Abstract
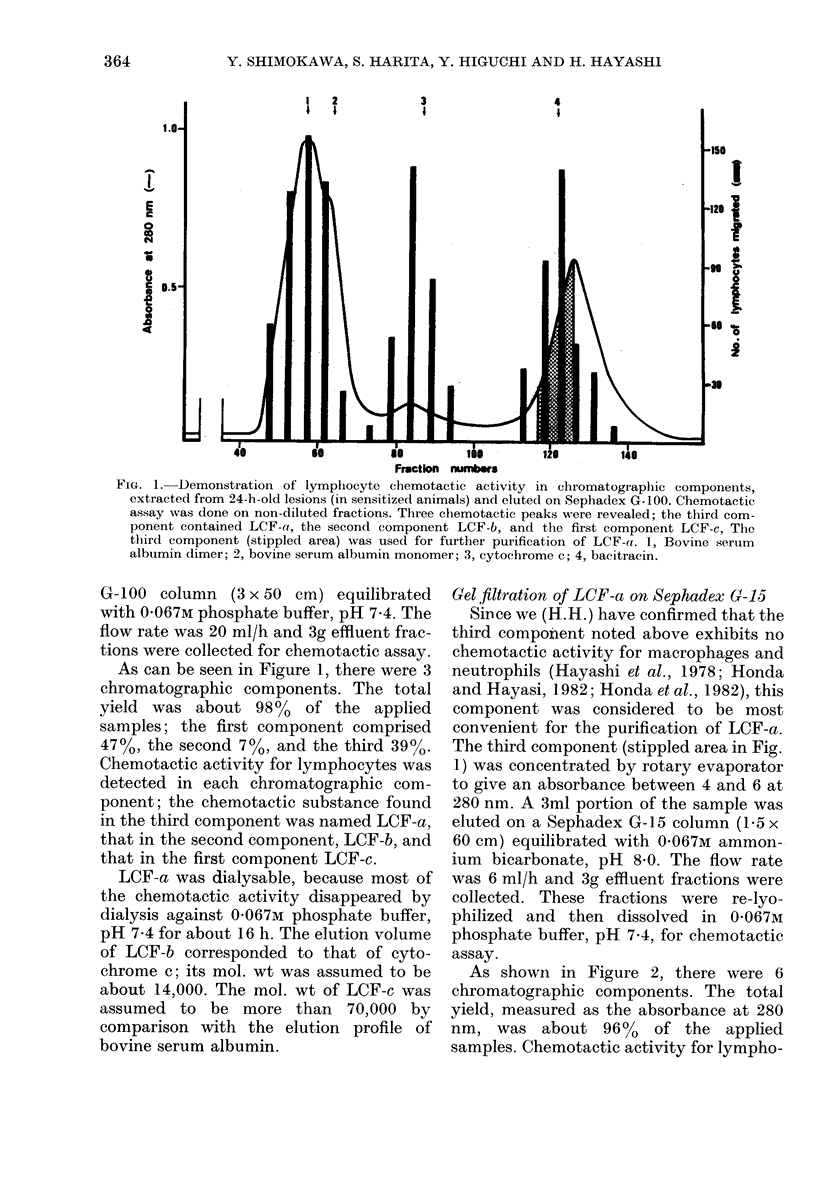
Lymphocyte chemotactic factors were extracted from PPD-induced delayed hypersensitivity skin reaction sites in guinea-pigs. The presence of 3 chemotactic factors (LCF-a, LCF-b and LCF-c) was suggested by gel filtration on Sephadex G100. LCF-a was purified by gel filtration on Sephadex G-15 followed by peptide mapping. This substance was considered to be a thermostable and dialysable peptide; it appeared to be effective for B cells but not for T cells.
Full text
PDF





Selected References
These references are in PubMed. This may not be the complete list of references from this article.
- Braathen L. R., Førre O., Natvig J. B. An anti-human T-lymphocyte antiserum: in situ identification of T cells in the skin of delayed-type hypersensitivity reactions, chronic photosensitivity dermatitis, and mycosis fungoides. Clin Immunol Immunopathol. 1979 Jun;13(2):211–219. doi: 10.1016/0090-1229(79)90065-5. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Claudy A. L., Schmitt D., Viac J., Alario A., Staquet M. J., Thivolet J. Morphological, immunological and immunocytochemical identification of lymphocytes extracted from cutaneous infiltrates. Clin Exp Immunol. 1976 Jan;23(1):61–68. [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Cohen S., Ward P. A., Yoshida T., Burek C. L. Biologic activity of extracts of delayed hypersensitivity skin reaction sites. Cell Immunol. 1973 Dec;9(3):363–376. doi: 10.1016/0008-8749(73)90051-8. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- El-Naggar A. K., Van Epps D. E., Williams R. C., Jr Human-B and T-lymphocyte locomotion in response to casein, C5a, and f-met-leu-phe. Cell Immunol. 1980 Dec;56(2):365–373. doi: 10.1016/0008-8749(80)90112-4. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Goetzl E. J., Austen K. F. Purification and synthesis of eosinophilotactic tetrapeptides of human lung tissue: identification as eosinophil chemotactic factor of anaphylaxis. Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A. 1975 Oct;72(10):4123–4127. doi: 10.1073/pnas.72.10.4123. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Higuchi Y., Honda M., Hayashi H. Production of chemotactic factor for lymphocytes by neutral SH-dependent protease of rabbit PMN leukocytes from immunoglobulins, especially IgM. Cell Immunol. 1975 Jan;15(1):100–108. doi: 10.1016/0008-8749(75)90168-9. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Higuchi Y., Ishida M., Hayashi H. A lymphocyte chemotactic peptide released from immunoglobulin G by neutrophil neutral thiol protease. Cell Immunol. 1979 Sep 1;46(2):297–308. doi: 10.1016/0008-8749(79)90418-0. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Honda M., Miura K., Kuratsu J., Hayashi H. Characterization of a macrophage chemotactic lymphokine produced by purified protein derivative stimulation in vitro and in vivo. Cell Immunol. 1982 Mar 1;67(2):213–228. doi: 10.1016/0008-8749(82)90215-5. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Houck J. C., Chang C. M. The purification and characterization of a lymphokine chemotactic for lymphocytes--lymphotactin. Inflammation. 1977 Jun;2(2):105–113. doi: 10.1007/BF00918672. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- KATZ A. M., DREYER W. J., ANFINSEN C. B. Peptide separation by two-dimensional chromatography and electrophoresis. J Biol Chem. 1959 Nov;234:2897–2900. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- MAYASHI H., MIYOSHI H., NITTA R., UDAKA K. Proteolytic mechanism in recurrence of Arthus-type inflammation by thiol compounds. Br J Exp Pathol. 1962 Oct;43:564–573. [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Mendez E., Lai C. Y. Reaction of peptides with fluorescamine on paper after chromatography or electrophoresis. Anal Biochem. 1975 May 12;65(1-2):281–292. doi: 10.1016/0003-2697(75)90511-4. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- O'Neill G. J., Parrott D. M. Locomotion of human lymphoid cells. I. Effect of culture and con A on T and non-T lymphocytes. Cell Immunol. 1977 Oct;33(2):257–267. doi: 10.1016/0008-8749(77)90156-3. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Schiffmann E., Corcoran B. A., Wahl S. M. N-formylmethionyl peptides as chemoattractants for leucocytes. Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A. 1975 Mar;72(3):1059–1062. doi: 10.1073/pnas.72.3.1059. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Schreiner G. F., Unanue E. R. Anti-Ig-triggered movements of lymphocytes-specificity and lack of evidence for directional migration. J Immunol. 1975 Feb;114(2 Pt 2):809–814. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Shimokawa Y., Harita S., Higuchi Y., Hayashi H. Lymphocyte chemotaxis in inflammation. III. Demonstration of lymphocyte chemotactic activity in extract from PPD-induced delayed hypersensitivity skin reaction site in the guinea-pig. Br J Exp Pathol. 1982 Aug;63(4):355–361. [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Ward P. A., Offen C. D., Montgomery J. R. Chemoattractants of leukocytes, with special reference to lymphocytes. Fed Proc. 1971 Nov-Dec;30(6):1721–1724. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Ward P. A., Unanue E. R., Goralnick S. J., Schreiner G. F. Chemotaxis of rat lymphocytes. J Immunol. 1977 Aug;119(2):416–421. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]



