Potila M. Recent investigations on macrophage proteins and of fibroblast RNA in silicotic lung fibrosis. Contrib Microbiol Immunol. 1983;7:204–211. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Kulonen E., Potila M. Macrophages and the synthesis of connective tissue components. Acta Pathol Microbiol Scand C. 1980 Feb;88(1):7–13. doi: 10.1111/j.1699-0463.1980.tb00066.x. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- LOWRY O. H., ROSEBROUGH N. J., FARR A. L., RANDALL R. J. Protein measurement with the Folin phenol reagent. J Biol Chem. 1951 Nov;193(1):265–275. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Lehtinen P., Aho S., Kulonen E. Effect of silica on the rat lung with special reference to RNA. Ann Occup Hyg. 1983;27(1):81–87. doi: 10.1093/annhyg/27.1.81. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- O'Farrell P. H. High resolution two-dimensional electrophoresis of proteins. J Biol Chem. 1975 May 25;250(10):4007–4021. [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Oppenheim J. J., Stadler B. M., Siraganian R. P., Mage M., Mathieson B. Lymphokines: their role in lymphocyte responses. Properties of interleukin 1. Fed Proc. 1982 Feb;41(2):257–262. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Pikkarainen J. The molecular structures of vertebrate skin collagens. A comparative study. Acta Physiol Scand Suppl. 1968;309:1–72. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Trotter J. A., Adelstein R. S. Macrophage myosin. Regulation of actin-activated ATPase, activity by phosphorylation of the 20,000-dalton light chain. J Biol Chem. 1979 Sep 25;254(18):8781–8785. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- VILJANTO J., KULONEN E. Correlation of tensile strength and chemical composition in experimental granuloma. Acta Pathol Microbiol Scand. 1962;56:120–126. doi: 10.1111/j.1699-0463.1962.tb04173.x. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Vaux D. J., Gordon S. Monoclonal antibody defines a macrophage intracellular Ca2+-binding protein which is phosphorylated by phagocytosis. Nature. 1982 Sep 2;299(5878):70–72. doi: 10.1038/299070a0. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- WOESSNER J. F., Jr The determination of hydroxyproline in tissue and protein samples containing small proportions of this imino acid. Arch Biochem Biophys. 1961 May;93:440–447. doi: 10.1016/0003-9861(61)90291-0. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]