Abstract
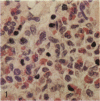
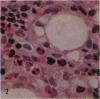
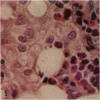
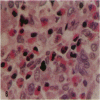
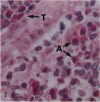
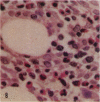
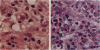
Pulmonary granulomas induced in rabbits by the endobronchial instillation of mycobacterial chemical fractions were re-examined for eosinophilic infiltration. Delayed type hypersensitivity reactions either of tuberculin type or of wax D type did not induce but rather suppressed eosinophilic infiltration in the inflamed area, although some peptidoglycans which are antigenic for the induction of immediate hypersensitivity and fatty acid fractions were weak stimulators of eosinophilic infiltration. Bacterial endotoxin, LPS, was a potent stimulator. It was found that some long chain fatty acids can cause severe eosinophilic infiltration in the induced granulomas. Arachidonic acid was the most active of those examined, so the activity of its metabolites was tested and PGE2 was found to be most active. As the eosinophilic infiltration was markedly suppressed in animals treated with a cyclooxygenase inhibitor (aspirin), the stimulators of eosinophilic infiltration were not fatty acids themselves but their metabolites, PGE2 and some others. The site of permeation of eosinophils from the circulation was found to be arteriolar in the inflamed lung. The granulomatous lesion with eosinophilic infiltration in rabbits is discussed to shed light on the aetiology of eosinophilic granuloma in the human lung.
Full text
PDF







Images in this article
Selected References
These references are in PubMed. This may not be the complete list of references from this article.
- Cohen S., Ward P. A. In vitro and in vivo activity of a lymphocyte and immune complex-dependent chemotactic factor for eosinophils. J Exp Med. 1971 Jan 1;133(1):133–146. doi: 10.1084/jem.133.1.133. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Colley D. G. Eosinophils and immune mechanisms. Eosinophil stimulation promoter (ESP): a lymphokine induced by specific antigen or phytohemagglutinin. J Immunol. 1973 May;110(5):1419–1423. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Goetzl E. J., Austen K. F. Purification and synthesis of eosinophilotactic tetrapeptides of human lung tissue: identification as eosinophil chemotactic factor of anaphylaxis. Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A. 1975 Oct;72(10):4123–4127. doi: 10.1073/pnas.72.10.4123. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Goetzl E. J., Woods J. M., Gorman R. R. Stimulation of human eosinophil and neutrophil polymorphonuclear leukocyte chemotaxis and random migration by 12-L-hydroxy-5,8,10,14-eicosatetraenoic acid. J Clin Invest. 1977 Jan;59(1):179–183. doi: 10.1172/JCI108617. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Hamamoto Y., Kobara Y., Kojima A., Kumazawa Y., Yasuhira K. Experimental production of pulmonary granulomas. I. Immune granulomas induced by chemically modified cell walls and their constituents. Br J Exp Pathol. 1981 Jun;62(3):259–269. [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Kay A. B., Stechschulte D. J., Austen K. F. An eosinophil leukocyte chemotactic factor of anaphylaxis. J Exp Med. 1971 Mar 1;133(3):602–619. doi: 10.1084/jem.133.3.602. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- LICHTENSTEIN L. Histiocytosis X; integration of eosinophilic granuloma of bone, Letterer-Siwe disease, and Schüller-Christian disease as related manifestations of a single nosologic entity. AMA Arch Pathol. 1953 Jul;56(1):84–102. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- VIRSHUP M., GOLDMAN A. Eosinophilic granuloma of the lung. J Thorac Surg. 1956 Feb;31(2):226–237. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]