Abstract
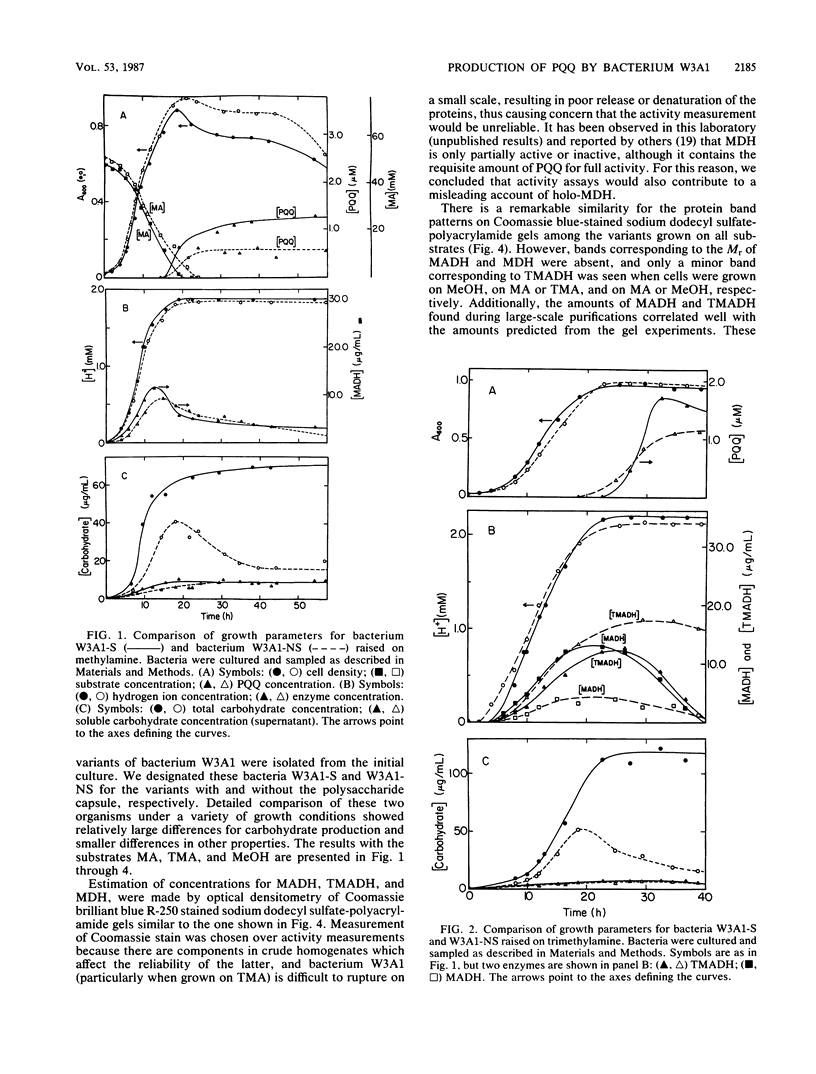
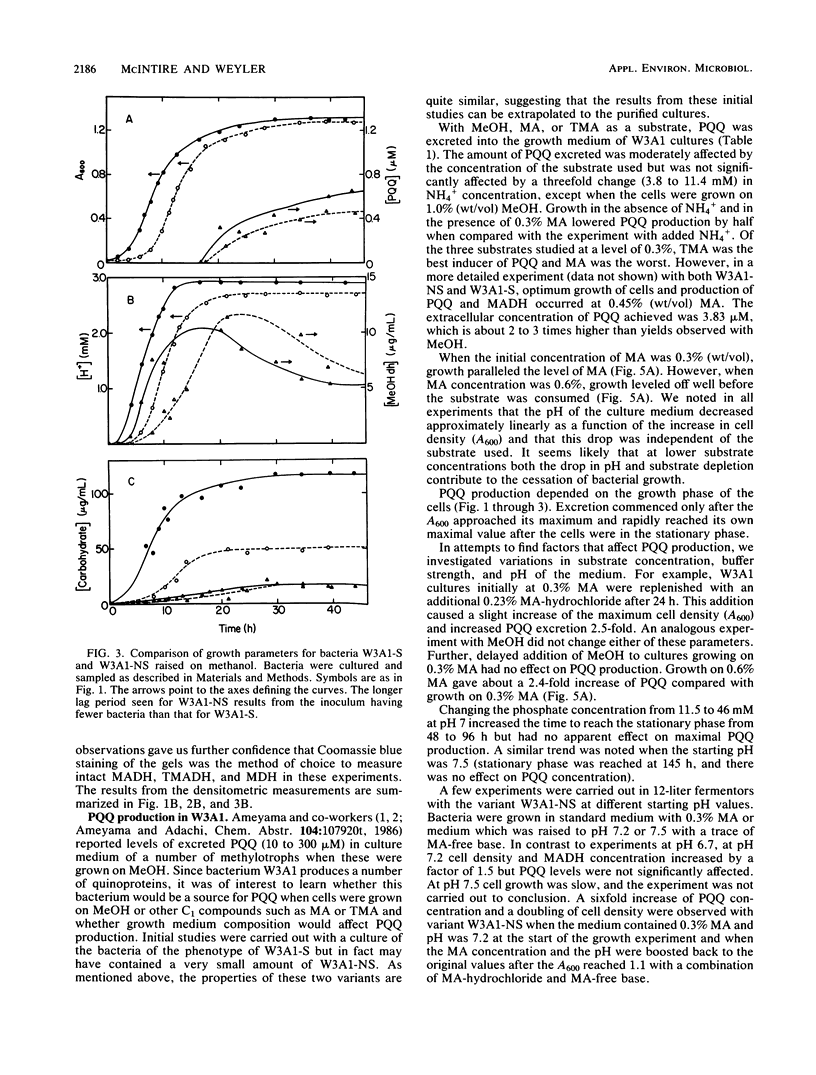
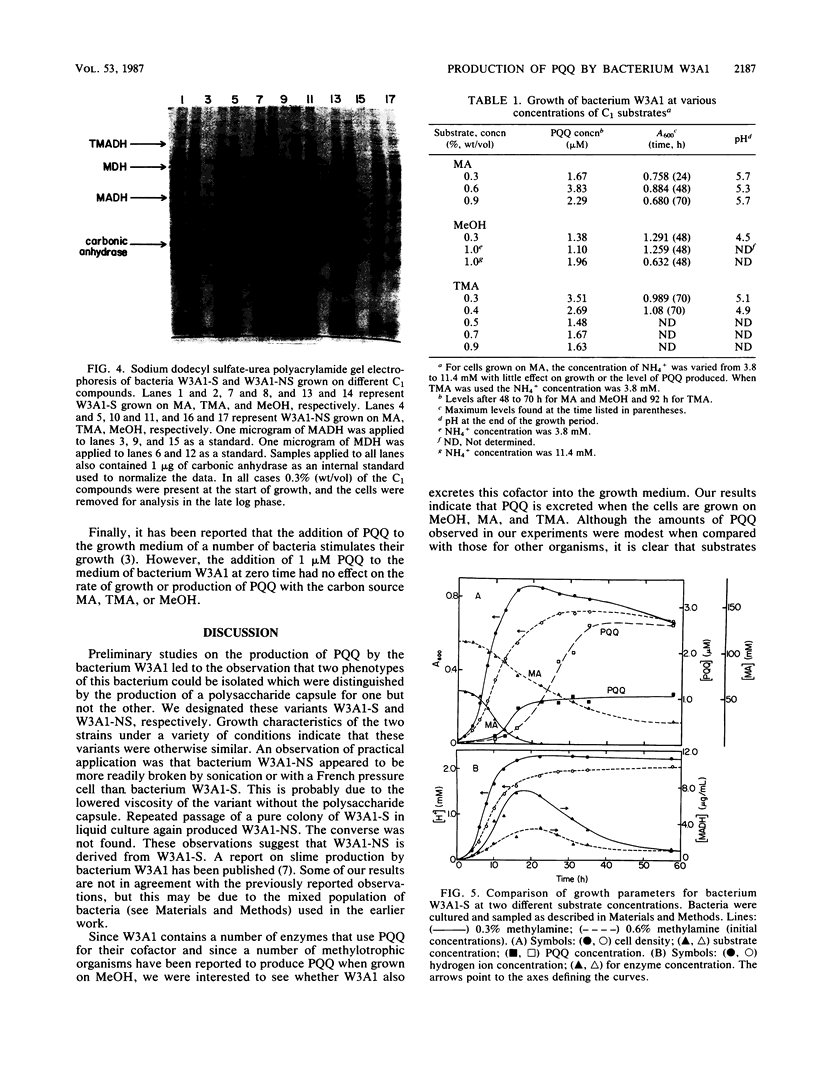
Two variants of the methylotrophic bacterium W3A1, designated W3A1-S (slimy) and W3A1-NS (nonslimy), were compared with respect to their ability to grow in batch culture on the C1 substrates methylamine, methanol, and trimethylamine. Substrate utilization, cell density, pH, cellular and soluble polysaccharide production, and concentrations of the enzymes methylamine dehydrogenase, trimethylamine dehydrogenase, and methanol dehydrogenase produced were measured as a function of growth. The ability of the two bacterial variants to excrete the redox cofactor pyrroloquinoline quinone into the growth medium was also investigated. The two variants were similar with respect to all properties measured, except that W3A1-S produced significantly more capsular polysaccharides than variant W3A1-NS. Pyrroloquinoline quinone was excreted when either variant was grown on any of the C1 substrates investigated but was maximally produced when the methylamine concentration was 0.45% (wt/vol). This cofactor is excreted only as bacterial growth enters the stationary phase, a time when the levels of trimethylamine dehydrogenase and the quinoproteins methanol dehydrogenase and methylamine dehydrogenase begin to decline. It is not known whether the pyrroloquinoline quinone found in the medium is made de novo for excretion, derived from the quinoprotein pool, or both. Pyrroloquinoline quinone excretion has been observed with other methylotrophs, but this is the first instance where the excretion was observed with substrates other than methanol.
Full text
PDF


Images in this article
Selected References
These references are in PubMed. This may not be the complete list of references from this article.
- Colby J., Zatman L. J. Tricarboxylic acid-cycle and related enzymes in restricted facultative methylotrophs. Biochem J. 1975 Jun;148(3):505–511. doi: 10.1042/bj1480505. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Davidson V. L., Neher J. W., Cecchini G. The biosynthesis and assembly of methanol dehydrogenase in bacterium W3A1. J Biol Chem. 1985 Aug 15;260(17):9642–9647. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Davidson V. L. Regulation by carbon source of enzyme expression and slime production in bacterium W3A1. J Bacteriol. 1985 Nov;164(2):941–943. doi: 10.1128/jb.164.2.941-943.1985. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Glatz Z., Kovár J., Macholán L., Pec P. Pea (Pisum sativum) diamine oxidase contains pyrroloquinoline quinone as a cofactor. Biochem J. 1987 Mar 1;242(2):603–606. doi: 10.1042/bj2420603. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Haber C. L., Allen L. N., Zhao S., Hanson R. S. Methylotrophic bacteria: biochemical diversity and genetics. Science. 1983 Sep 16;221(4616):1147–1153. doi: 10.1126/science.221.4616.1147. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Kenney W. C., McIntire W. Characterization of methylamine dehydrogenase from bacterium W3A1. Interaction with reductants and amino-containing compounds. Biochemistry. 1983 Aug 2;22(16):3858–3868. doi: 10.1021/bi00285a022. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Laemmli U. K. Cleavage of structural proteins during the assembly of the head of bacteriophage T4. Nature. 1970 Aug 15;227(5259):680–685. doi: 10.1038/227680a0. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Lobenstein-Verbeek C. L., Jongejan J. A., Frank J., Duine J. A. Bovine serum amine oxidase: a mammalian enzyme having covalently bound PQQ as prosthetic group. FEBS Lett. 1984 May 21;170(2):305–309. doi: 10.1016/0014-5793(84)81333-2. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- McIntire W. S., Stults J. T. On the structure and linkage of the covalent cofactor of methylamine dehydrogenase from the methylotrophic bacterium W3A1. Biochem Biophys Res Commun. 1986 Dec 15;141(2):562–568. doi: 10.1016/s0006-291x(86)80210-8. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Owens J. D., Keddie R. M. The nitrogen nutrition of soil and herbage coryneform bacteria. J Appl Bacteriol. 1969 Sep;32(3):338–347. doi: 10.1111/j.1365-2672.1969.tb00981.x. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Parkes C., Abeles R. H. Studies on the mechanism of action of methoxatin-requiring methanol dehydrogenase: reaction of enzyme with electron-acceptor dye. Biochemistry. 1984 Dec 18;23(26):6355–6363. doi: 10.1021/bi00321a011. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- van der Meer R. A., Duine J. A. Covalently bound pyrroloquinoline quinone is the organic prosthetic group in human placental lysyl oxidase. Biochem J. 1986 Nov 1;239(3):789–791. doi: 10.1042/bj2390789. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- van der Meer R. A., Jongejan J. A., Frank J., Duine J. A. Hydrazone formation of 2,4-dinitrophenylhydrazine with pyrroloquinoline quinone in porcine kidney diamine oxidase. FEBS Lett. 1986 Sep 29;206(1):111–114. doi: 10.1016/0014-5793(86)81350-3. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]