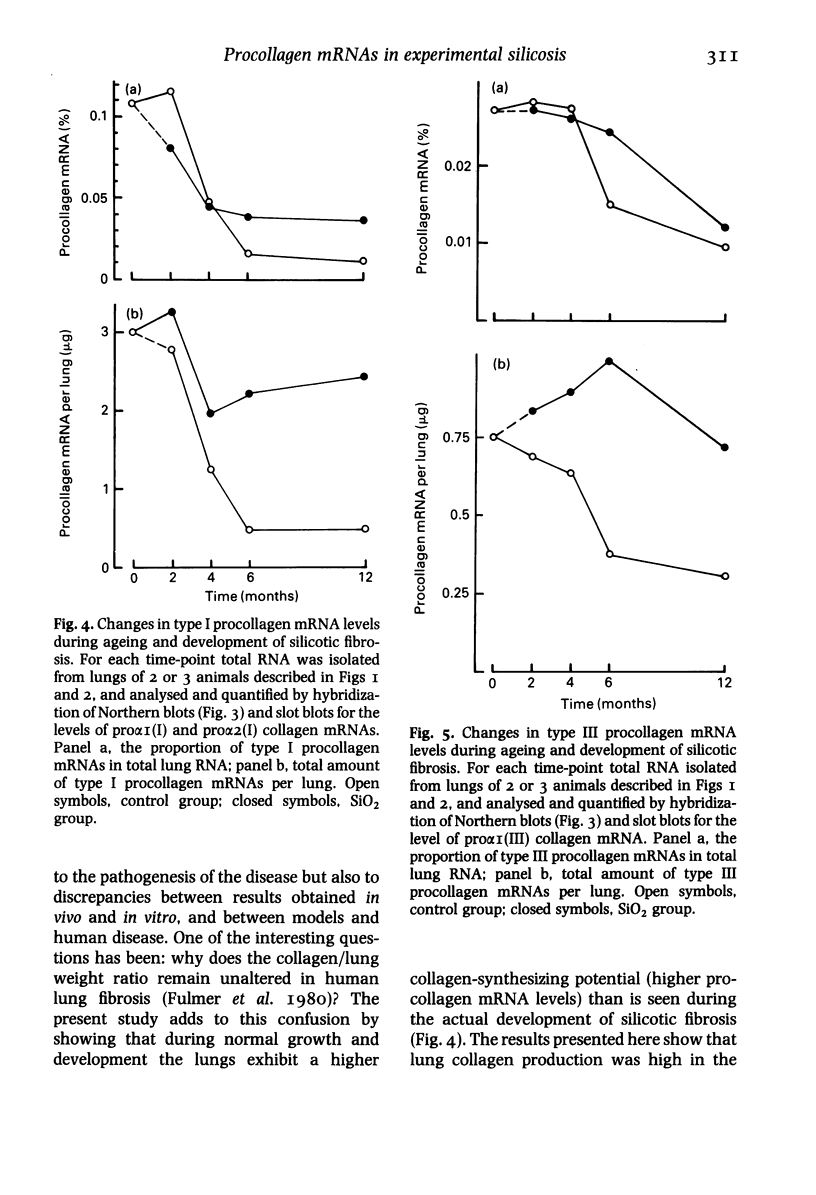
Abstract
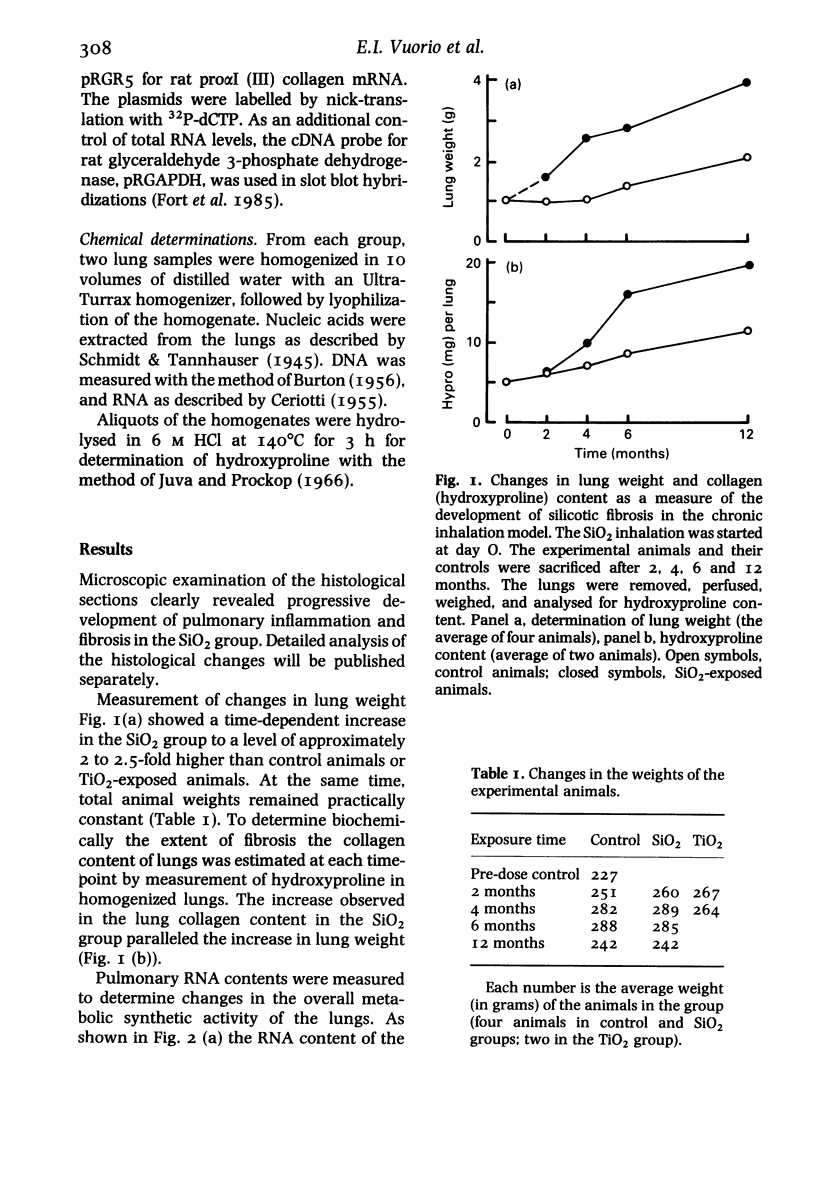
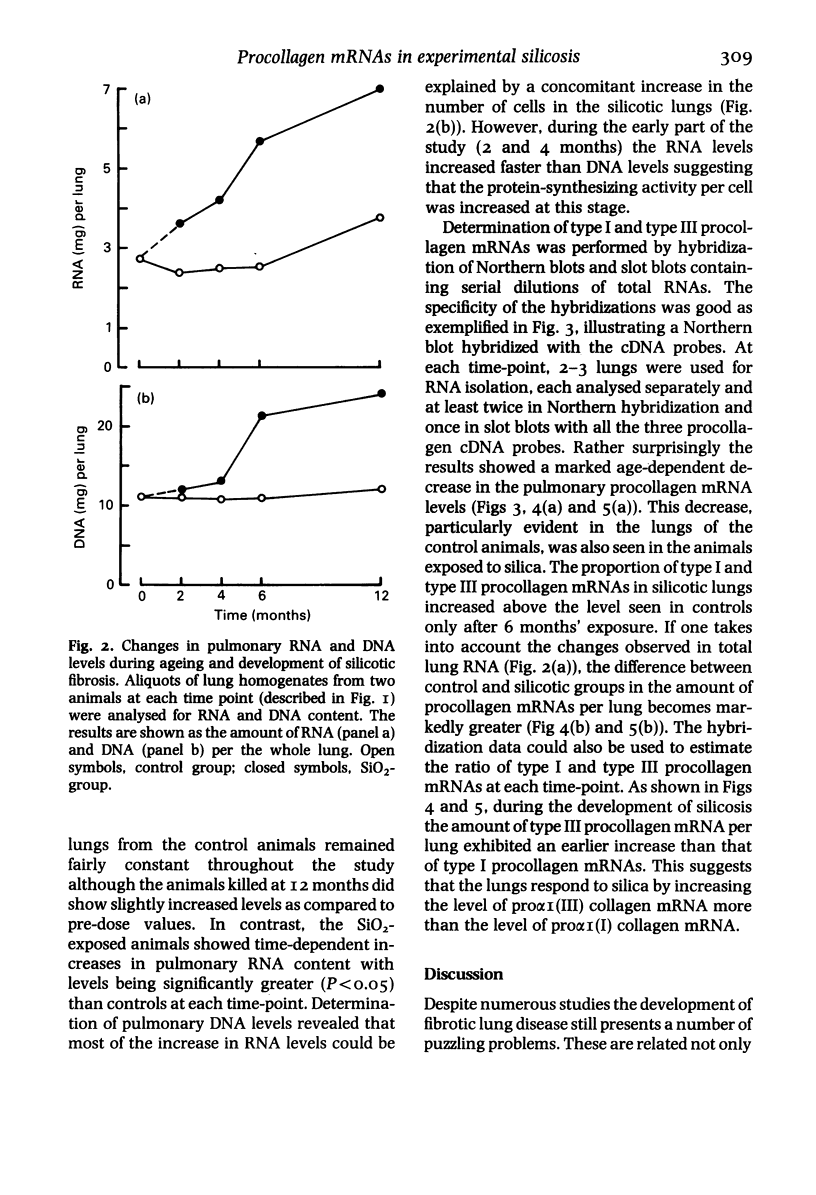
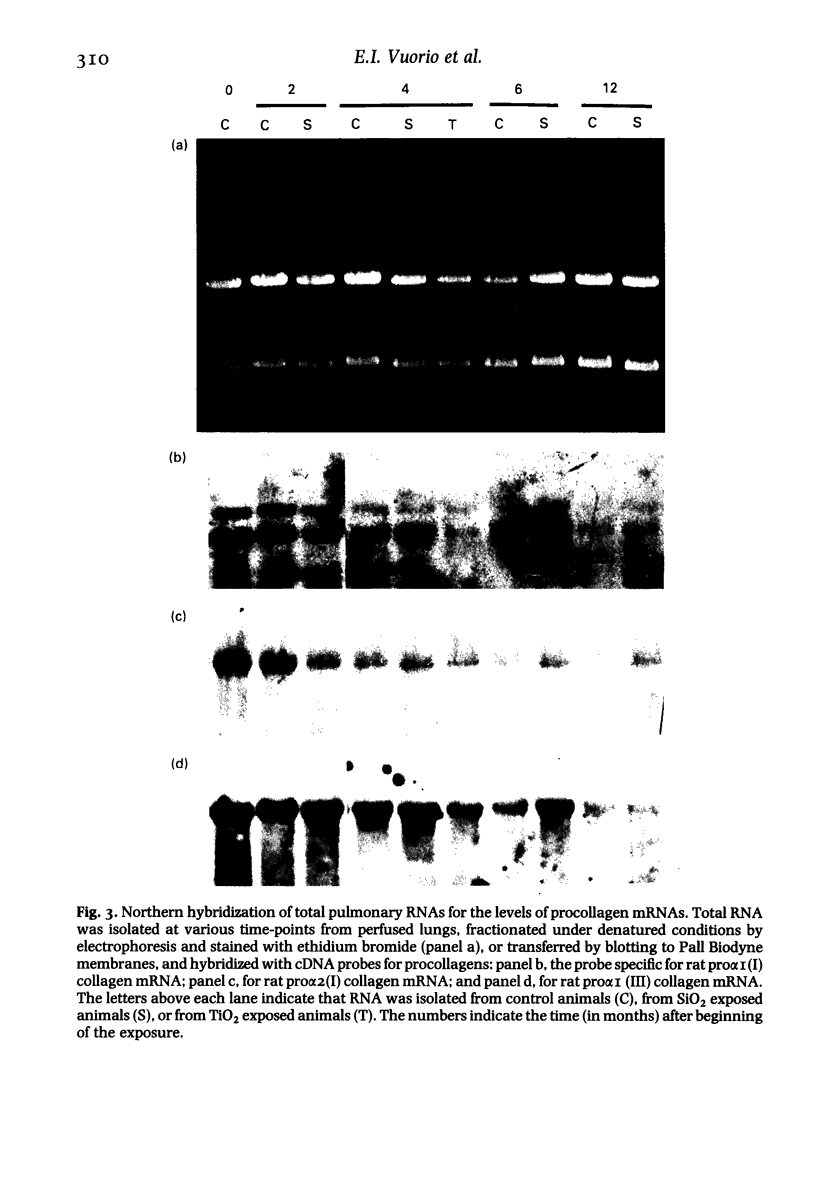
The activation of collagen synthesis during development of silicotic fibrosis was studied in rats exposed, in dusting chambers, to respirable SiO2 for periods of 2, 4, 6 or 12 months. Control animals were exposed similarly to clean air or TiO2. Development of fibrosis was followed by histological examination, measurement of lung weight and determination of lung collagen content (as hydroxyproline). A steady increase in lung weight and collagen content together with changes in cellularity and metabolic activity of the lungs, as ascertained by chemical determination of DNA and RNA, were measured in the lungs of the SiO2-exposed animals. Hybridization of total lung RNA, extracted at each time point, with cDNA probes specific for type I and type III procollagen mRNA levels showed that the development of fibrosis was associated with increased levels, as compared to age matched controls, of pulmonary procollagen mRNAs. Interestingly, the highest levels of procollagen mRNAs were observed in young (pretreatment control) animals, suggesting that during pulmonary development collagen metabolism in lungs is even greater than during development of fibrosis. In rats exposed to SiO2 the increase in type III procollagen mRNA occurred earlier than the increase in type I procollagen mRNAs. These observations demonstrate both age-dependent and silicosis-related changes in pulmonary procollagen mRNA levels. The results suggest that development of silicosis is associated with an altered capacity of the lungs to regulate collagen accumulation.
Full text
PDF






Images in this article
Selected References
These references are in PubMed. This may not be the complete list of references from this article.
- Aho S. A., Lehtinen P. A., Viljanen M. K., Kulonen E. I. Antifibrogenic effects of antiserum against the macrophage RNase. Am Rev Respir Dis. 1983 Feb;127(2):180–184. doi: 10.1164/arrd.1983.127.2.180. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Ala-Kokko L., Pihlajaniemi T., Myers J. C., Kivirikko K. I., Savolainen E. R. Gene expression of type I, III and IV collagens in hepatic fibrosis induced by dimethylnitrosamine in the rat. Biochem J. 1987 May 15;244(1):75–79. doi: 10.1042/bj2440075. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Bitterman P. B., Wewers M. D., Rennard S. I., Adelberg S., Crystal R. G. Modulation of alveolar macrophage-driven fibroblast proliferation by alternative macrophage mediators. J Clin Invest. 1986 Mar;77(3):700–708. doi: 10.1172/JCI112364. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Brody A. R., Roe M. W., Evans J. N., Davis G. S. Deposition and translocation of inhaled silica in rats. Quantification of particle distribution, macrophage participation, and function. Lab Invest. 1982 Dec;47(6):533–542. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Callis A. H., Sohnle P. G., Mandel G. S., Wiessner J., Mandel N. S. Kinetics of inflammatory and fibrotic pulmonary changes in a murine model of silicosis. J Lab Clin Med. 1985 May;105(5):547–553. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Dauber J. H., Rossman M. D., Pietra G. G., Jimenez S. A., Daniele R. P. Experimental silicosis: morphologic and biochemical abnormalities produced by intratracheal instillation of quartz into guinea pig lungs. Am J Pathol. 1980 Dec;101(3):595–612. [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Fulmer J. D., Bienkowski R. S., Cowan M. J., Breul S. D., Bradley K. M., Ferrans V. J., Roberts W. C., Crystal R. G. Collagen concentration and rates of synthesis in idiopathic pulmonary fibrosis. Am Rev Respir Dis. 1980 Aug;122(2):289–301. doi: 10.1164/arrd.1980.122.2.289. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Gay S., Vijanto J., Raekallio J., Penttinen R. Collagen types in early phases of wound healing in children. Acta Chir Scand. 1978;144(4):205–211. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Genovese C., Rowe D., Kream B. Construction of DNA sequences complementary to rat alpha 1 and alpha 2 collagen mRNA and their use in studying the regulation of type I collagen synthesis by 1,25-dihydroxyvitamin D. Biochemistry. 1984 Dec 4;23(25):6210–6216. doi: 10.1021/bi00320a049. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Hance A. J., Bradley K., Crystal R. G. Lung collagen heterogeneity. Synthesis of type I and type III collagen by rabbit and human lung cells in culture. J Clin Invest. 1976 Jan;57(1):102–111. doi: 10.1172/JCI108250. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Heppleston A. G., Kulonen E., Potila M. In vitro assessment of the fibrogenicity of mineral dusts. Am J Ind Med. 1984;6(5):373–386. doi: 10.1002/ajim.4700060507. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Juva K., Prockop D. J. Modified procedure for the assay of H-3-or C-14-labeled hydroxyproline. Anal Biochem. 1966 Apr;15(1):77–83. doi: 10.1016/0003-2697(66)90249-1. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Lugano E. M., Dauber J. H., Elias J. A., Bashey R. I., Jimenez S. A., Daniele R. P. The regulation of lung fibroblast proliferation by alveolar macrophages in experimental silicosis. Am Rev Respir Dis. 1984 May;129(5):767–771. doi: 10.1164/arrd.1984.129.5.767. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- McAnulty R. J., Laurent G. J. Collagen synthesis and degradation in vivo. Evidence for rapid rates of collagen turnover with extensive degradation of newly synthesized collagen in tissues of the adult rat. Coll Relat Res. 1987 Jun;7(2):93–104. doi: 10.1016/s0174-173x(87)80001-8. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Mäkelä J. K., Vuorio E. Type I collagen messenger RNA levels in experimental granulation tissue and silicosis in rats. Med Biol. 1986;64(1):15–22. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Poole A. Measurements of enzymes of collagen synthesis in rats with experimental silicosis. Br J Exp Pathol. 1985 Feb;66(1):89–94. [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Poole A., Myllyla R., Wagner J. C., Brown R. C. Collagen biosynthesis enzymes in lung tissue and serum of rats with experimental silicosis. Br J Exp Pathol. 1985 Oct;66(5):567–575. [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Reiser K. M., Haschek W. M., Hesterberg T. W., Last J. A. Experimental silicosis. II. Long-term effects of intratracheally instilled quartz on collagen metabolism and morphologic characteristics of rat lungs. Am J Pathol. 1983 Jan;110(1):30–40. [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Sandberg M., Vuorio E. Localization of types I, II, and III collagen mRNAs in developing human skeletal tissues by in situ hybridization. J Cell Biol. 1987 Apr;104(4):1077–1084. doi: 10.1083/jcb.104.4.1077. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Thomas P. S. Hybridization of denatured RNA and small DNA fragments transferred to nitrocellulose. Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A. 1980 Sep;77(9):5201–5205. doi: 10.1073/pnas.77.9.5201. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Vuorio T., Mäkelä J. K., Kähäri V. M., Vuorio E. Coordinated regulation of type I and type III collagen production and mRNA levels of pro alpha 1(I) and pro alpha 2(I) collagen in cultured morphea fibroblasts. Arch Dermatol Res. 1987;279(3):154–160. doi: 10.1007/BF00413250. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Wagner J. C., Berry G., Skidmore J. W., Timbrell V. The effects of the inhalation of asbestos in rats. Br J Cancer. 1974 Mar;29(3):252–269. doi: 10.1038/bjc.1974.65. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]