Abstract
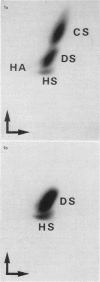
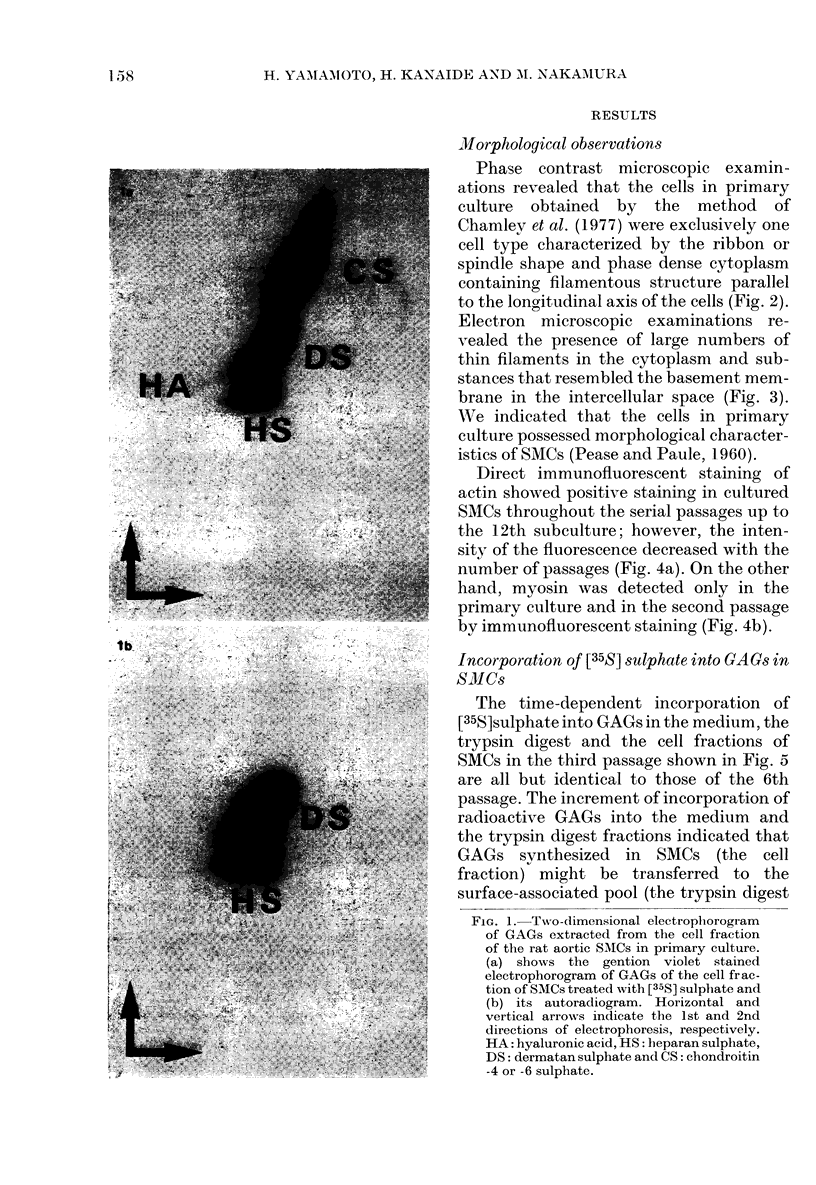
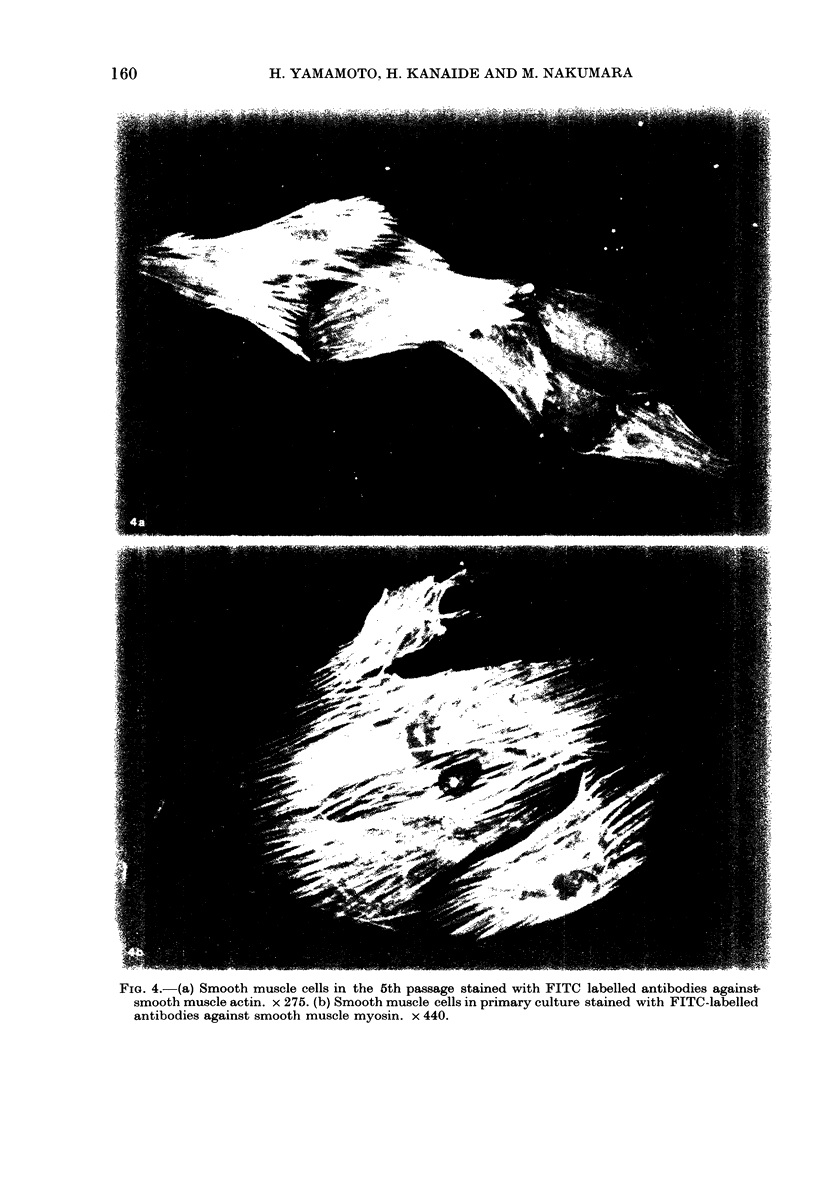
We observed the changes in the metabolism of glycosaminoglycans of cultured smooth muscle cells from the rat aorta during subculture. The primary culture was achieved by the enzymatic dispersion method. The metabolism of glycosaminoglycans in smooth muscle cells was estimated by measuring the incorporation rate of D-[1-14C] glucosamine and [35S] sulphate. Smooth muscle cells were harvested by trypsinization, and glycosaminoglycans were separately extracted and purified from trypsin digest and cells. In the cells of the stationary phase of primary culture, the incorporation of both D-[1-14C] glucosamine and [35S] sulphate into dermatan sulphate was greater than that into heparan sulphate. However, in the trypsin digest, the incorporation of D-[1-14C] glucosamine and [35S] sulphate into dermatan sulphate was less than and equal to that into heparan sulphate. In both the cells and the trypsin digest, the incorporation of D-[1-14C] glucosamine and [35S] sulphate into heparan sulphate decreased and that into dermatan sulphate increased with increase in the number of passages. These results indicate that there is a development of serial modulation in the metabolism of glycosaminoglycans in the cultured smooth muscle cells, in the early passage of subculture and that such should be taken into consideration when analysing the observations.
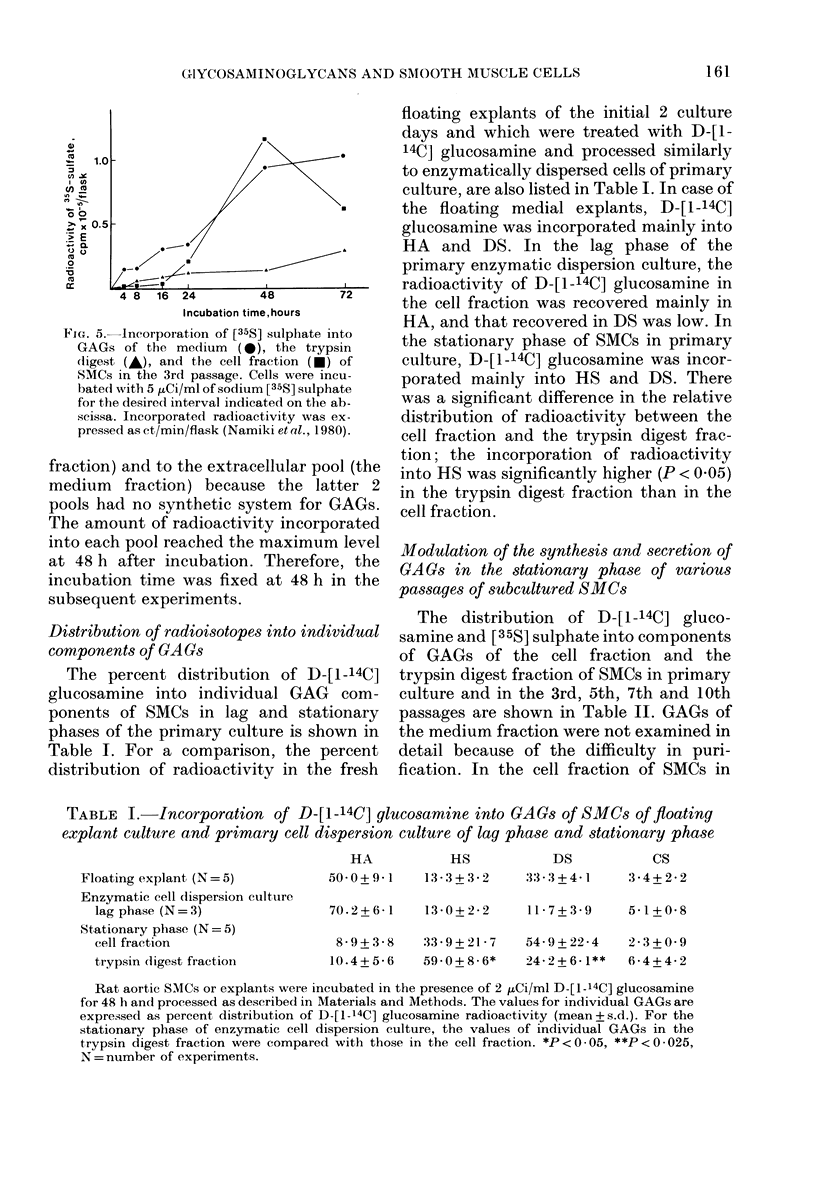
Full text
PDF
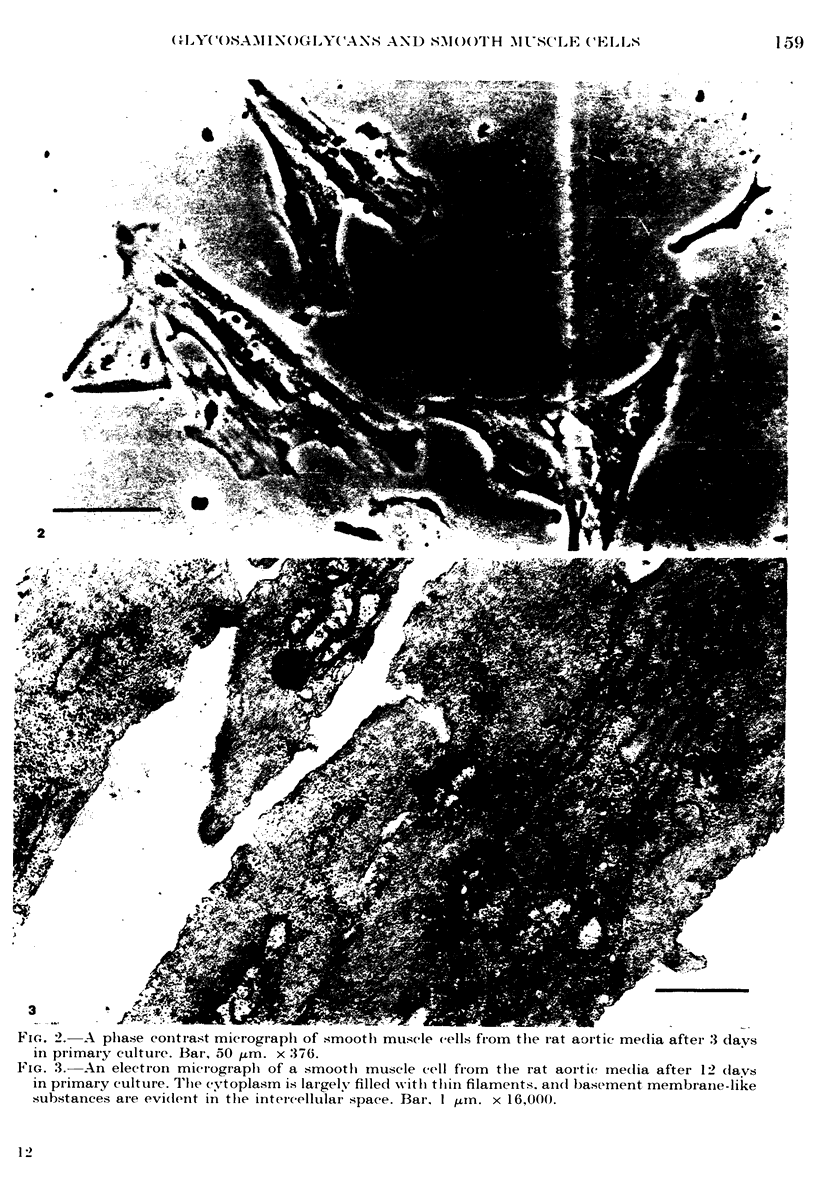






Images in this article
Selected References
These references are in PubMed. This may not be the complete list of references from this article.
- Chamley-Campbell J., Campbell G. R., Ross R. The smooth muscle cell in culture. Physiol Rev. 1979 Jan;59(1):1–61. doi: 10.1152/physrev.1979.59.1.1. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Chamley J. H., Campbell G. R., McConnell J. D., Gröschel-Stewart U. Comparison of vascular smooth muscle cells from adult human, monkey and rabbit in primary culture and in subculture. Cell Tissue Res. 1977 Feb 14;177(4):503–522. doi: 10.1007/BF00220611. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- GORE I., LARKEY B. J. Functional activity of aortic mucopolysaccharides. J Lab Clin Med. 1960 Dec;56:839–846. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Gamse G., Fromme H. G., Kresse H. Metabolism of sulfated glycosaminoglycans in cultured endothelial cells and smooth muscle cells from bovine aorta. Biochim Biophys Acta. 1978 Dec 18;544(3):514–528. doi: 10.1016/0304-4165(78)90326-4. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Hata R., Nagai Y. A rapid and micro method for separation of acidic glycosaminoglycans by two-dimensional electrophoresis. Anal Biochem. 1972 Feb;45(2):462–468. doi: 10.1016/0003-2697(72)90208-4. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Iverius P. H. The interaction between human plasma lipoproteins and connective tissue glycosaminoglycans. J Biol Chem. 1972 Apr 25;247(8):2607–2613. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Jarmolych J., Daoud A. S., Landau J., Fritz K. E., McElvene E. Aortic media explants. Cell proliferation and production of mucopolysaccharides, collagen, and elastic tissue. Exp Mol Pathol. 1968 Oct;9(2):171–188. doi: 10.1016/0014-4800(68)90033-6. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Kresse H., von Figura K., Buddecke E., Fromme H. G. Metabolism of sulfated glycosaminoglycans in cultivated bovine arterial cells. I. Characterization of different pools of sulfated glycosaminoglycans. Hoppe Seylers Z Physiol Chem. 1975 Jun;356(6):929–941. doi: 10.1515/bchm2.1975.356.s1.929. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Kumar V., Berenson G. S., Ruiz H., Dalferes E. R., Jr, Strong J. P. Acid mucopolysaccharides of human aorta. 2. Variations with atherosclerotic involvement. J Atheroscler Res. 1967 Sep-Oct;7(5):583–590. doi: 10.1016/s0368-1319(67)80036-x. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Nakamura M., Torii S., Yatsuki K., Kikuchi Y., Yamamoto H. Cerebral atherosclerosis in Japanese. 1. Lipids and glycosaminoglycans in cerebral arteries. Atherosclerosis. 1971 Mar-Apr;13(2):185–197. doi: 10.1016/0021-9150(71)90021-9. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Namiki O., Faris B., Tschopp F., Füglistaller P., Hollander W., Franzblau C., Schmid K. Synthesis of glycosaminoglycans by cultured rabbit smooth muscle cells. Biochemistry. 1980 Apr 29;19(9):1900–1904. doi: 10.1021/bi00550a026. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Ohya T., Kaneko Y. Novel hyaluronidase from streptomyces. Biochim Biophys Acta. 1970 Mar 18;198(3):607–609. doi: 10.1016/0005-2744(70)90139-7. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- PEASE D. C., PAULE W. J. Electron microscopy of elastic arteries; the thoracic aorta of the rat. J Ultrastruct Res. 1960 Jun;3:469–483. doi: 10.1016/s0022-5320(60)90023-x. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Pietilä K., Ylä-Herttuala S., Jaakkola O., Nikkari T. Metabolism of glycosaminoglycans and lipids in smooth muscle cells from atherosclerotic rabbit aortas in culture. Atherosclerosis. 1980 Nov;37(3):449–456. doi: 10.1016/0021-9150(80)90150-1. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Ross R. The smooth muscle cell. II. Growth of smooth muscle in culture and formation of elastic fibers. J Cell Biol. 1971 Jul;50(1):172–186. doi: 10.1083/jcb.50.1.172. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Schuck P. H., Wellford H. Botulism and nitrites. Science. 1973 Jun 29;180(4093):1322–1322. doi: 10.1126/science.180.4093.1322. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Sobieszek A., Small J. V. Myosin-linked calcium regulation in vertebrate smooth muscle. J Mol Biol. 1976 Mar 25;102(1):75–92. doi: 10.1016/0022-2836(76)90074-7. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Spudich J. A., Watt S. The regulation of rabbit skeletal muscle contraction. I. Biochemical studies of the interaction of the tropomyosin-troponin complex with actin and the proteolytic fragments of myosin. J Biol Chem. 1971 Aug 10;246(15):4866–4871. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Wight T. N., Ross R. Proteoglycans in primate arteries. I. Ultrastructural localization and distribution in the intima. J Cell Biol. 1975 Dec;67(3):660–674. doi: 10.1083/jcb.67.3.660. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Wight T. N., Ross R. Proteoglycans in primate arteries. II. Synthesis and secretion of glycosaminoglycans by arterial smooth muscle cells in culture. J Cell Biol. 1975 Dec;67(3):675–686. doi: 10.1083/jcb.67.3.675. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Yamagata T., Saito H., Habuchi O., Suzuki S. Purification and properties of bacterial chondroitinases and chondrosulfatases. J Biol Chem. 1968 Apr 10;243(7):1523–1535. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]